Mod 1 Ch 3 - Linn-Benton Community College
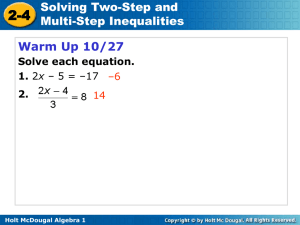
... Non-Linear Equations: When graphing non-linear equations more points will be needed to create the graph. On the graph of the quadratic equation: y x 2 2 x 3 , each square is 2 units. Locate and label: The vertex:___________ The Axis of Symmetry (AOS):__________ The x-intercept(s): ____________ ...
... Non-Linear Equations: When graphing non-linear equations more points will be needed to create the graph. On the graph of the quadratic equation: y x 2 2 x 3 , each square is 2 units. Locate and label: The vertex:___________ The Axis of Symmetry (AOS):__________ The x-intercept(s): ____________ ...
Topic 4 Notes 4 Complex numbers and exponentials Jeremy Orloff 4.1 Goals
... This is how the quadratic formula is derived and is well worth knowing! 4.2.1 Fundamental theorem of algebra One of the reasons for using complex numbers is because by allowing complex roots every polynomial has exactly the expected number of roots. Fundamental theorem of algebra. A polynomial of de ...
... This is how the quadratic formula is derived and is well worth knowing! 4.2.1 Fundamental theorem of algebra One of the reasons for using complex numbers is because by allowing complex roots every polynomial has exactly the expected number of roots. Fundamental theorem of algebra. A polynomial of de ...
Full text
... Integer representations by forms are sources of a series of very interesting Diophantine equations. For instance, the cubic form x3 +y3+z3 represents 1 and 2 in an infinite number of ways, whereas only two representations (1,1,1) and (4,4, -5) are known for the number 3 and it is unknown whether the ...
... Integer representations by forms are sources of a series of very interesting Diophantine equations. For instance, the cubic form x3 +y3+z3 represents 1 and 2 in an infinite number of ways, whereas only two representations (1,1,1) and (4,4, -5) are known for the number 3 and it is unknown whether the ...
Hausdorff dimension and Diophantine approximation Yann
... of approximation, that is, of a function defined on the set of real irrational numbers by means of consideration from Diophantine approximation. Definition 1.2. The spectrum of an exponent of approximation is the set of values taken by this exponent. For an exponent of approximation w, there are two ...
... of approximation, that is, of a function defined on the set of real irrational numbers by means of consideration from Diophantine approximation. Definition 1.2. The spectrum of an exponent of approximation is the set of values taken by this exponent. For an exponent of approximation w, there are two ...
3. - My CCSD
... Each row of Pascal’s triangle gives the coefficients of the corresponding binomial expansion. The pattern in the table can be extended to apply to the expansion of any binomial of the form (a + b)n, where n is a whole number. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 ...
... Each row of Pascal’s triangle gives the coefficients of the corresponding binomial expansion. The pattern in the table can be extended to apply to the expansion of any binomial of the form (a + b)n, where n is a whole number. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 ...
November 16, 2015- 3.1
... In most states, the price of each item is not the total cost. Sales tax must be added. If sales tax is 7.5%, the equation for total cost is c = 1.075p, where p is the price before tax. How much will a $22 item cost after sales tax? ...
... In most states, the price of each item is not the total cost. Sales tax must be added. If sales tax is 7.5%, the equation for total cost is c = 1.075p, where p is the price before tax. How much will a $22 item cost after sales tax? ...
04 commutative rings I
... such factorization. Then F is not irreducible (or the non-factorization is the factorization), so R = A · B with both of A, B of lower degree but not degree 0. By induction, both A and B have factorizations into primes. Uniqueness is a sharper result, proven via the property that P |AB implies P |A ...
... such factorization. Then F is not irreducible (or the non-factorization is the factorization), so R = A · B with both of A, B of lower degree but not degree 0. By induction, both A and B have factorizations into primes. Uniqueness is a sharper result, proven via the property that P |AB implies P |A ...
LOCAL CLASS GROUPS All rings considered here are commutative
... xr + c1 xr−1 + · · · + cr = 0 with ci ∈ Z with (a, b) = 1, multiplying by br gives ar + c1 ar−1 b + . . . cr br = 0 so that b|ar and it follows that b = 1. ...
... xr + c1 xr−1 + · · · + cr = 0 with ci ∈ Z with (a, b) = 1, multiplying by br gives ar + c1 ar−1 b + . . . cr br = 0 so that b|ar and it follows that b = 1. ...
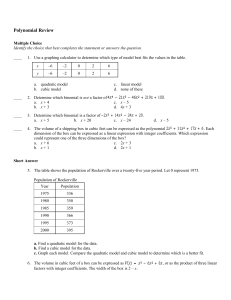
Algebra 1 Name: 4.1 – 4.3 Review Period: _____ For problems 1
... a. Write an equation in intercept to model how much money is in his pocket after buying x number of candy bars. b. What does a represent in this situation? What does b represent in this situation? c. If he bought 22 candy bars, how much money does he have left? d. If he has $9.73 in his pocket, how ...
... a. Write an equation in intercept to model how much money is in his pocket after buying x number of candy bars. b. What does a represent in this situation? What does b represent in this situation? c. If he bought 22 candy bars, how much money does he have left? d. If he has $9.73 in his pocket, how ...