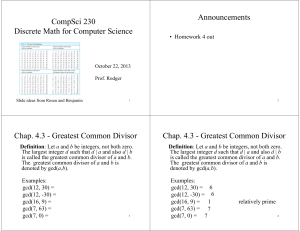
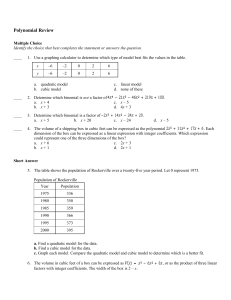
Polynomial Review Answer Section
... a. Factor the polynomial to find linear expressions for the height and the width. b. Graph the function. Find the x-intercepts. What do they represent? c. Describe a realistic domain for the function. d. Find the maximum volume of the box. 7. The volume in cubic feet of a workshop’s storage chest c ...
... a. Factor the polynomial to find linear expressions for the height and the width. b. Graph the function. Find the x-intercepts. What do they represent? c. Describe a realistic domain for the function. d. Find the maximum volume of the box. 7. The volume in cubic feet of a workshop’s storage chest c ...
Introduction to amoebas and tropical geometry
... The proof can be found in [26] in chapter 1 and is harder than one would expect. It is now immediately clear that the intersection of two polytopes is again a polytope, which is not easy to prove directly from the definition. If we would define a polytope as a bounded polyhedron then it would be har ...
... The proof can be found in [26] in chapter 1 and is harder than one would expect. It is now immediately clear that the intersection of two polytopes is again a polytope, which is not easy to prove directly from the definition. If we would define a polytope as a bounded polyhedron then it would be har ...
ON COMPACTNESS OF LOGICS THAT CAN EXPRESS
... have the compactness property. The result is used to prove that for a number of natural properties P speaking about automorphism groups or connectivity, every logic which is at least as strong as first-order logic and can express P fails to have the compactness property. The basic idea underlying th ...
... have the compactness property. The result is used to prove that for a number of natural properties P speaking about automorphism groups or connectivity, every logic which is at least as strong as first-order logic and can express P fails to have the compactness property. The basic idea underlying th ...
Dynamic Programming
... Application domain of DP • Optimization problem: find a solution with optimal (maximum or minimum) value. • An optimal solution, not the optimal solution, since may more than one optimal solution, any one is OK. ...
... Application domain of DP • Optimization problem: find a solution with optimal (maximum or minimum) value. • An optimal solution, not the optimal solution, since may more than one optimal solution, any one is OK. ...