M. Chen, K.K. Afridi, S. Chakraborty, and D.J. Perreault, “A High-Power-Density Wide-Input-Voltage-Range Isolated dc-dc Converter Having a MultiTrack Architecture,” 2015 Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition , pp. 2017-2026, Sept. 2015.
... into the multiple levels of the switched-capacitor circuit block to form a merged regulation stage. Likewise, by using a single set of switches to perform charge transfer and voltage balancing among different levels of the capacitor stack, and to drive the parallel-track magnetic isolation device, w ...
... into the multiple levels of the switched-capacitor circuit block to form a merged regulation stage. Likewise, by using a single set of switches to perform charge transfer and voltage balancing among different levels of the capacitor stack, and to drive the parallel-track magnetic isolation device, w ...
REG71055-Q1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... A conversion clock of 50% duty cycle is generated. During the first half cycle the FET switches are configured as shown in Figure 9A, and CPUMP charges to VIN. During the second half cycle the FET switched are configured as shown in Figure 9B, and the voltage on CPUMP is added to VIN. The output vol ...
... A conversion clock of 50% duty cycle is generated. During the first half cycle the FET switches are configured as shown in Figure 9A, and CPUMP charges to VIN. During the second half cycle the FET switched are configured as shown in Figure 9B, and the voltage on CPUMP is added to VIN. The output vol ...
Logic Switches Operating at the Minimum Energy of Computing
... Several measurements have been performed following the procedure previously described. Anyway a preliminary test of the system has been conducted to check that each part was properly working. In particular, Fig. 2 depicts the propagation delay difference between the two channels of the GUT boards. A ...
... Several measurements have been performed following the procedure previously described. Anyway a preliminary test of the system has been conducted to check that each part was properly working. In particular, Fig. 2 depicts the propagation delay difference between the two channels of the GUT boards. A ...
MAX1802 Digital Camera Step-Down Power Supply General Description
... from 2.5V to 11V and regulates a resistor-adjustable output from 2.7V to 5.5V. It uses a synchronous rectifier to regulate the output with up to 94% efficiency. An adjustable operating frequency (up to 1MHz) facilitates designs for optimum size, cost, and efficiency. The core step-down DC-DC convert ...
... from 2.5V to 11V and regulates a resistor-adjustable output from 2.7V to 5.5V. It uses a synchronous rectifier to regulate the output with up to 94% efficiency. An adjustable operating frequency (up to 1MHz) facilitates designs for optimum size, cost, and efficiency. The core step-down DC-DC convert ...
FSFR-HS Series — Advanced Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters
... This pin is used for controlling the switching frequency in normal operation. When any protections are triggered, the internal Auto/Restart (A/R) circuit starts to sense the voltage on the pin, which is discharged naturally by external resistance. The IC can be operated with A/R when the voltage dec ...
... This pin is used for controlling the switching frequency in normal operation. When any protections are triggered, the internal Auto/Restart (A/R) circuit starts to sense the voltage on the pin, which is discharged naturally by external resistance. The IC can be operated with A/R when the voltage dec ...
DMOS dual full bridge driver with PWM current controller
... RDS(on) = 0.73 Ω (typical value @ 25 °C), with intrinsic fast freewheeling diode. Cross conduction protection is achieved using a dead time (td = 1 µs typical) between the switch off and switch on of two power MOS in one leg of a bridge. Using N-channel power MOS for the upper transistors in the bri ...
... RDS(on) = 0.73 Ω (typical value @ 25 °C), with intrinsic fast freewheeling diode. Cross conduction protection is achieved using a dead time (td = 1 µs typical) between the switch off and switch on of two power MOS in one leg of a bridge. Using N-channel power MOS for the upper transistors in the bri ...
MPQ2451-5/33-AEC1 - Monolithic Power System
... and SW nodes falls below its regulation, a PMOS pass transistor connected from VIN to BST turns on. The charging current path goes from VIN → BST → SW. The external circuit must provide enough voltage headroom to facilitate charging. If VIN is sufficiently higher than VSW, the bootstrap capacitor wi ...
... and SW nodes falls below its regulation, a PMOS pass transistor connected from VIN to BST turns on. The charging current path goes from VIN → BST → SW. The external circuit must provide enough voltage headroom to facilitate charging. If VIN is sufficiently higher than VSW, the bootstrap capacitor wi ...
INA101 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... drift. Most applications require no external offset adjustment. Figure 2 shows connection of an optional potentiometer connected to the Offset Adjust pins for trimming the input offset voltage. (Pin numbers shown are for the DIP package.) Use this adjustment to null the offset voltage in high gain ( ...
... drift. Most applications require no external offset adjustment. Figure 2 shows connection of an optional potentiometer connected to the Offset Adjust pins for trimming the input offset voltage. (Pin numbers shown are for the DIP package.) Use this adjustment to null the offset voltage in high gain ( ...
DS90LV001 800 Mbps LVDS Buffer DS90LV001 800 Mbps LVDS Buffer General Description
... The DS90LV001 LVDS-LVDS Buffer takes an LVDS input signal and provides an LVDS output signal. In many large systems, signals are distributed across backplanes, and one of the limiting factors for system speed is the "stub length" or the distance between the transmission line and the unterminated rec ...
... The DS90LV001 LVDS-LVDS Buffer takes an LVDS input signal and provides an LVDS output signal. In many large systems, signals are distributed across backplanes, and one of the limiting factors for system speed is the "stub length" or the distance between the transmission line and the unterminated rec ...
