Back
... other, both pairs of opposite sides are congruent, both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Back ...
... other, both pairs of opposite sides are congruent, both pairs of opposite angles are congruent. Back ...
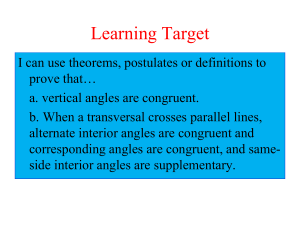
Vertical Angles and Transversal Powerpoint
... Estimating Earth’s Circumference: History Connection ...
... Estimating Earth’s Circumference: History Connection ...
1.4 Angles and Their Measures
... • Name the angles in the figure: S SOLUTION: There are three Q different angles. R • PQS or SQP You should not name any of • SQR or RQS these angles as Q because • PQR or RQP all three angles have Q as their P ...
... • Name the angles in the figure: S SOLUTION: There are three Q different angles. R • PQS or SQP You should not name any of • SQR or RQS these angles as Q because • PQR or RQP all three angles have Q as their P ...
Algebra_Math-a-thon_Study_Guide
... directly as x, or y is proportional to x. Direct variation formulas are of the form y = kx, where the number represented by k does not change and is called a constant of variation. Indirect variation equations are of the form y = k/x and show a relationship between two quantities such that when one ...
... directly as x, or y is proportional to x. Direct variation formulas are of the form y = kx, where the number represented by k does not change and is called a constant of variation. Indirect variation equations are of the form y = k/x and show a relationship between two quantities such that when one ...
Math Homework Helper
... Symbols are used to show how the size of one number compares to another. These symbols are < (less than), > (greater than), and = (equals). For example, since 2 is smaller than 4 and 4 is larger than 2, we can write: 2 < 4, which says the same as 4 > 2 and of course, 4 = 4. • To compare two wh ...
... Symbols are used to show how the size of one number compares to another. These symbols are < (less than), > (greater than), and = (equals). For example, since 2 is smaller than 4 and 4 is larger than 2, we can write: 2 < 4, which says the same as 4 > 2 and of course, 4 = 4. • To compare two wh ...
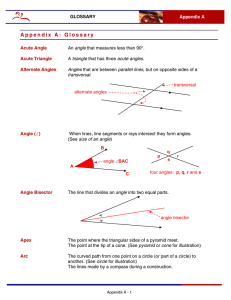
Geometric Shapes - Glossary
... The number that all the lengths of a pre-image shape are multiplied by to get the image shape during a magnification. If it is greater than 1, the image is larger than the pre-image. If it is smaller than 1, the image is smaller than the pre-image. ...
... The number that all the lengths of a pre-image shape are multiplied by to get the image shape during a magnification. If it is greater than 1, the image is larger than the pre-image. If it is smaller than 1, the image is smaller than the pre-image. ...
Line (geometry)
The notion of line or straight line was introduced by ancient mathematicians to represent straight objects (i.e., having no curvature) with negligible width and depth. Lines are an idealization of such objects. Until the seventeenth century, lines were defined in this manner: ""The [straight or curved] line is the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width. […] The straight line is that which is equally extended between its points""Euclid described a line as ""breadthless length"" which ""lies equally with respect to the points on itself""; he introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties from which he constructed the geometry, which is now called Euclidean geometry to avoid confusion with other geometries which have been introduced since the end of nineteenth century (such as non-Euclidean, projective and affine geometry).In modern mathematics, given the multitude of geometries, the concept of a line is closely tied to the way the geometry is described. For instance, in analytic geometry, a line in the plane is often defined as the set of points whose coordinates satisfy a given linear equation, but in a more abstract setting, such as incidence geometry, a line may be an independent object, distinct from the set of points which lie on it.When a geometry is described by a set of axioms, the notion of a line is usually left undefined (a so-called primitive object). The properties of lines are then determined by the axioms which refer to them. One advantage to this approach is the flexibility it gives to users of the geometry. Thus in differential geometry a line may be interpreted as a geodesic (shortest path between points), while in some projective geometries a line is a 2-dimensional vector space (all linear combinations of two independent vectors). This flexibility also extends beyond mathematics and, for example, permits physicists to think of the path of a light ray as being a line.A line segment is a part of a line that is bounded by two distinct end points and contains every point on the line between its end points. Depending on how the line segment is defined, either of the two end points may or may not be part of the line segment. Two or more line segments may have some of the same relationships as lines, such as being parallel, intersecting, or skew, but unlike lines they may be none of these, if they are coplanar and either do not intersect or are collinear.