File - Warta MHS Science
... assume a wide variety of shapes. One of the more intriguing aspects of dinoflagellates is that some species are autotrophic and possess pigments necessary for photosynthesis (fig. 12.7a and b); some species are heterotrophic (fig. 12.7c and d) and are incapable of photosynthesis; and some species ar ...
... assume a wide variety of shapes. One of the more intriguing aspects of dinoflagellates is that some species are autotrophic and possess pigments necessary for photosynthesis (fig. 12.7a and b); some species are heterotrophic (fig. 12.7c and d) and are incapable of photosynthesis; and some species ar ...
- Sir Peter Blake Trust
... they carry out photosynthesis, turning it into sugars and other chemicals in their bodies. Phytoplankton also release carbon dioxide when they break down sugars during respiration to provide themselves with energy. Phytoplankton only live for a few days so carbon is stored in their bodies short term ...
... they carry out photosynthesis, turning it into sugars and other chemicals in their bodies. Phytoplankton also release carbon dioxide when they break down sugars during respiration to provide themselves with energy. Phytoplankton only live for a few days so carbon is stored in their bodies short term ...
Chapter 15
... b. are able to migrate vertically in response to changes in sunlight, c. are able to photosynthesize like a plant and feed by ingesting organic material like an animal, so they are both autotrophic and heterotrophic (heterotrophic organisms feed on other organisms or on organic material), d. sometim ...
... b. are able to migrate vertically in response to changes in sunlight, c. are able to photosynthesize like a plant and feed by ingesting organic material like an animal, so they are both autotrophic and heterotrophic (heterotrophic organisms feed on other organisms or on organic material), d. sometim ...
Comparative “Systems” - Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
... not provide benefits that are specific to upwelling systems, particularly given the water depths in these systems. Likewise, both species are toxic, but again, this may not explain their dominance in these systems. Only through careful studies using similar methods and approaches can comparable data ...
... not provide benefits that are specific to upwelling systems, particularly given the water depths in these systems. Likewise, both species are toxic, but again, this may not explain their dominance in these systems. Only through careful studies using similar methods and approaches can comparable data ...
- White Rose Research Online
... are continually exposed by the regular discovery of new clades of often large, active and conspicuous organisms [12] whenever surveys are undertaken. Even a charismatic, widely distributed and very large species, the megamouth shark Megachasma pelagios, was not discovered until 1976, and has since b ...
... are continually exposed by the regular discovery of new clades of often large, active and conspicuous organisms [12] whenever surveys are undertaken. Even a charismatic, widely distributed and very large species, the megamouth shark Megachasma pelagios, was not discovered until 1976, and has since b ...
Modeling Biogeochemical Processes in Marine Ecosystems
... the water column. (see Marine biogeochemical cycles: effects on climate and response to climate change). All the biogeochemical processes and interactions between living and non-living components of the ecosystems cannot possibly be explored through observations alone. The satellite-based observatio ...
... the water column. (see Marine biogeochemical cycles: effects on climate and response to climate change). All the biogeochemical processes and interactions between living and non-living components of the ecosystems cannot possibly be explored through observations alone. The satellite-based observatio ...
Remote sensing of water depths in shallow - Everglades-HUB
... imagery with modeling flexibility of ANN. Its main advantage in practice is that it enables to directly use image reflectance values in depth estimations, without refining depth-caused scatterings from other environmental factors (e.g. bottom material and vegetation). Its function-free structure allows ...
... imagery with modeling flexibility of ANN. Its main advantage in practice is that it enables to directly use image reflectance values in depth estimations, without refining depth-caused scatterings from other environmental factors (e.g. bottom material and vegetation). Its function-free structure allows ...
The Possible Importance of Silicon in Marine Eutrophication
... from river runoff inputs including sewage, industrial and agricultural sources. When the solar conditions are appropriate, which usually occurs in late spring or early summer but also in midwinter in some shallow estuaries, a common event is a diatom dominated bloom. The organic nitrogen and phospho ...
... from river runoff inputs including sewage, industrial and agricultural sources. When the solar conditions are appropriate, which usually occurs in late spring or early summer but also in midwinter in some shallow estuaries, a common event is a diatom dominated bloom. The organic nitrogen and phospho ...
Appendix D: Plankton
... non-living organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the water for subsequent uptake by the phytoplankton. Although limited in coverage, available data suggests that Pacific North Coast Integrated Management Area (PNCIMA, Figure D.0) averages of plankton standing stock, species composition, a ...
