Curved Mirrors, Ray Diagrams, and Simulations Background Information
... Determine the focal length of a concave mirror – quickly with a minimum of materials. For a spherical concave mirror – parallel rays of light focus to a point. The distance from the mirror to the focused point image is the focal length of the mirror. Materials Included: ...
... Determine the focal length of a concave mirror – quickly with a minimum of materials. For a spherical concave mirror – parallel rays of light focus to a point. The distance from the mirror to the focused point image is the focal length of the mirror. Materials Included: ...
Fluorescence Microscopy
... Initially, fluorescence microscopy was performed with transmitted light, but because the emitted fluorescence is weak in comparison to the excitation light, it was necessary to view the fluorescence with filters capable of blocking very bright transmitted excitation light. Overall, this scheme was not v ...
... Initially, fluorescence microscopy was performed with transmitted light, but because the emitted fluorescence is weak in comparison to the excitation light, it was necessary to view the fluorescence with filters capable of blocking very bright transmitted excitation light. Overall, this scheme was not v ...
Optics Image Formation from Mirrors and Lenses
... However, we already concluded that f = R/2, so ...
... However, we already concluded that f = R/2, so ...
Chapter 9 Notes
... A ray initially parallel to the optical axis passes through the focal point on the other side of the lens. A ray that passes through the focal point (on the same side as the object) emerges parallel to the optical axis on the other side. A ray that passes exactly through the optical axis emerges alo ...
... A ray initially parallel to the optical axis passes through the focal point on the other side of the lens. A ray that passes through the focal point (on the same side as the object) emerges parallel to the optical axis on the other side. A ray that passes exactly through the optical axis emerges alo ...
Preview of “ZEISS Microscopy Online ...Aperture and Resolution”
... lens of the objective and the specimen cover slip must be increased. The highest angular aperture obtainable with a standard microscope objective would theoretically be 180 degrees, resulting in a value of 90 degrees for the half-angle used in the numerical ap ...
... lens of the objective and the specimen cover slip must be increased. The highest angular aperture obtainable with a standard microscope objective would theoretically be 180 degrees, resulting in a value of 90 degrees for the half-angle used in the numerical ap ...
Microscopes - OpenStax CNX
... Both the objective and the eyepiece contribute to the overall magni cation, which is large and negative, consistent with Figure 2, where the image is seen to be large and inverted. In this case, the image is virtual and inverted, which cannot happen for a single element (case 2 and case 3 images for ...
... Both the objective and the eyepiece contribute to the overall magni cation, which is large and negative, consistent with Figure 2, where the image is seen to be large and inverted. In this case, the image is virtual and inverted, which cannot happen for a single element (case 2 and case 3 images for ...
HOLO TEXT
... divisions which focus upon these specific properties of light. In ascending order of complexity they are: Geometrical optics - this area of optics operates on the primary assumption that light travels in a straight line. Although this is an abstraction of reality, it nevertheless permits rather dire ...
... divisions which focus upon these specific properties of light. In ascending order of complexity they are: Geometrical optics - this area of optics operates on the primary assumption that light travels in a straight line. Although this is an abstraction of reality, it nevertheless permits rather dire ...
IX71/IX81 - Olympus Microscopy Resource Center
... for all applications. In addition to their high fluorescence S/N ratio, both these lenses are able to handle UV excitation light at parfocal 45mm. The UPLSAPO100XO provides a transmittance of up to 340nm. ...
... for all applications. In addition to their high fluorescence S/N ratio, both these lenses are able to handle UV excitation light at parfocal 45mm. The UPLSAPO100XO provides a transmittance of up to 340nm. ...
Lecture 6: Waves Review and Examples PLEASE REVIEW ON
... Suppose that when we pass red light (λ = 600 nm) through a slit of unknown width a, the width of the spot (the distance between the first zeros on each side of the bright peak) is W = 1 cm on a screen that is L = 2 m behind the slit. How wide is the slit? ...
... Suppose that when we pass red light (λ = 600 nm) through a slit of unknown width a, the width of the spot (the distance between the first zeros on each side of the bright peak) is W = 1 cm on a screen that is L = 2 m behind the slit. How wide is the slit? ...
Blind Optical Aberration Correction by Exploring
... from aberration corrupted inputs captured by simple lenses, with the PSFs calibrated from the degenerated images of several random patterns. Instead of a fully pre-calibration of the PSFs, Shih et al. [14] only measure the PSF at a single depth, and then simulate the lens and trace the light rays to ...
... from aberration corrupted inputs captured by simple lenses, with the PSFs calibrated from the degenerated images of several random patterns. Instead of a fully pre-calibration of the PSFs, Shih et al. [14] only measure the PSF at a single depth, and then simulate the lens and trace the light rays to ...
Advanced Microscopy
... the pinhole resolution and contrast • the pinhole does not change the psf • the psf is a property of the objective (NA) but the pinhole corresponds to a certain area in the object plane the bigger the pinhole, the more photons will go through it example: 1 mm pinhole corresponds to 10 µm in the obj ...
... the pinhole resolution and contrast • the pinhole does not change the psf • the psf is a property of the objective (NA) but the pinhole corresponds to a certain area in the object plane the bigger the pinhole, the more photons will go through it example: 1 mm pinhole corresponds to 10 µm in the obj ...
Introduction: - TechSapphire
... and 1mm. Infrared light is invisible to our eyes because its wavelength is below the visible spectrum. Infrared can be easily generated and doesn’t suffer electromagnetic interference, so it is nicely used in communication and control. Remote control uses 36 kHz frequency to transmit information . I ...
... and 1mm. Infrared light is invisible to our eyes because its wavelength is below the visible spectrum. Infrared can be easily generated and doesn’t suffer electromagnetic interference, so it is nicely used in communication and control. Remote control uses 36 kHz frequency to transmit information . I ...
