11.2, 11.3 Surface Areas of Prisms, Cylinders, Pyramids, and Cones
... joins the bases Height – the length of an ...
... joins the bases Height – the length of an ...
Observation and Modeling of High Individual Ocean Waves and
... observed and its parameters can be determined. Thus, a new technique can be used by applying the wind gustiness parameters within numerical modeling by Lagrange’s method. This means to follow the cells and their impact across the model domain. The difference between these two approaches is significa ...
... observed and its parameters can be determined. Thus, a new technique can be used by applying the wind gustiness parameters within numerical modeling by Lagrange’s method. This means to follow the cells and their impact across the model domain. The difference between these two approaches is significa ...
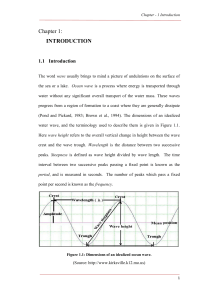
Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION
... energy proportional to the time. Once the waves exit, they may modify the air flow so that the growth rate becomes proportional to the wave amplitude and hence exponential in time. ...
... energy proportional to the time. Once the waves exit, they may modify the air flow so that the growth rate becomes proportional to the wave amplitude and hence exponential in time. ...
1 The basic equations of fluid dynamics
... The main task in fluid dynamics is to find the velocity field describing the flow in a given domain. To do this, one uses the basic equations of fluid flow, which we derive in this section. These encode the familiar laws of mechanics: • conservation of mass (the continuity equation, Sec. 1.2) • cons ...
... The main task in fluid dynamics is to find the velocity field describing the flow in a given domain. To do this, one uses the basic equations of fluid flow, which we derive in this section. These encode the familiar laws of mechanics: • conservation of mass (the continuity equation, Sec. 1.2) • cons ...
A generalized reciprocal theorem for predicting the force
... Fluid Mechanics. Specific formulations of the problem have been developed in the two limits where the governing equations become linear, namely Stokes flows and potential flows. However the general case where inertial and viscous effects are both present poses much greater difficulties, owing to the ...
... Fluid Mechanics. Specific formulations of the problem have been developed in the two limits where the governing equations become linear, namely Stokes flows and potential flows. However the general case where inertial and viscous effects are both present poses much greater difficulties, owing to the ...
Characteristics Method applied to the shock tube problem
... The objective of the course being CFD, it is assumed at this point that stationary shock waves are known. The solution is presented without demonstration (it is the only solution satisfying initial conditions and thermodynamic principles). The rupture of the diaphragm causes a shock wave that travel ...
... The objective of the course being CFD, it is assumed at this point that stationary shock waves are known. The solution is presented without demonstration (it is the only solution satisfying initial conditions and thermodynamic principles). The rupture of the diaphragm causes a shock wave that travel ...
spontaneously generated waves in perurbed evolution equations
... Physics Department & Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Midreshet Ben-Gurion, Israel ...
... Physics Department & Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Midreshet Ben-Gurion, Israel ...
contributed papers - Department of Mathematical Sciences
... neurons that make up these networks are known to be highly plastic both in the intact ganglion as well as in dissociated culture conditions. In the intact network, it is known that the mechanisms of rhythm generation by the pyloric network can switch between two modes: one in which rhythm generation ...
... neurons that make up these networks are known to be highly plastic both in the intact ganglion as well as in dissociated culture conditions. In the intact network, it is known that the mechanisms of rhythm generation by the pyloric network can switch between two modes: one in which rhythm generation ...
PHY1025F-2014-V01-Oscillations-Lecture Slides
... A simple example of a standing wave is a wave on a string, like you will see in Vibrating String practical. The mechanical oscillator creates a traveling wave that is reflected off the fixed end and interferes with itself. The result is a series of nodes and antinodes, with the exact number dependin ...
... A simple example of a standing wave is a wave on a string, like you will see in Vibrating String practical. The mechanical oscillator creates a traveling wave that is reflected off the fixed end and interferes with itself. The result is a series of nodes and antinodes, with the exact number dependin ...
