Introduction to Unix
... Most personal PCs (either Windows or Macintosh based) are single-user machines. 1 keyboard, 1 monitor, intended to serve just one person. ...
... Most personal PCs (either Windows or Macintosh based) are single-user machines. 1 keyboard, 1 monitor, intended to serve just one person. ...
Operating Systems Course Outline
... Rationale: Operating systems are central to computing activities. An operating system is a program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware. Two primary aims of an operating systems are to manage resources (e.g. CPU time, memory) and to control users and so ...
... Rationale: Operating systems are central to computing activities. An operating system is a program that acts as an intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware. Two primary aims of an operating systems are to manage resources (e.g. CPU time, memory) and to control users and so ...
Operating System Architecture and Distributed Systems
... while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. That is kernel would provide only the most basic mechanisms upon which the general resource management tasks at a node are carried out. Server modules would be dynamically loaded as required, to implement the required RM policie ...
... while coexisting with a non-real-time application such as web browsing. That is kernel would provide only the most basic mechanisms upon which the general resource management tasks at a node are carried out. Server modules would be dynamically loaded as required, to implement the required RM policie ...
l34
... PC's in early 80’s: Operating Systems for PC Apple: Macintosh (Xerox PARC) Workstations o UNIX -- AT&T: License Wars -- LINUX ...
... PC's in early 80’s: Operating Systems for PC Apple: Macintosh (Xerox PARC) Workstations o UNIX -- AT&T: License Wars -- LINUX ...
Slides
... • With modularity, layers are selected such that each uses functions (operations) and services of only lower-level layers ...
... • With modularity, layers are selected such that each uses functions (operations) and services of only lower-level layers ...
Introduction to UNIX System
... program and the file containing the kernel for the system. The name of the kernel file varies , but will usually include the letters “nix” so you can search for it with wildcard characters. ...
... program and the file containing the kernel for the system. The name of the kernel file varies , but will usually include the letters “nix” so you can search for it with wildcard characters. ...
Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures
... • With modularity, layers are selected such that each uses functions (operations) and services of only lower-level layers ...
... • With modularity, layers are selected such that each uses functions (operations) and services of only lower-level layers ...
csc1 intro
... 2. File Allocation Table (FAT)…. (list of file locations: starting position/cluster number on the disk) ...
... 2. File Allocation Table (FAT)…. (list of file locations: starting position/cluster number on the disk) ...
Course objectives: 1. To learn the fundamentals of Operating
... File Management: Overview, file Organization and access, file directories, File sharing, Record blocking, secondary storage management, File System Security, UNIX file Management. Case Study: Linux system, Design Principles, kernel modules, process management, scheduling, memory management, file sys ...
... File Management: Overview, file Organization and access, file directories, File sharing, Record blocking, secondary storage management, File System Security, UNIX file Management. Case Study: Linux system, Design Principles, kernel modules, process management, scheduling, memory management, file sys ...
Module 3: Operating
... The virtual-machine concept provides complete protection of system resources since each virtual machine is isolated from all other virtual machines. This isolation, however, permits no direct sharing of resources. A virtual-machine system is a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and d ...
... The virtual-machine concept provides complete protection of system resources since each virtual machine is isolated from all other virtual machines. This isolation, however, permits no direct sharing of resources. A virtual-machine system is a perfect vehicle for operating-systems research and d ...
Operating- System Structures
... As in all cases of modular design, designing an operating system in a modular way has several advantages. The system is easier to debug and modify because changes affect only limited sections of the system rather than touching all sections of the operating system. Information is kept only where it i ...
... As in all cases of modular design, designing an operating system in a modular way has several advantages. The system is easier to debug and modify because changes affect only limited sections of the system rather than touching all sections of the operating system. Information is kept only where it i ...
different people attempt to accomplish the
... While I have been busy ranting about the need for new operating system design, Andrew Tanenbaum and his students have been busy writing MINIX 3. I don’t know how many times I have written about the need for a small kernel that can be trusted and running services without privileges, in their own prot ...
... While I have been busy ranting about the need for new operating system design, Andrew Tanenbaum and his students have been busy writing MINIX 3. I don’t know how many times I have written about the need for a small kernel that can be trusted and running services without privileges, in their own prot ...
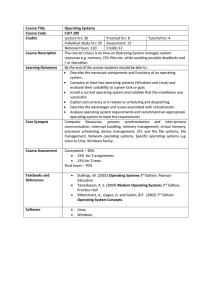
Course Title Operating Systems Course Code CUIT 109 Credits
... Individual Study hrs: 59 Assessment: 13 Notional Hours: 120 Credits 12 The course’s focus is on how an Operating System manages system resources e.g. memory, CPU files etc, while avoiding possible deadlocks and / or starvation. By the end of the course students should be able to : Describe the nec ...
