Probability and statistics
... l Must I wait for more than 10 minutes for the next bus? The answers to all these questions are uncertain. These are good examples of experiments. ...
... l Must I wait for more than 10 minutes for the next bus? The answers to all these questions are uncertain. These are good examples of experiments. ...
Basic Probability
... calculator list with the numbers 1 through 100. Use your formula from Step 5 to make a second list of the probabilities of rolling the first 4 on the first roll, the second roll, the third roll, and so on, up to the 100th roll. Create a third list that is the product of these two lists. Calculate th ...
... calculator list with the numbers 1 through 100. Use your formula from Step 5 to make a second list of the probabilities of rolling the first 4 on the first roll, the second roll, the third roll, and so on, up to the 100th roll. Create a third list that is the product of these two lists. Calculate th ...
1.017 Class 10: Common Distributions
... A random variable is a function (or rule) x() that associates a real number x with each outcome in the sample space S of an experiment. Assignment of such rules enables us to quantify a wide range of real-world experimental outcomes. Example: Experiment: Toss of a coin Outcome: Heads or tails Ran ...
... A random variable is a function (or rule) x() that associates a real number x with each outcome in the sample space S of an experiment. Assignment of such rules enables us to quantify a wide range of real-world experimental outcomes. Example: Experiment: Toss of a coin Outcome: Heads or tails Ran ...
Chapter 7 Lesson 8 - Mrs.Lemons Geometry
... Chapter 7 Lesson 8 Objective: To use segment and area models to find the probabilities of events. ...
... Chapter 7 Lesson 8 Objective: To use segment and area models to find the probabilities of events. ...
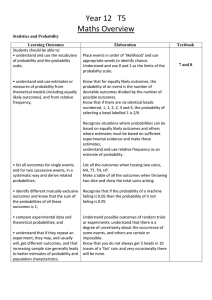
T5 Statistics and Probability
... Understand and use 0 and 1 as the limits of the probability scale. Know that for equally likely outcomes, the probability of an event is the number of desirable outcomes divided by the number of possible outcomes. Know that if there are six identical beads numbered, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 and 4, the probabil ...
... Understand and use 0 and 1 as the limits of the probability scale. Know that for equally likely outcomes, the probability of an event is the number of desirable outcomes divided by the number of possible outcomes. Know that if there are six identical beads numbered, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3 and 4, the probabil ...
Number of times resulting in event Total number of times experiment
... Random Phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes can occur, but we do not know which outcome will occur. We cannot predict each outcome, but there will be a regular distribution over many repetitions. ...
... Random Phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes can occur, but we do not know which outcome will occur. We cannot predict each outcome, but there will be a regular distribution over many repetitions. ...