(131904) Topic: Fracture of Metal Temperature Embrittlement
... metal with expenditure of considerable energy. ...
... metal with expenditure of considerable energy. ...
collimator survival IWLC 2010 JL Fernández
... There are studies of rotatable spoilers but as I see it any deformation generated by the bunch train could block the gap and avoid the rotation. Also, circular spoilers do not insure 0.2Xo of material at any given depth. ...
... There are studies of rotatable spoilers but as I see it any deformation generated by the bunch train could block the gap and avoid the rotation. Also, circular spoilers do not insure 0.2Xo of material at any given depth. ...
application of infinite-element calculations for consolidating a
... stiffness matrix is not symmetric; therefore, the unsymmetrical matrix storage and solution scheme should be used. If the difference between b and y is not large and the region of the model, in which the inelastic deformation is occurring is confined, it is possible that a symmetric approximation of ...
... stiffness matrix is not symmetric; therefore, the unsymmetrical matrix storage and solution scheme should be used. If the difference between b and y is not large and the region of the model, in which the inelastic deformation is occurring is confined, it is possible that a symmetric approximation of ...
POLYMERS
... Diffusion in Polymers Polymers can also act as solvents for low molecular weight compounds. The diffusion of small molecular weight components in polymers is important in a number of fields : ...
... Diffusion in Polymers Polymers can also act as solvents for low molecular weight compounds. The diffusion of small molecular weight components in polymers is important in a number of fields : ...
9. Short overview of rheology very short for 2 credit course
... “The resistance which arises from the lack of slipperiness of the parts of the liquid, other things being equal, is proportional to the velocity with which the parts of the liquid are separated from one another.” ...
... “The resistance which arises from the lack of slipperiness of the parts of the liquid, other things being equal, is proportional to the velocity with which the parts of the liquid are separated from one another.” ...
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THERMAL INSULATING
... thickness from 1.5 mm to 2 mm leads to increase of the compressive stress up to 24%. Increase of the reinforcing layer form 4 mm to 9 mm leads to change of the compressive stress up to 62%. ...
... thickness from 1.5 mm to 2 mm leads to increase of the compressive stress up to 24%. Increase of the reinforcing layer form 4 mm to 9 mm leads to change of the compressive stress up to 62%. ...
Module
... Stresses computed on the basis of the original area of the specimen are often referred to as the conventional or nominal stresses. Alternately, the stresses computed on the basis of the actual area of the specimen gives the so called true stress. Within the elastic limit, the material returns to it ...
... Stresses computed on the basis of the original area of the specimen are often referred to as the conventional or nominal stresses. Alternately, the stresses computed on the basis of the actual area of the specimen gives the so called true stress. Within the elastic limit, the material returns to it ...
Fluid Dynamics: The Navier-Stokes Equations
... Classical mechanics, the father of physics and perhaps of scientific thought, was initially developed in the 1600s by the famous natural philosophers (the codename for ’physicists’) of the 17th century such as Isaac Newton building on the data and observations of astronomers including Tycho Brahe, G ...
... Classical mechanics, the father of physics and perhaps of scientific thought, was initially developed in the 1600s by the famous natural philosophers (the codename for ’physicists’) of the 17th century such as Isaac Newton building on the data and observations of astronomers including Tycho Brahe, G ...
Glossary for Chapter 1
... tubes driven by a pump and fan-driven air flow for cooling computer components. Natural flows, in contrast, result from internal buoyancy forces driven by temperature (i.e., density) variations within a fluid in the presence of a gravitational field. Examples include buoyant plumes around a human bo ...
... tubes driven by a pump and fan-driven air flow for cooling computer components. Natural flows, in contrast, result from internal buoyancy forces driven by temperature (i.e., density) variations within a fluid in the presence of a gravitational field. Examples include buoyant plumes around a human bo ...