Document
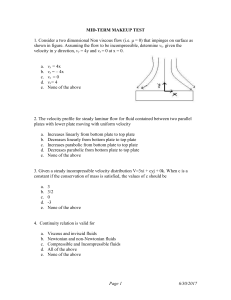
... MID-TERM MAKEUP TEST 1. Consider a two dimensional Non viscous flow (i.e. μ = 0) that impinges on surface as shown in figure. Assuming the flow to be incompressible, determine vx, given the velocity in y direction, vy = 4y and vx = 0 at x = 0. ...
... MID-TERM MAKEUP TEST 1. Consider a two dimensional Non viscous flow (i.e. μ = 0) that impinges on surface as shown in figure. Assuming the flow to be incompressible, determine vx, given the velocity in y direction, vy = 4y and vx = 0 at x = 0. ...
Slides
... result of surface tension and adhesive forces The liquid rises in the tube when adhesive forces are greater than cohesive forces At the point of contact between the liquid and the solid, the upward forces are as shown in the diagram ...
... result of surface tension and adhesive forces The liquid rises in the tube when adhesive forces are greater than cohesive forces At the point of contact between the liquid and the solid, the upward forces are as shown in the diagram ...
國立臺北科技大學九十一學年度
... the x-component of fluid velocity u as a function of time t, fluid viscosity μ, top plate speed V, distance h, fluid densityρ, and distance y (i.e. u= f(t,μ, V, h,ρ, y)). Show details of your work. 5) An incompressible, viscous fluid is placed between two horizontal, infinite, parallel plates as is ...
... the x-component of fluid velocity u as a function of time t, fluid viscosity μ, top plate speed V, distance h, fluid densityρ, and distance y (i.e. u= f(t,μ, V, h,ρ, y)). Show details of your work. 5) An incompressible, viscous fluid is placed between two horizontal, infinite, parallel plates as is ...
Coastal Processes: WAVES - Organization of American States
... As noted above the boundary conditions used to obtain a solution for wave motion were linearised, that is, applied at y = 0 not on the free water surface, y = η, hence the term Linear (or Airy) Wave Theory. For a non-linear solution the free surface boundary conditions have to be applied at that fre ...
... As noted above the boundary conditions used to obtain a solution for wave motion were linearised, that is, applied at y = 0 not on the free water surface, y = η, hence the term Linear (or Airy) Wave Theory. For a non-linear solution the free surface boundary conditions have to be applied at that fre ...
ch.14 student notes
... Water waves, sound waves, and the waves that travel down a rope or spring are types of mechanical waves. Mechanical waves require a medium, such as water, air, ropes, or a spring. Because many other waves cannot be directly observed, mechanical waves can serve as models. The two disturbances shown i ...
... Water waves, sound waves, and the waves that travel down a rope or spring are types of mechanical waves. Mechanical waves require a medium, such as water, air, ropes, or a spring. Because many other waves cannot be directly observed, mechanical waves can serve as models. The two disturbances shown i ...
Stokes wave
In fluid dynamics, a Stokes wave is a non-linear and periodic surface wave on an inviscid fluid layer of constant mean depth.This type of modelling has its origins in the mid 19th century when Sir George Stokes – using a perturbation series approach, now known as the Stokes expansion – obtained approximate solutions for non-linear wave motion.Stokes' wave theory is of direct practical use for waves on intermediate and deep water. It is used in the design of coastal and offshore structures, in order to determine the wave kinematics (free surface elevation and flow velocities). The wave kinematics are subsequently needed in the design process to determine the wave loads on a structure. For long waves (as compared to depth) – and using only a few terms in the Stokes expansion – its applicability is limited to waves of small amplitude. In such shallow water, a cnoidal wave theory often provides better periodic-wave approximations.While, in the strict sense, Stokes wave refers to progressive periodic waves of permanent form, the term is also used in connection with standing waves and even for random waves.