Unit 1: PARALLEL ALGORITHMS
... algorightm, parallel computer model and specific set of inputs. Mostly the size of the input is a function of time complexity of the algorithm. The generic notation for describing the time-complexity of any algorithm is discussed in the subsequent sections. ...
... algorightm, parallel computer model and specific set of inputs. Mostly the size of the input is a function of time complexity of the algorithm. The generic notation for describing the time-complexity of any algorithm is discussed in the subsequent sections. ...
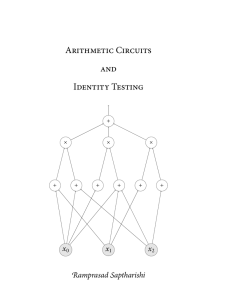
Arithmetic Circuits and Identity Testing
... As for PIT, the problem has drawn significant attention due to its role in various fields of theoretical computer science. Besides being a natural problem in algebraic computation, identity testing has found applications in various fundamental results like Shamir’s IP = PSPACE [Sha90], the PCP Theor ...
... As for PIT, the problem has drawn significant attention due to its role in various fields of theoretical computer science. Besides being a natural problem in algebraic computation, identity testing has found applications in various fundamental results like Shamir’s IP = PSPACE [Sha90], the PCP Theor ...
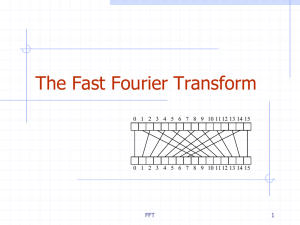
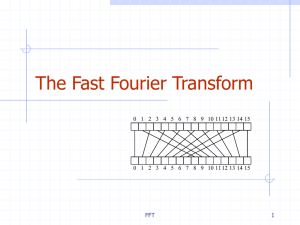
FFT - Personal Web Pages
... Given N-bit integers I and J, compute IJ. Assume: we can multiply words of O(log N) bits in constant time. Setup: Find a prime p=cn+1 that can be represented in one word, and set m=(log p)/3, so that we can view I and J as n-length vectors of m-bit words. Finding a primitive root of unity. ...
... Given N-bit integers I and J, compute IJ. Assume: we can multiply words of O(log N) bits in constant time. Setup: Find a prime p=cn+1 that can be represented in one word, and set m=(log p)/3, so that we can view I and J as n-length vectors of m-bit words. Finding a primitive root of unity. ...