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
... as given in the problem. (A real object can only be in front of the mirror, But in a combination of mirrors, the object for the second mirror is the image of the first mirror, which can lie in the back of the second mirror. That is, the light rays can be reflected by the second mirror before they fo ...
... as given in the problem. (A real object can only be in front of the mirror, But in a combination of mirrors, the object for the second mirror is the image of the first mirror, which can lie in the back of the second mirror. That is, the light rays can be reflected by the second mirror before they fo ...
Blind Correction of Optical Aberrations - Max-Planck
... lens of the vertebrate eye creates images on the retina, the lens of a photographic camera creates images on digital sensors. This transformation should ideally satisfy a number of constraints formalizing our notion of a veridical imaging process. The design of any lens forms a trade-off between the ...
... lens of the vertebrate eye creates images on the retina, the lens of a photographic camera creates images on digital sensors. This transformation should ideally satisfy a number of constraints formalizing our notion of a veridical imaging process. The design of any lens forms a trade-off between the ...
Super-resolution Microscopy
... invention of fluorescence microscopy towards the beginning of the 20th century, significant technological advances have enabled elucidation of biological phenomenon at cellular, subcellular and even at molecular levels. However, the latest incarnation of the modern fluorescence microscope has led to ...
... invention of fluorescence microscopy towards the beginning of the 20th century, significant technological advances have enabled elucidation of biological phenomenon at cellular, subcellular and even at molecular levels. However, the latest incarnation of the modern fluorescence microscope has led to ...
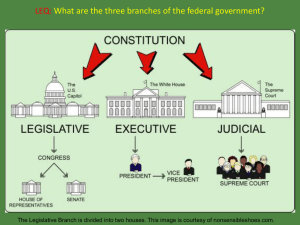
Constitutional Convention
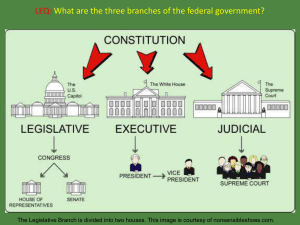
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
The Constitutional Convention Basics PDF
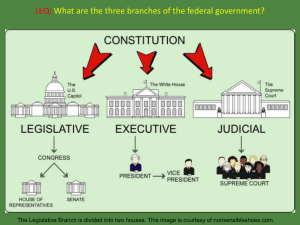
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
English Colonial Failures in the 1500s
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
... James Madison (1751-1836) was a Virginia lawyer who studied how governments worked. This painting was created by John Vanderlyn (1775-1852) in 1816. This image is courtesy of Wikimedia Commons. ...
Light Field Microscopy - Stanford Computer Graphics Laboratory
... thin. However, humans are more tolerant of low angular resolution than low spatial resolution, and it is easier to build one field lens of high quality than thousands of lenslets of high quality, so if system thickness is not an issue, the latter arrangement is preferred. For a microscope, where res ...
... thin. However, humans are more tolerant of low angular resolution than low spatial resolution, and it is easier to build one field lens of high quality than thousands of lenslets of high quality, so if system thickness is not an issue, the latter arrangement is preferred. For a microscope, where res ...
Lenses, the eye and other applications of light
... The diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass. On the diagram, use a ruler to draw two rays from the top of the object which show how and where the image is formed. Represent the image by an arrow drawn at the correct position. ...
... The diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass. On the diagram, use a ruler to draw two rays from the top of the object which show how and where the image is formed. Represent the image by an arrow drawn at the correct position. ...
24.1 Physics 6C Geometrical Optics
... Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then bounces off the mirror and goes through the focal point (f). Ray 3 is the tricky one. Si ...
... Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then bounces off the mirror and goes through the focal point (f). Ray 3 is the tricky one. Si ...
"Contrast Enhancement in Light Microscopy". In: Current Protocols in
... oldest instruments of scientific discovery, continue to be key tools in both biomedical research and routine diagnosis. This remains true despite the development of a wide range of new imaging technologies, many with far greater resolution—ranging from electron microscopes to the multitude of scanni ...
... oldest instruments of scientific discovery, continue to be key tools in both biomedical research and routine diagnosis. This remains true despite the development of a wide range of new imaging technologies, many with far greater resolution—ranging from electron microscopes to the multitude of scanni ...
rtf
... In an electron microscope the specimen scatters the electron wave and the lenses produce the image. The two are very different processes and have to be dealt with quite separately. The reason why imaging is such an important area is that images can lie. As human beings we are conditioned to interpre ...
... In an electron microscope the specimen scatters the electron wave and the lenses produce the image. The two are very different processes and have to be dealt with quite separately. The reason why imaging is such an important area is that images can lie. As human beings we are conditioned to interpre ...
INDIAN SCHOOL DARSAIT
... on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. Akshay could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it ...
... on the blackboard. When the teacher noticed it, he announced if any student sitting in the front row could volunteer to exchange his seat with Akshay. Salman immediately agreed to exchange his seat with Akshay. Akshay could now see the words written on the blackboard clearly. The teacher thought it ...
urved - St. Thomas Aquinas Catholic Secondary School
... The image formed by a concave mirror depends on how far the object is from the focal point of the mirror. The image can be larger or smaller than the object as well as inverted ...
... The image formed by a concave mirror depends on how far the object is from the focal point of the mirror. The image can be larger or smaller than the object as well as inverted ...
Image intensifier

An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light processes, such as fluorescence of materials in x-rays or gamma rays (x-ray image intensifier), or for conversion of non-visible light sources, such as near-infrared or short wave infrared to visible. They operate by converting photons of light into electrons, amplifying the electrons (usually with a microchannel plate), and then converting the amplified electrons back into photons for viewing. They are used in devices such as night vision goggles.