Methods of Strengthening Ceramics
... damaged or missing teeth. The other three classes being metals, polymers and composites. The word Ceramic is derived from the Greek word “keramos”, which literally means ‘burnt stuff’, but which has come to mean more specifically a material produced by burning or firing [1]. A ceramic is an earthly ...
... damaged or missing teeth. The other three classes being metals, polymers and composites. The word Ceramic is derived from the Greek word “keramos”, which literally means ‘burnt stuff’, but which has come to mean more specifically a material produced by burning or firing [1]. A ceramic is an earthly ...
PROPERIES OF MATTER HANDOUTS AND PROBLEMS
... (b) Plastics have low Young modulus, large elongation and do not obey Hooke’s Laws ...
... (b) Plastics have low Young modulus, large elongation and do not obey Hooke’s Laws ...
National Diploma in Engineering Mechanical Principles for
... expanded according to the law pV1.2 to a final volume of 100 litres determine (a) its initial volume, (b) its final pressure, (c) its final temperature. For air, take R = 287 Jkgˉ¹ Kˉ¹. (ii) Air with an initial volume of 0.1m³, pressure 1 bar and temperature 15°C is compressed according to the law p ...
... expanded according to the law pV1.2 to a final volume of 100 litres determine (a) its initial volume, (b) its final pressure, (c) its final temperature. For air, take R = 287 Jkgˉ¹ Kˉ¹. (ii) Air with an initial volume of 0.1m³, pressure 1 bar and temperature 15°C is compressed according to the law p ...
Chapter 6. Mechanical Properties of Metals
... Shear and Torsion Shear stress: = F / Ao F is applied parallel to upper and lower faces each having area A0. ...
... Shear and Torsion Shear stress: = F / Ao F is applied parallel to upper and lower faces each having area A0. ...
3 - USNA
... The first term in the above expression is called the strain rate tensor which is a measure of the deformational properties of the fluid medium. The second terms is called the rotation tensor and is a measure of the rotational properties of the fluid. Note that by merit of the fact that rij is anti-s ...
... The first term in the above expression is called the strain rate tensor which is a measure of the deformational properties of the fluid medium. The second terms is called the rotation tensor and is a measure of the rotational properties of the fluid. Note that by merit of the fact that rij is anti-s ...
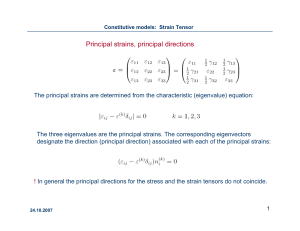
Principal strains, principal directions
... In case the deformations are small and the bady is elastic, then relations (E1) are linear. linear ...
... In case the deformations are small and the bady is elastic, then relations (E1) are linear. linear ...
Influence of the cutting regime on the residual stresses generated by
... processing or in serving conditions. Residual stress can lead to unexpected and premature failures and geometric distortions of a component/structure, especially those subjected to alternating service loads and/or corrosive environments. It arises from the elastic response of material to inhomogeneo ...
... processing or in serving conditions. Residual stress can lead to unexpected and premature failures and geometric distortions of a component/structure, especially those subjected to alternating service loads and/or corrosive environments. It arises from the elastic response of material to inhomogeneo ...
Analysis of process-induced residual stresses in tape placement
... composites is highly anisotropic. This is due to the large discrepancy in the thermal expansion coefficients of the matrix and fiber materials. In a typical carbon-reinforced unidirectional thermoplastic composite, a temperature increase induces considerable expansion of the laminate in the transver ...
... composites is highly anisotropic. This is due to the large discrepancy in the thermal expansion coefficients of the matrix and fiber materials. In a typical carbon-reinforced unidirectional thermoplastic composite, a temperature increase induces considerable expansion of the laminate in the transver ...
