STAAR Algebra II - ESC-20
... logb (x) where b is 2, 10, and ewhen f(x) is replaced by af(x), f(x) + d, and f(x - c) for specific positive and negative real values of a, c, and d Formulate exponential and logarithmic equations that model real-world situations, including exponential relationships written in recursive notation Rew ...
... logb (x) where b is 2, 10, and ewhen f(x) is replaced by af(x), f(x) + d, and f(x - c) for specific positive and negative real values of a, c, and d Formulate exponential and logarithmic equations that model real-world situations, including exponential relationships written in recursive notation Rew ...
Chapter 2
... Use the normal order of operations and problem solving steps to get the specific variable on one side of the equal sign and everything else on the other side of the equal ...
... Use the normal order of operations and problem solving steps to get the specific variable on one side of the equal sign and everything else on the other side of the equal ...
Section 9.4
... Eliminate x from equations (4) and (5). 15x – 10y = 20 15x + 15y = 15 5y = 5 Use y = 1, to find x in equation 4. y = 1 3x + 2y = 4 3x + 2(1) = 4 x=2 ...
... Eliminate x from equations (4) and (5). 15x – 10y = 20 15x + 15y = 15 5y = 5 Use y = 1, to find x in equation 4. y = 1 3x + 2y = 4 3x + 2(1) = 4 x=2 ...
Secondary Math 3 I Can Statements.docx
... I can create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. I can create inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. I can create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities. I can graph equations on a coordinate axis with labels and s ...
... I can create equations in one variable and use them to solve problems. I can create inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. I can create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities. I can graph equations on a coordinate axis with labels and s ...
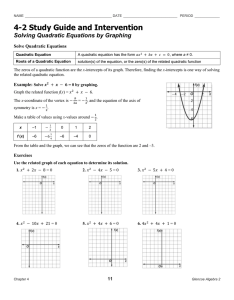
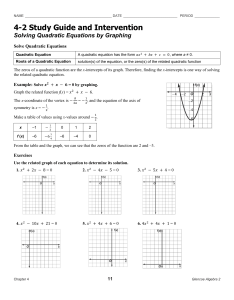
Chapter “-1” Study Guide- Key Factoring The purpose of factoring is
... 2) If the leading coefficient of the QT is different than a “1”, divide the QT and the LT by it. 3) Take ½ of your LT and square it. 4) Add the result of step #3 to both sides of your equation. If you divided out a number from step #2 be sure to add the product of that number and the number you adde ...
... 2) If the leading coefficient of the QT is different than a “1”, divide the QT and the LT by it. 3) Take ½ of your LT and square it. 4) Add the result of step #3 to both sides of your equation. If you divided out a number from step #2 be sure to add the product of that number and the number you adde ...
systems_of_linear_equations
... A solution of a system of two linear equations in two variables is an ordered pair of numbers satisfying both equations simultaneously. In the above example (2,4) is a solution of both equations. In fact, 2+4 = 6 and 3(2)-4 = 2. Therefore the ordered pair (2,4) is a solution of the system. Graphical ...
... A solution of a system of two linear equations in two variables is an ordered pair of numbers satisfying both equations simultaneously. In the above example (2,4) is a solution of both equations. In fact, 2+4 = 6 and 3(2)-4 = 2. Therefore the ordered pair (2,4) is a solution of the system. Graphical ...