MAX8633–MAX8636 Dual 300mA Pin-Programmable LDO Linear Regulators General Description
... require low equivalent-series resistance (ESR) to achieve the stated specifications for low-output noise and power-supply rejection. To ensure proper operation over the specified temperature range, dielectrics such as X7R or X5R are recommended. If Z5U or Y5V dielectrics are used, it may be necessar ...
... require low equivalent-series resistance (ESR) to achieve the stated specifications for low-output noise and power-supply rejection. To ensure proper operation over the specified temperature range, dielectrics such as X7R or X5R are recommended. If Z5U or Y5V dielectrics are used, it may be necessar ...
14ELN15_Question Bank
... 16). The most commonly used transistor Configuration is a). CCC b). CEC c). CBC d). None of the above Ans - CEC 17). The voltage gain of a transistor connected in CCC is a). Equal to 1 b). More than 10 c). More than 100 d). Less than 1 Ans - Less than 1 18). In a transistor, signal is transferred fr ...
... 16). The most commonly used transistor Configuration is a). CCC b). CEC c). CBC d). None of the above Ans - CEC 17). The voltage gain of a transistor connected in CCC is a). Equal to 1 b). More than 10 c). More than 100 d). Less than 1 Ans - Less than 1 18). In a transistor, signal is transferred fr ...
AB18 RC-COUPLED AMPLIFIER Analog Lab - Hik
... Fig. 4 The f1 and f2 points are also known as half power points. The half power points are the points at which the signal amplitude has dropped to .707 percent of the maximum signal amplitude. Any frequency below the f1 or above the f2 point is not considered a usable output from the amplifier. The ...
... Fig. 4 The f1 and f2 points are also known as half power points. The half power points are the points at which the signal amplitude has dropped to .707 percent of the maximum signal amplitude. Any frequency below the f1 or above the f2 point is not considered a usable output from the amplifier. The ...
Rail-to-Rail, Very Fast, 2.5 V to 5.5 V, Single-Supply TTL/CMOS Comparator ADCMP603
... input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output low-to-high transition. Propagation delay measured from the time the input signal crosses the reference (± the input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output high-to-low transition. Propagation delay measured from the 50% point of the latch en ...
... input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output low-to-high transition. Propagation delay measured from the time the input signal crosses the reference (± the input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output high-to-low transition. Propagation delay measured from the 50% point of the latch en ...
MAX1856 Wide Input Range, Synchronizable, PWM SLIC Power Supply General Description
... for cost-sensitive applications like xDSL, cable modems, set-top boxes, LMDS, MMDS, WLL, and FTTH CPE. The MAX1856 provides low audio-band noise for talk battery and a sturdy output capable of handling the ring trip conditions for ring battery. The operating frequency can be set between 100kHz and 5 ...
... for cost-sensitive applications like xDSL, cable modems, set-top boxes, LMDS, MMDS, WLL, and FTTH CPE. The MAX1856 provides low audio-band noise for talk battery and a sturdy output capable of handling the ring trip conditions for ring battery. The operating frequency can be set between 100kHz and 5 ...
Dithering Digital Ripple Correlation Control for Maximum Power
... the highest DC measurement precision Noise-free resolution is DC equivalent of ENOB for AC RMS value of the measurement noise equal to standard deviation assuming noise source near ...
... the highest DC measurement precision Noise-free resolution is DC equivalent of ENOB for AC RMS value of the measurement noise equal to standard deviation assuming noise source near ...
Introduction to Semiconductor Devices
... • This is the reverse break down voltage which may be only a few volts or hundreds or thousands of volts. A presentation of eSyst.org ...
... • This is the reverse break down voltage which may be only a few volts or hundreds or thousands of volts. A presentation of eSyst.org ...
Intro to Arduino
... normal, fixed resistor (usually 10 Bottom resistor KΩ). When top resistor is connected to 5V and the bottom resistor to ground, the middle will output a voltage proportional to the values of the two resistors. ...
... normal, fixed resistor (usually 10 Bottom resistor KΩ). When top resistor is connected to 5V and the bottom resistor to ground, the middle will output a voltage proportional to the values of the two resistors. ...
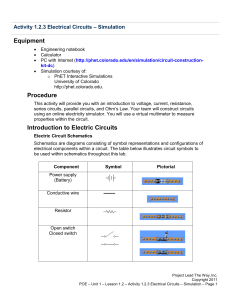
Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits – Simulation
... 1. Explain the difference between a series and a parallel circuit. 2. Explain the difference between the voltage output at the battery and the voltage across each bulb in the series circuit. Explain the relationship between the current output at the battery and the current through each bulb in the s ...
... 1. Explain the difference between a series and a parallel circuit. 2. Explain the difference between the voltage output at the battery and the voltage across each bulb in the series circuit. Explain the relationship between the current output at the battery and the current through each bulb in the s ...
J.A. Santiago-Gonzalez, K.K. Afridi and D.J. Perreault, Design of Resistive-Input Class E Resonant Rectifiers for Variable-Power Operation, 14th IEEE Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL ’13), June 2013.
... possible (i.e., minimize the worst-case phase angle of the input impedance) over the entire power range, while using a 60 V diode with nominal capacitance of 50 pF (based on the PMEG6030EP diode which has average current rating of 3A). Thus, the normalized peak diode voltage capability is about 4 (a ...
... possible (i.e., minimize the worst-case phase angle of the input impedance) over the entire power range, while using a 60 V diode with nominal capacitance of 50 pF (based on the PMEG6030EP diode which has average current rating of 3A). Thus, the normalized peak diode voltage capability is about 4 (a ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.