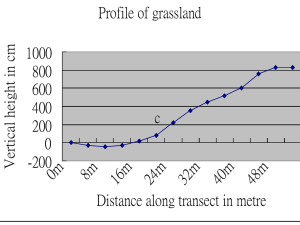
MarineBiology - Invertebrate Investigation Notes (Powerpoint)
... Sand Crab, dig and move up to 10 mph, sharp 360 degree vision. ...
... Sand Crab, dig and move up to 10 mph, sharp 360 degree vision. ...
Phylum Cnidaria - Jellyfish - about 9,000 species, all aquatic, and
... - Obelia and Hydra (which doesn’t alternate, and is not typical of Hydrozoans) are two good examples of members of this group. Scyphozoa: - medusa stage predominates. Typical jellyfish - some examples [OVERHEAD, also not in book]. - many are obviously dangerous, and even smaller ones can hurt. Cuboz ...
... - Obelia and Hydra (which doesn’t alternate, and is not typical of Hydrozoans) are two good examples of members of this group. Scyphozoa: - medusa stage predominates. Typical jellyfish - some examples [OVERHEAD, also not in book]. - many are obviously dangerous, and even smaller ones can hurt. Cuboz ...
Species found in the trip:
... normal spiders. They kill prey by secreting fluid from their stink glands. With regard to the number of legs they posses, each apparent body segment is actually composed of two adjacent segments fused together, so there is in fact only one pair if legs per body segment. ...
... normal spiders. They kill prey by secreting fluid from their stink glands. With regard to the number of legs they posses, each apparent body segment is actually composed of two adjacent segments fused together, so there is in fact only one pair if legs per body segment. ...
Lesson 7.1
... is: all species will choose the best partner possible for what they consider to be the most desirable traits. It happens biologically, without conscious thought. Marine animals are not different! Natural selection frequently leads to speciation. ...
... is: all species will choose the best partner possible for what they consider to be the most desirable traits. It happens biologically, without conscious thought. Marine animals are not different! Natural selection frequently leads to speciation. ...
File
... help them grip the soil and move along. • Earthworms eat rotting matter and soil and they help to aerate the soil so gardeners and farmers love them! ...
... help them grip the soil and move along. • Earthworms eat rotting matter and soil and they help to aerate the soil so gardeners and farmers love them! ...
Mountain Stream Sardine
... characteristics (Armi, 2015). The number of branched anal fin rays, of which there are 25-29 is one of these characteristics as other fishes belonging to the same genus have around 15-24. Another unique characteristic of the mountain stream sardine is the number of vertebrae. Compared to the normal ...
... characteristics (Armi, 2015). The number of branched anal fin rays, of which there are 25-29 is one of these characteristics as other fishes belonging to the same genus have around 15-24. Another unique characteristic of the mountain stream sardine is the number of vertebrae. Compared to the normal ...
AmphibianTalkingPoin..
... health of the planet or of individual habitats; amphibians are considered indicator species. Since amphibian skin is permeable, pollutants that threaten an ecosystem’s health will also affect the frog. • Frogs produce a wide array of skin secretions, many of which have significant potential to impro ...
... health of the planet or of individual habitats; amphibians are considered indicator species. Since amphibian skin is permeable, pollutants that threaten an ecosystem’s health will also affect the frog. • Frogs produce a wide array of skin secretions, many of which have significant potential to impro ...
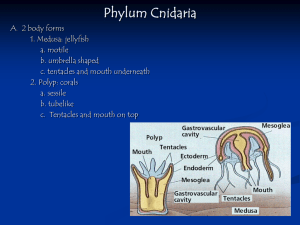
Unit 9 - Phylum Cnidaria – Guided Notes Introduction Body forms
... -Tentacles up to __________ long, nematocysts poison can be fatal Ex. Obelia -many polyps attached to branched stalks Colonialism in Hydroids ...
... -Tentacles up to __________ long, nematocysts poison can be fatal Ex. Obelia -many polyps attached to branched stalks Colonialism in Hydroids ...
the junior version pdf file
... scalpel-like spine in the tail) are the main herbivores. Even butterfly fish feed largely on coral polyps and other small animals that they capture in the cracks and the natural hiding places that the reef offers. These fish have small protruding mouths similar to forceps that can reach even the nar ...
... scalpel-like spine in the tail) are the main herbivores. Even butterfly fish feed largely on coral polyps and other small animals that they capture in the cracks and the natural hiding places that the reef offers. These fish have small protruding mouths similar to forceps that can reach even the nar ...
المحاضرة السادسة عشر Sixteenth lecture
... The anus and mantle cavity are above the head in adults. ...
... The anus and mantle cavity are above the head in adults. ...
in the National Hunting Grounds of Mafra
... Diet: flies, mosquitos, grasshoppers and beetles while also eating forest fruits. They are preyed upon by birds of prey, storks, ginets and otters. Their defence mechanisms span fleeing, camouflage and the ability to shed its tail. This species remains active from February to October when it goes in ...
... Diet: flies, mosquitos, grasshoppers and beetles while also eating forest fruits. They are preyed upon by birds of prey, storks, ginets and otters. Their defence mechanisms span fleeing, camouflage and the ability to shed its tail. This species remains active from February to October when it goes in ...
waf fact sheets - World Animal Foundation
... They clip the wings of aphids that have them or produce chemicals from glands in their jaws to stop the development of their wings. They can also use chemicals to tranquilize aphids. Ants "hear" by feeling vibrations in the ground with pecial sensors on their feet and knees. Their antennae and body ...