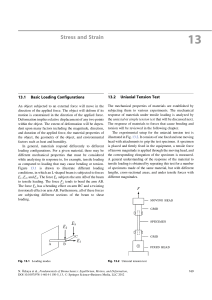
Stress and Strain
... Another method of representing the results obtained in a uniaxial tension test is by first dividing the magnitude of the applied force F with the cross-sectional area A of the specimen, normalizing the amount of deformation by dividing the measured elongation with the original length of the specimen, ...
... Another method of representing the results obtained in a uniaxial tension test is by first dividing the magnitude of the applied force F with the cross-sectional area A of the specimen, normalizing the amount of deformation by dividing the measured elongation with the original length of the specimen, ...
a new frontier for deposit stress measurement
... A new geometry solves problems related to an exposed interior that allows deposition of the applied deposit to occur on the inside surface. Interior deposits reverse the type of stress and reduce calculated results as much as 30%. Interior masking is critical. ...
... A new geometry solves problems related to an exposed interior that allows deposition of the applied deposit to occur on the inside surface. Interior deposits reverse the type of stress and reduce calculated results as much as 30%. Interior masking is critical. ...
Slides for lecture #23
... ultimate shear stress. If nothing but the grain size changes and the first term is negligible ...
... ultimate shear stress. If nothing but the grain size changes and the first term is negligible ...
MCEN 2024, Spring 2008 The week of Apr 07 HW 9–with Solutions
... This plot is left to the students. 7. Why, in Problem 6, does the elastic constant of iron remain essentially unchanged while the fracture toughness and the work of fracture vary widely. The elastic constants of materials is related to the bonding between the atoms, which, on the average remains app ...
... This plot is left to the students. 7. Why, in Problem 6, does the elastic constant of iron remain essentially unchanged while the fracture toughness and the work of fracture vary widely. The elastic constants of materials is related to the bonding between the atoms, which, on the average remains app ...
Thermal and Mechanical Characterizations of W-armoured
... figure 4-a, and it can be observed that the adapted theoretical relation does not fit at all to the experimental results. As a consequence, an adaption of the Hall-Petch relation by fitting the experimental data has been carried out, leading to a reassessment of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ at 65.5 and 7 ...
... figure 4-a, and it can be observed that the adapted theoretical relation does not fit at all to the experimental results. As a consequence, an adaption of the Hall-Petch relation by fitting the experimental data has been carried out, leading to a reassessment of parameters ‘a’ and ‘b’ at 65.5 and 7 ...
Material Selection - Web Services Overview
... – A toy is expected to last for a year or two, low quality gears and other components do fine. – Tooling materials for a one-year production can wear more quickly ...
... – A toy is expected to last for a year or two, low quality gears and other components do fine. – Tooling materials for a one-year production can wear more quickly ...
Fluid/Solid coupling for the simulation of welding process Y
... led to the development of several numerical simulation approaches, which may provide valuable assistance to study the process’s effects on the final parts. During this process, the material undergoes thermal cycles which lead to state changes (liquid and solid) and fluid flows in weld pool. These fl ...
... led to the development of several numerical simulation approaches, which may provide valuable assistance to study the process’s effects on the final parts. During this process, the material undergoes thermal cycles which lead to state changes (liquid and solid) and fluid flows in weld pool. These fl ...
Fatigue (material)

In materials science, fatigue is the weakening of a material caused by repeatedly applied loads. It is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. The nominal maximum stress values that cause such damage may be much less than the strength of the material typically quoted as the ultimate tensile stress limit, or the yield stress limit.Fatigue occurs when a material is subjected to repeated loading and unloading. If the loads are above a certain threshold, microscopic cracks will begin to form at the stress concentrators such as the surface, persistent slip bands (PSBs), and grain interfaces. Eventually a crack will reach a critical size, the crack will propagate suddenly, and the structure will fracture. The shape of the structure will significantly affect the fatigue life; square holes or sharp corners will lead to elevated local stresses where fatigue cracks can initiate. Round holes and smooth transitions or fillets will therefore increase the fatigue strength of the structure.