with solutions - MIT Mathematics
... Solution. There are many ways to see that the answer is no for both questions. For example, if both sides are zero, then c can be scaled at will. 7. Consider the (filled) cylinder of radius 2 and height 6 with axis of symmetry along the z-axis. Cut the cylinder in half along the y-z plane and keep ...
... Solution. There are many ways to see that the answer is no for both questions. For example, if both sides are zero, then c can be scaled at will. 7. Consider the (filled) cylinder of radius 2 and height 6 with axis of symmetry along the z-axis. Cut the cylinder in half along the y-z plane and keep ...
Vector geometry (v2) R2,R3
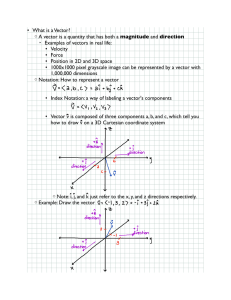
... we have vector b, and vector a which is not collinear to b. We can view vector a as being composted of some part that is parallel to b, and some part that are orthogonal to b. This is called the projection of a on to (or in the direction of) b. ...
... we have vector b, and vector a which is not collinear to b. We can view vector a as being composted of some part that is parallel to b, and some part that are orthogonal to b. This is called the projection of a on to (or in the direction of) b. ...
Vector Spaces
... The set of integers Z and the set of rational numbers Q are commutative groups under normal addition. But the set of natural numbers ℵ is not a group because there are no additive inverses in ℵ and there is no zero element. The following theorem holds for any group V , in particular for a vector spa ...
... The set of integers Z and the set of rational numbers Q are commutative groups under normal addition. But the set of natural numbers ℵ is not a group because there are no additive inverses in ℵ and there is no zero element. The following theorem holds for any group V , in particular for a vector spa ...