the user program.
... • This instruction switches the processor into a privileged operating mode (kernel mode) and jumps into the kernel through a well-defined trap address. • Parameters passed with the trap instruction tell the kernel what service is requested. • When the function is completed, the processor flips back ...
... • This instruction switches the processor into a privileged operating mode (kernel mode) and jumps into the kernel through a well-defined trap address. • Parameters passed with the trap instruction tell the kernel what service is requested. • When the function is completed, the processor flips back ...
Principles of Operating Systems Lecture 15b
... fair share and more to those who have had less than their fair share ...
... fair share and more to those who have had less than their fair share ...
Operating System
... • When one job needs to wait for I/O, the processor can switch to the other job ...
... • When one job needs to wait for I/O, the processor can switch to the other job ...
Systems II
... Protection refers to a mechanism for controlling the access of programs, processes or users to the resources defined by a computer system The processes in an operating system must be protected from one another’s activities Various mechanisms can be used to ensure that the files, memory segments, ...
... Protection refers to a mechanism for controlling the access of programs, processes or users to the resources defined by a computer system The processes in an operating system must be protected from one another’s activities Various mechanisms can be used to ensure that the files, memory segments, ...
OPERATING SYSTEMS:
... Multiprogramming: partitioning the memory with a different job in each partition. Special hardware protects each job against other jobs running in memory at once Spooling “Simultaneous Peripheral Operation On Line”: whenever a running job finished, O/S load a new job from disk to the now-empty parti ...
... Multiprogramming: partitioning the memory with a different job in each partition. Special hardware protects each job against other jobs running in memory at once Spooling “Simultaneous Peripheral Operation On Line”: whenever a running job finished, O/S load a new job from disk to the now-empty parti ...
A Five-State Process Model (Review) The not
... Process is created or terminated Process switches from running to blocked ...
... Process is created or terminated Process switches from running to blocked ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
... – Prevents a job from monopolizing the system (when allocated time is up, job is stopped) ...
... – Prevents a job from monopolizing the system (when allocated time is up, job is stopped) ...
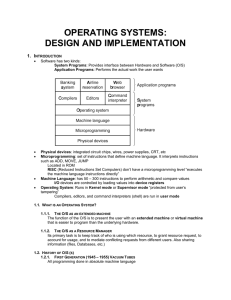
Introduction
... that is currently executing. • The actual contents of all programs are initially stored in persistent storage, such as a hard drive. • In order to be executed, a program must be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and uniquely identified as a process. • In this way, multiple copies of the same pr ...
... that is currently executing. • The actual contents of all programs are initially stored in persistent storage, such as a hard drive. • In order to be executed, a program must be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and uniquely identified as a process. • In this way, multiple copies of the same pr ...
Solution to assignment 2(B)
... Ques4: Some early computers protected the operating system by placing it in a memory partition that could not be modified by either the user job or the operating system itself. Describe two difficulties that you think could arise with such a scheme. Answer: The data required by the operating system ...
... Ques4: Some early computers protected the operating system by placing it in a memory partition that could not be modified by either the user job or the operating system itself. Describe two difficulties that you think could arise with such a scheme. Answer: The data required by the operating system ...
SE U 513 Exam
... o Example: write to read-only file Arithmetic error Time overrun o Process waited longer than a specified maximum for an event I/O failure Invalid instruction o Happens when try to execute data Privileged instruction Operating system intervention o such as when deadlock occurs Parent request to term ...
... o Example: write to read-only file Arithmetic error Time overrun o Process waited longer than a specified maximum for an event I/O failure Invalid instruction o Happens when try to execute data Privileged instruction Operating system intervention o such as when deadlock occurs Parent request to term ...
QUIZ1
... example of a process that might be preemptive. What type of processes would probably nonpreemptive? 21. In a time-sharing system, a process might be temporarily deprived of CPU. Indicate those cases in which such possibilities might result. What must OS require of CPU to do to facilitate a smooth tr ...
