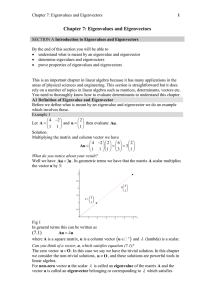
Chapter 1 : Overview
... Since every term can be written in a unique way as f or f (t1 , . . . , tρ(f ) ) for terms t1 , . . . , tρ(f ) , the value tM of t is well defined. The mapping t 7→ tM , also denoted by val M , is the unique F -algebra homomorphism from T(F ) into M.7 An F -algebra M is generated by F if every eleme ...
... Since every term can be written in a unique way as f or f (t1 , . . . , tρ(f ) ) for terms t1 , . . . , tρ(f ) , the value tM of t is well defined. The mapping t 7→ tM , also denoted by val M , is the unique F -algebra homomorphism from T(F ) into M.7 An F -algebra M is generated by F if every eleme ...
Graph Partitioning with AMPL - Antonio Mucherino Home Page
... How can we solve a graph partitioning problem? We need to find a partition in clusters of a weighted undirected graph G = (V , E, c), where V is the set of vertices of G, E is the set of edges of G, c is the set of weights eventually assigned to the edges. This problem can be formulated as a global ...
... How can we solve a graph partitioning problem? We need to find a partition in clusters of a weighted undirected graph G = (V , E, c), where V is the set of vertices of G, E is the set of edges of G, c is the set of weights eventually assigned to the edges. This problem can be formulated as a global ...
pdf [local copy]
... solvability of digraphs of various classes. These questions, apparently of purely graph theoretic flavor, have strong logical import. Section 2 starts with the definitions of kernels and solutions of digraphs, and introduces functions between digraphs and propositional theories mapping satisfiable t ...
... solvability of digraphs of various classes. These questions, apparently of purely graph theoretic flavor, have strong logical import. Section 2 starts with the definitions of kernels and solutions of digraphs, and introduces functions between digraphs and propositional theories mapping satisfiable t ...
Semantical evaluations as monadic second-order
... 1) The existence of properties forming an inductive set (w.r.t. operations of F) is equivalent to recognizability in the considered F-algebra. 2) The simultaneous computation of m inductive properties can be implemented by a "tree" automaton with 2m states working on terms t. This computation takes ...
... 1) The existence of properties forming an inductive set (w.r.t. operations of F) is equivalent to recognizability in the considered F-algebra. 2) The simultaneous computation of m inductive properties can be implemented by a "tree" automaton with 2m states working on terms t. This computation takes ...
Discrete Mathematics
... An upper bound of a subset S of some partially ordered set (P, ≤) is an element of P which is greater than or equal to every element of S.[1] The term lower bound is ...
... An upper bound of a subset S of some partially ordered set (P, ≤) is an element of P which is greater than or equal to every element of S.[1] The term lower bound is ...
Procedure to create a linked list with two nodes of type list - E
... To complete the list naturally we want to add 8 to the list. The insertion will require us to move elements already in the list either one location lower or higher. We must either move 10, 12, 14 or else move 2, 4, 6. If we have to do many insertions into the middle, then neither alternative is attr ...
... To complete the list naturally we want to add 8 to the list. The insertion will require us to move elements already in the list either one location lower or higher. We must either move 10, 12, 14 or else move 2, 4, 6. If we have to do many insertions into the middle, then neither alternative is attr ...
Centrality

In graph theory and network analysis, indicators of centrality identify the most important vertices within a graph. Applications include identifying the most influential person(s) in a social network, key infrastructure nodes in the Internet or urban networks, and super-spreaders of disease. Centrality concepts were first developed in social network analysis, and many of the terms used to measure centrality reflect their sociological origin.They should not be confused with node influence metrics, which seek to quantify the influence of every node in the network.







![pdf [local copy]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003897753_1-78a7dbe322dae43ae963f2a2fbd70110-300x300.png)