... Individual Study hrs: 59 Assessment: 13 Notional Hours: 120 Credits 12 The course’s focus is on how an Operating System manages system resources e.g. memory, CPU files etc, while avoiding possible deadlocks and / or starvation. By the end of the course students should be able to : Describe the nec ...
Lecture 3
... Portability: Code should run on any system that supports the same API. Ease of use. ...
... Portability: Code should run on any system that supports the same API. Ease of use. ...
CMPT 880: Internet Architectures and Protocols
... A programming interface to OS services Typically written in high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API), rather than direct system call ...
... A programming interface to OS services Typically written in high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level Application Program Interface (API), rather than direct system call ...
Computer science The Tired Librarian 80
... Voltaire: “When he who hears does not know what he who speaks means, and when he who speaks does not know what he himself means, that is philosophy.” and “If God did not exist, it would be necessary to invent Him.” ...
... Voltaire: “When he who hears does not know what he who speaks means, and when he who speaks does not know what he himself means, that is philosophy.” and “If God did not exist, it would be necessary to invent Him.” ...
Homework 1 Solutions
... 10. On all current computers, at least part of the interrupt handlers are written in assembly language. Why? There are actions (such as saving registers) that happen while an interrupt is being handled. These actions need to be written in assembly because they cannot be expressed in higher level lan ...
... 10. On all current computers, at least part of the interrupt handlers are written in assembly language. Why? There are actions (such as saving registers) that happen while an interrupt is being handled. These actions need to be written in assembly because they cannot be expressed in higher level lan ...
Operating System - Linux - Home Pages of People@DU
... system starts and runs till the session gets terminated Different from BIOS which is hardware dependent. Kernel is software dependent ...
... system starts and runs till the session gets terminated Different from BIOS which is hardware dependent. Kernel is software dependent ...
Import Settings:
... 28. Describe how Mac OS X is considered a hybrid system. 29. Describe how Android uses a unique virtual machine for running Java programs. True/False 30. KDE and GNOME desktops are available under open-source licenses. 31. Many operating system merge I/O devices and files into a combined file becaus ...
... 28. Describe how Mac OS X is considered a hybrid system. 29. Describe how Android uses a unique virtual machine for running Java programs. True/False 30. KDE and GNOME desktops are available under open-source licenses. 31. Many operating system merge I/O devices and files into a combined file becaus ...
PowerPoint - cse.sc.edu
... contributions to Linux come from proprietary licensed code – AIX is based on System V r4, now owned by SCO ...
... contributions to Linux come from proprietary licensed code – AIX is based on System V r4, now owned by SCO ...
What is an operating system?
... instructions). Concurrent threads may interfere one with another. This leads to the necessity for resource protection by using user/supervisor modes. For example, the I/O instructions are privileged, it can be run only in supervisor mode. The system calls are making the transfer from user mode into ...
... instructions). Concurrent threads may interfere one with another. This leads to the necessity for resource protection by using user/supervisor modes. For example, the I/O instructions are privileged, it can be run only in supervisor mode. The system calls are making the transfer from user mode into ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
... • Allows process to be comprised of a number of fixed-size blocks, called pages • Virtual address is a page number and an offset within the page • Each page may be located anywhere in main memory – page frame • Real address or physical address in main memory ...
... • Allows process to be comprised of a number of fixed-size blocks, called pages • Virtual address is a page number and an offset within the page • Each page may be located anywhere in main memory – page frame • Real address or physical address in main memory ...
Operating System
... Outcomes: Students should be able to use his knowledge to develop/design any new Operating System. UNIT I Lectures: 14 Introduction: Introduction to OS. Operating system functions, evaluation of O.S., Different types of O.S.: batch, multi-programmed, time-sharing, real-time, distributed, parallel. P ...
... Outcomes: Students should be able to use his knowledge to develop/design any new Operating System. UNIT I Lectures: 14 Introduction: Introduction to OS. Operating system functions, evaluation of O.S., Different types of O.S.: batch, multi-programmed, time-sharing, real-time, distributed, parallel. P ...
Operating- System Structures
... the system rather than touching all sections of the operating system. Information is kept only where it is needed and is accessible only within a defined and restricted area, so any bugs affecting that data must be limited to a specific module or layer. ...
... the system rather than touching all sections of the operating system. Information is kept only where it is needed and is accessible only within a defined and restricted area, so any bugs affecting that data must be limited to a specific module or layer. ...