... example of a process that might be preemptive. What type of processes would probably nonpreemptive? 21. In a time-sharing system, a process might be temporarily deprived of CPU. Indicate those cases in which such possibilities might result. What must OS require of CPU to do to facilitate a smooth tr ...
Downlaod File
... switching between jobs occurs so frequently that the users can interact with each program while it is running. A time-shared operating system uses CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to provide each user with a small portion of time-shared system. ...
... switching between jobs occurs so frequently that the users can interact with each program while it is running. A time-shared operating system uses CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to provide each user with a small portion of time-shared system. ...
Al- Balqa Applied University Al-huson University College Dept. of
... 17- To access the services of operating system, the interface is provided by the A) system calls B) API C) library D) assembly instructions 18- Which one of the following is not true? A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of op ...
... 17- To access the services of operating system, the interface is provided by the A) system calls B) API C) library D) assembly instructions 18- Which one of the following is not true? A) kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system B) kernel is the first part of op ...
Operating Systems CMPSC 473
... – E.g., OS protects access to disk via protecting access to file abstraction ...
... – E.g., OS protects access to disk via protecting access to file abstraction ...
Batching processing
... A timer circuit counts down the quantum and generates an interrupt at the end. Such process switch involves updating the snapshot of the current process, restoring the snapshot of the next process, and then starting its execution. A program, called interrupt handler, is run for scheduler to update t ...
... A timer circuit counts down the quantum and generates an interrupt at the end. Such process switch involves updating the snapshot of the current process, restoring the snapshot of the next process, and then starting its execution. A program, called interrupt handler, is run for scheduler to update t ...
Operating Systems (OS)
... when a process ends, or uses up its scheduled time, or cannot be continued because an interrupt occurred or the process is waiting for something or the error trap suspends the execution of the process while an error is handled the despatcher executes the next process in the process queue according t ...
... when a process ends, or uses up its scheduled time, or cannot be continued because an interrupt occurred or the process is waiting for something or the error trap suspends the execution of the process while an error is handled the despatcher executes the next process in the process queue according t ...
Chapter 2 Operating System Overview
... to communicate via RPCs • Provides base for distributed computing ...
... to communicate via RPCs • Provides base for distributed computing ...
KernelSec: An Authorization Model in the Operating System Kernel
... to change the privileges available (dynamically) at run-time. Associated with every process is a domain which describes its privileges. In KernelSec, the domain may be changed to obtain a needed (but missing) privilege. Such dynamic domain transitions allows KernelSec to track process history and su ...
... to change the privileges available (dynamically) at run-time. Associated with every process is a domain which describes its privileges. In KernelSec, the domain may be changed to obtain a needed (but missing) privilege. Such dynamic domain transitions allows KernelSec to track process history and su ...
Principles of Operating System
... • The kernel itself is an executable; on Linux, this executable is located at /boot/vmlinuz ...
... • The kernel itself is an executable; on Linux, this executable is located at /boot/vmlinuz ...
OPERATING SYSTEM CONCEPTS
... Switching the CPU to another process requires saving the state of the old process and loading the saved state for the new process. This task is known as a context switch. Context-switch time is pure overhead, because the system does no useful work while switching. Its speed varies from machine to m ...
... Switching the CPU to another process requires saving the state of the old process and loading the saved state for the new process. This task is known as a context switch. Context-switch time is pure overhead, because the system does no useful work while switching. Its speed varies from machine to m ...
1 - Erode Sengunthar Engineering College
... primary memory, but partial portion of the process or job may be in secondary memory. It requires CPU scheduling scheme , job synchronization , job communication also jobs should not get stuck in deadlock. 6.Differentiate TCS & LCS ? LCS 1.Each processor has its own local memory 2.Each processor can ...
... primary memory, but partial portion of the process or job may be in secondary memory. It requires CPU scheduling scheme , job synchronization , job communication also jobs should not get stuck in deadlock. 6.Differentiate TCS & LCS ? LCS 1.Each processor has its own local memory 2.Each processor can ...