fundamental topics in physics
... y-direction with an amplitude of H 0 k / 0 E0 E0 / 0 c , where c k is the speed of light. [8 marks] (ii) The Poynting vector for an EM wave is given by N E H . a. Discuss briefly the physical significance of the Poynting vector. b. Using your result in (i), calculate the magnitud ...
... y-direction with an amplitude of H 0 k / 0 E0 E0 / 0 c , where c k is the speed of light. [8 marks] (ii) The Poynting vector for an EM wave is given by N E H . a. Discuss briefly the physical significance of the Poynting vector. b. Using your result in (i), calculate the magnitud ...
Coriolis force, geometric phase, and spin
... vector k of a charge carrier leads to non-trivial gauge potentials that appear in the reciprocal momentum space9. The associated covariant gauge field enters the equation of motion for the group velocity of a wave-packet and may affect the coherent transport properties of holes in valence subbands10 ...
... vector k of a charge carrier leads to non-trivial gauge potentials that appear in the reciprocal momentum space9. The associated covariant gauge field enters the equation of motion for the group velocity of a wave-packet and may affect the coherent transport properties of holes in valence subbands10 ...
pdf file on-line
... in physics as provided by noncommutative geometry. The basic idea is to push further Einstein’s unified field approach to unify in a geometrical manner the gravitational force with the electromagnetic, weak and strong nuclear forces. Roughly speaking, in Einstein’s general theory of relativity the m ...
... in physics as provided by noncommutative geometry. The basic idea is to push further Einstein’s unified field approach to unify in a geometrical manner the gravitational force with the electromagnetic, weak and strong nuclear forces. Roughly speaking, in Einstein’s general theory of relativity the m ...
How can algebra be useful when expressing
... N-Q Vector & Matrix Quantities Represent and model with vector quantities VM.A.1 Recognize vector quantities as having both magnitude and direction. Represent vector quantities by directed line segments, and use appropriate symbols for vectors and their magnitudes VM.A.2 Find the components of a vec ...
... N-Q Vector & Matrix Quantities Represent and model with vector quantities VM.A.1 Recognize vector quantities as having both magnitude and direction. Represent vector quantities by directed line segments, and use appropriate symbols for vectors and their magnitudes VM.A.2 Find the components of a vec ...
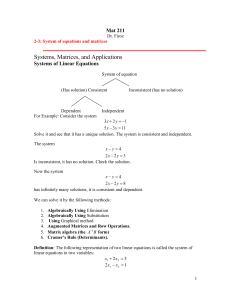
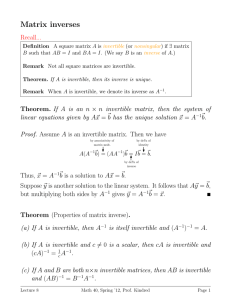
The Elimination Method for solving large systems of linear
... In this section we will learn a general method for finding possible solutions to a linear system of equations. The method involves systematic elimination of the unknown from each equation in turn. We will explain the method with examples. Example 1. Solve the system ...
... In this section we will learn a general method for finding possible solutions to a linear system of equations. The method involves systematic elimination of the unknown from each equation in turn. We will explain the method with examples. Example 1. Solve the system ...
Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
... a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely falling objects is proportional to their mass. d. If a net force does act on an ob ...
... a. For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. b. If no net force acts on an object, the object will remain at rest, or continue to move at a constant velocity. c. The acceleration of freely falling objects is proportional to their mass. d. If a net force does act on an ob ...