... They clip the wings of aphids that have them or produce chemicals from glands in their jaws to stop the development of their wings. They can also use chemicals to tranquilize aphids. Ants "hear" by feeling vibrations in the ground with pecial sensors on their feet and knees. Their antennae and body ...
File - Ms. Cash Science
... Coral What do they eat? * Tiny animals called zooplankton * Some catch larger food such as fish * They also get energy from special algae that live inside their body ...
... Coral What do they eat? * Tiny animals called zooplankton * Some catch larger food such as fish * They also get energy from special algae that live inside their body ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Natural Selection Predator VS. Prey
... has subsequently been confirmed, that the primary mechanism of adaptive evolutionary change is the process of natural selection. Given that evolutionary theory is the most important unifying principle in biology, the importance of understanding how natural selection works should be obvious. The prob ...
... has subsequently been confirmed, that the primary mechanism of adaptive evolutionary change is the process of natural selection. Given that evolutionary theory is the most important unifying principle in biology, the importance of understanding how natural selection works should be obvious. The prob ...
Unit 1 Lesson 4 - MrPetersenScience
... How do predator and prey interact? • The sizes of predator and prey populations are linked together very closely. • If one population grows or shrinks, the other population is affected. • As a predator population grows, the prey population may shrink. But if the prey population becomes too small, th ...
... How do predator and prey interact? • The sizes of predator and prey populations are linked together very closely. • If one population grows or shrinks, the other population is affected. • As a predator population grows, the prey population may shrink. But if the prey population becomes too small, th ...
Organisms in Their Environment Notes
... be there to eat it. Other animals which eat this prey would have more to eat and may increase in number. The missing animal will affect their predators, because they would have less food to help them survive. They would have to rely on other sources of and their numbers might decrease. If you remove ...
... be there to eat it. Other animals which eat this prey would have more to eat and may increase in number. The missing animal will affect their predators, because they would have less food to help them survive. They would have to rely on other sources of and their numbers might decrease. If you remove ...
Family Mitsukurinidae
... Elongated, flattened snout with electroreceptors Mouth ventral Jaws highly protrusible Small eyes Five gill slits Anal fin broadly rounded Upper lobe of caudal fin long (~ ½ length of body Lower lobe of caudal fin not developed Vertebrae 122-125 Body length 107-380 cm, max 3.8 m Pale grey, brown, to ...
... Elongated, flattened snout with electroreceptors Mouth ventral Jaws highly protrusible Small eyes Five gill slits Anal fin broadly rounded Upper lobe of caudal fin long (~ ½ length of body Lower lobe of caudal fin not developed Vertebrae 122-125 Body length 107-380 cm, max 3.8 m Pale grey, brown, to ...
The Coral Reef Ecosystem
... – Concentrate the plankton in the water making it available for other animals Sessile lifestyle fixed firmly to substrate Cilia set up water current to allow filter feeding ...
... – Concentrate the plankton in the water making it available for other animals Sessile lifestyle fixed firmly to substrate Cilia set up water current to allow filter feeding ...
Wisconsin`s Giant Silkworms
... One of the largest and showiest group of insects in the state are the giant silkworm moths ( Family Saturniidae) Adults can have wingspans of up to 6 inches and brightly colored with blue, red, and white spots and bands. The caterpillars can be up to 5 inches long Winter for most species is spent in ...
... One of the largest and showiest group of insects in the state are the giant silkworm moths ( Family Saturniidae) Adults can have wingspans of up to 6 inches and brightly colored with blue, red, and white spots and bands. The caterpillars can be up to 5 inches long Winter for most species is spent in ...
ESPM 134 Insects 1 Introduction to the Insects: Diversity and
... Diptera (flies) – single pair of wings, cone borers, parasitoids, predators, detritivores Success of the insects Small size – 1-10mm, facilitates partitioning of resources Short generation time – 7/10days-1.5 years, promotes more rapid genetic change in response to environment Sensory sophistication ...
... Diptera (flies) – single pair of wings, cone borers, parasitoids, predators, detritivores Success of the insects Small size – 1-10mm, facilitates partitioning of resources Short generation time – 7/10days-1.5 years, promotes more rapid genetic change in response to environment Sensory sophistication ...
Interactions Within Ecosystems
... 3. Community: The living organisms of an ecosystem 4. Population: A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area. 5. Organism: A single living thing, made up of one or many cells, that is capable of growing and reproducing. ...
... 3. Community: The living organisms of an ecosystem 4. Population: A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area. 5. Organism: A single living thing, made up of one or many cells, that is capable of growing and reproducing. ...
Aposematism

Aposematism (from Greek ἀπό apo away, σ̑ημα sema sign, coined by Edward Bagnall Poulton), perhaps most commonly known in the context of warning coloration, describes a family of antipredator adaptations where a warning signal is associated with the unprofitability of a prey item to potential predators. Aposematism is one form of an ""advertising"" signal (with many others existing, such as the bright colours of flowers which lure pollinators). The warning signal may take the form of conspicuous colours, sounds, odours or other perceivable characteristics. Aposematic signals are beneficial for both the predator and prey, both of which avoid potential harm.Aposematism is exploited in Müllerian mimicry, where species with strong defences evolve to resemble one another. By mimicking similarly coloured species, the warning signal to predators is shared, causing them to learn more quickly at less of a cost to each of the species.Warning signals do not necessarily require that a species actually possesses chemical or physical defences to deter predators. Mimics such as the nonvenomous California mountain kingsnake (Lampropeltis zonata), which has yellow, red, and black bands similar to those of the highly venomous Eastern Coral Snake (Micrurus fulvius), have essentially piggybacked on the successful aposematism of the model. The evolution of a warning signal by a mimicking species that resembles a species that possesses strong defences is known as Batesian mimicry.