... non-living organic matter and releasing nutrients back into the water for subsequent uptake by the phytoplankton. Although limited in coverage, available data suggests that Pacific North Coast Integrated Management Area (PNCIMA, Figure D.0) averages of plankton standing stock, species composition, a ...
Sediment Deposition Supports Seafloor Spreading
... The goal of the scientific ocean drilling program is to investigate the sediments and rocks beneath 500 m the deep oceans by drilling and coring. The seafloor is usually made up of a thick layer of sediment. The sediment is composed 1000 m of sand, silt, clay, and microfossils that drift down throug ...
... The goal of the scientific ocean drilling program is to investigate the sediments and rocks beneath 500 m the deep oceans by drilling and coring. The seafloor is usually made up of a thick layer of sediment. The sediment is composed 1000 m of sand, silt, clay, and microfossils that drift down throug ...
MicroSoar: A New Instrument for Measuring Microscale Turbulence
... instruments typically fall at speeds O(0.75 m s 21 ) and send signals through their umbilical tether for recording aboard the mother ship. The usual sensor suite includes a fast-responding thermistor, one or more airfoil shear sensors (Osborn 1980), a pressure sensor, and a conductivity sensor. A va ...
... instruments typically fall at speeds O(0.75 m s 21 ) and send signals through their umbilical tether for recording aboard the mother ship. The usual sensor suite includes a fast-responding thermistor, one or more airfoil shear sensors (Osborn 1980), a pressure sensor, and a conductivity sensor. A va ...
Lecture 2
... Ø NO3- is the most oxidized form of nitrogen and it is uptaken by phytoplankton, bacteria, and plants in aerobic environments. Ø NO3- is reduced by assimilation processes involving several enzymes (e.g. nitrate reductase) to -NH2 (amine) form. Amine is used in metabolic processes. Ø NO3- is also use ...
... Ø NO3- is the most oxidized form of nitrogen and it is uptaken by phytoplankton, bacteria, and plants in aerobic environments. Ø NO3- is reduced by assimilation processes involving several enzymes (e.g. nitrate reductase) to -NH2 (amine) form. Amine is used in metabolic processes. Ø NO3- is also use ...
Ammonia concentrations in nutrient deplete oceanic waters
... In wide areas of the world’s oceans phytoplankton productivity is limited by the availability of nitrogen. The surface waters and the surface mixed layers of many temperate oceans, eg the Atlantic, typically are greatly depleted of dissolved inorganic nitrogen species (ammonia, nitrate and nitrite ...
... In wide areas of the world’s oceans phytoplankton productivity is limited by the availability of nitrogen. The surface waters and the surface mixed layers of many temperate oceans, eg the Atlantic, typically are greatly depleted of dissolved inorganic nitrogen species (ammonia, nitrate and nitrite ...
Translation Series No. 421
... synthesis in the open water. The method of determining Kt and K r has been described in earlier articles (Sorokin, 1957 9 1958). The coefficients Kr (the relation between productivity of photosynthesis and the vertical distribution of phytoplankton)were determined during the present voyage at every ...
... synthesis in the open water. The method of determining Kt and K r has been described in earlier articles (Sorokin, 1957 9 1958). The coefficients Kr (the relation between productivity of photosynthesis and the vertical distribution of phytoplankton)were determined during the present voyage at every ...
Lecture 4 - Physical Factors - Aquatic
... Upwelling effects -‐ Ocean chlorophyll concentra6on and surface temperature off the California coast Phytoplankton blooms (orange color on leq image) correspond to cool regions (blue color on right image). ...
... Upwelling effects -‐ Ocean chlorophyll concentra6on and surface temperature off the California coast Phytoplankton blooms (orange color on leq image) correspond to cool regions (blue color on right image). ...
Chapter 13: Biological productivity and energy
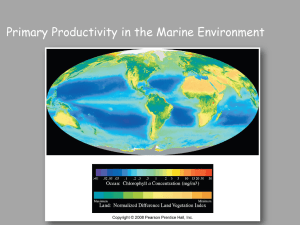
... Varies from very low to very high depending on Distribution of nutrients Seasonal changes in solar radiation ...
... Varies from very low to very high depending on Distribution of nutrients Seasonal changes in solar radiation ...
Chapter 13: Biological productivity and energy transfer
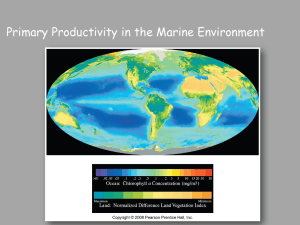
... Varies from very low to very high depending on Distribution of nutrients Seasonal changes in solar radiation ...
... Varies from very low to very high depending on Distribution of nutrients Seasonal changes in solar radiation ...