Human fetal normal cDNA panel
... Storage Conditions: Store at -20ºC. One year from the date of receipt under storage condition. Applications: The cDNA is primed with oligo dT primer and is ideal for gene expression analysis by PCR amplification of known genes, characterization of alternative splicing of mRNA, verification of geneti ...
... Storage Conditions: Store at -20ºC. One year from the date of receipt under storage condition. Applications: The cDNA is primed with oligo dT primer and is ideal for gene expression analysis by PCR amplification of known genes, characterization of alternative splicing of mRNA, verification of geneti ...
population
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
1 - flickbio
... If genes are 17 map units apart this means they have a 17% crossover frequency. Each of the two crossover genotypes should occur approximately 8.5% of the time. The two noncrossover genotypes should each occur 41.5% of the time. 41.5% gray vestigial 41.5%black normal 8.5% gray normal 8.5% bl ...
... If genes are 17 map units apart this means they have a 17% crossover frequency. Each of the two crossover genotypes should occur approximately 8.5% of the time. The two noncrossover genotypes should each occur 41.5% of the time. 41.5% gray vestigial 41.5%black normal 8.5% gray normal 8.5% bl ...
Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
... today, biologists often focus on a particular population. This evolution of populations is called microevolution. ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
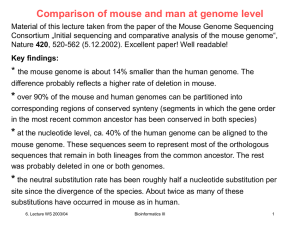
... sequences that remain in both lineages from the common ancestor. The rest was probably deleted in one or both genomes. ...
... sequences that remain in both lineages from the common ancestor. The rest was probably deleted in one or both genomes. ...
What you get
... adult and immature characteristics, so that domestic dogs may be regarded as a blend of immature and adult characteristics. Sometimes this creates problems for the dog breeder; as in the case of toy breeds with disproportionately large eyes. The eye seems to be relatively immune to neoteny, and is d ...
... adult and immature characteristics, so that domestic dogs may be regarded as a blend of immature and adult characteristics. Sometimes this creates problems for the dog breeder; as in the case of toy breeds with disproportionately large eyes. The eye seems to be relatively immune to neoteny, and is d ...
DNA Mismatch Repair and Synonymous Codon Evolution in
... Department of Biological Sciences, Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey 08855 1059. Mol. Biol. Evol. 11(1):88-98. 1994. ...
... Department of Biological Sciences, Rutgers University, Piscataway, New Jersey 08855 1059. Mol. Biol. Evol. 11(1):88-98. 1994. ...
Eukaryogenesis, endosymbiosis, LECA (HGT) RAL evoluzon? RAL
... amer these radiaQons, supported by ophistokonts (supposedly “short” amer LECA) being within archaeal genus • Proto-‐eukaryote sQll seems to have had a long way to go to a eukaryote:, “feca-‐2-‐leca” • Na ...
... amer these radiaQons, supported by ophistokonts (supposedly “short” amer LECA) being within archaeal genus • Proto-‐eukaryote sQll seems to have had a long way to go to a eukaryote:, “feca-‐2-‐leca” • Na ...
Keystone Biology
... A. Bacteria are prokaryotes and reproduce by binary fission; most organisms that are eukaryotes reproduce by mitosis and meiosis. B. Bacteria are prokaryotes, lacking membrane-bound organelles, which respond to changes in their environment differently than eukaryotic cells. C. Bacteria are prokaryot ...
... A. Bacteria are prokaryotes and reproduce by binary fission; most organisms that are eukaryotes reproduce by mitosis and meiosis. B. Bacteria are prokaryotes, lacking membrane-bound organelles, which respond to changes in their environment differently than eukaryotic cells. C. Bacteria are prokaryot ...
Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the future of genetic
... technologies for DNA sequencing. First, so much sequence variation has been identified across individuals that questions about the origin and maintenance of such variation in the population at large have been raised. The traditional belief that mutation drove the compilation or build-up of sequence ...
... technologies for DNA sequencing. First, so much sequence variation has been identified across individuals that questions about the origin and maintenance of such variation in the population at large have been raised. The traditional belief that mutation drove the compilation or build-up of sequence ...
forever young: a gene facilitating the study of the third larval instar of
... was homozygous lethal and had a sra phenotype in trans-heterozygous sra/sral1 or sra/sral2 animals. A genomic rescue with a construct containing the sra genomic DNA including the 5’ regulatory sequences was performed. This rescue construct reverted the sra phenotype (studied in trans-heterozygotes) ...
... was homozygous lethal and had a sra phenotype in trans-heterozygous sra/sral1 or sra/sral2 animals. A genomic rescue with a construct containing the sra genomic DNA including the 5’ regulatory sequences was performed. This rescue construct reverted the sra phenotype (studied in trans-heterozygotes) ...
NARRATOR: Pembrey was stunned. Angelman syndrome and
... light switch. Switch on the gene, the light is shining, the gene is active... makes the cell do a certain thing. Or the light switch is off, everything is dark. That gene is off. And as the cells divide, the memory of whether it's a liver cell or a brain cell, that's brought about by these switches. ...
... light switch. Switch on the gene, the light is shining, the gene is active... makes the cell do a certain thing. Or the light switch is off, everything is dark. That gene is off. And as the cells divide, the memory of whether it's a liver cell or a brain cell, that's brought about by these switches. ...
DNA Lesson 2 Guide
... of its picture. Double check your work, too! Remember to be careful with the arrows. Any questions? You may begin.” ☞☞ Hand out gene strips. Make sure to hand out least 1 alpha, 1 alpha mutated, 1 beta, and 1 beta mutated. You will need all 4 strips of genes, built to teach the class in the next act ...
... of its picture. Double check your work, too! Remember to be careful with the arrows. Any questions? You may begin.” ☞☞ Hand out gene strips. Make sure to hand out least 1 alpha, 1 alpha mutated, 1 beta, and 1 beta mutated. You will need all 4 strips of genes, built to teach the class in the next act ...
Revision Notes
... Nearly all sexually reproducing organisms have paired sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent. ...
... Nearly all sexually reproducing organisms have paired sets of chromosomes, one set from each parent. ...
Télécharger - Options Méditerranéennes
... also now possible to envisage the use of sequencing as a direct genotyping method. Plant genotyping has also reaped the benefits from developments made in human research in the area of new high throughput technologies based on DNA chips and SNPs (for review see Syvanen, 2005). However for applied MA ...
... also now possible to envisage the use of sequencing as a direct genotyping method. Plant genotyping has also reaped the benefits from developments made in human research in the area of new high throughput technologies based on DNA chips and SNPs (for review see Syvanen, 2005). However for applied MA ...
You Light Up My Life
... • A __ ________________ can alter phenotype because a gene’s expression is influenced by its location. Example- Leukemia is due to a growth gene being placed next to an active region resulting in cancer • Approx. _____ of human embryos are aneuploid and die early in ...
... • A __ ________________ can alter phenotype because a gene’s expression is influenced by its location. Example- Leukemia is due to a growth gene being placed next to an active region resulting in cancer • Approx. _____ of human embryos are aneuploid and die early in ...
Identification of Mga1, a G‐protein α‐subunit gene involved in
... clusters involved in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites of Monascus spp., such as citrinin and monacolin K, have been identified (Shimizu et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2008b). Based on the genetic information, a genetic modification method has also been proposed (Fu et al., 2007; Jia et al., 201 ...
... clusters involved in the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites of Monascus spp., such as citrinin and monacolin K, have been identified (Shimizu et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2008b). Based on the genetic information, a genetic modification method has also been proposed (Fu et al., 2007; Jia et al., 201 ...
answers to exam 2011 - Learning on the Loop
... Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis. At fertilisation, which sperm fertilise which egg is due to chance and this results in new combinations of alleles. The advantage of variation to a species is that it may enable s ...
... Meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes. This means that pairs of alleles are separated at meiosis. At fertilisation, which sperm fertilise which egg is due to chance and this results in new combinations of alleles. The advantage of variation to a species is that it may enable s ...
Chromosome Rearrangements Concepts: Chromosome
... fragment, which is lost and deletion products. These deletion products, if incorporate into a zygote, are usually lethal. Only two of the four gametes would produce viable gametes, both of which are parental in organization: one normal + one inversion. Consequence is that: 1) "recombinants" (vs. par ...
... fragment, which is lost and deletion products. These deletion products, if incorporate into a zygote, are usually lethal. Only two of the four gametes would produce viable gametes, both of which are parental in organization: one normal + one inversion. Consequence is that: 1) "recombinants" (vs. par ...
Introduction to Genetics
... PROBABILITY & GENETICS • Diploid Organisms have 2 copies of each numbers chromosome. • Remember, chromosomes of the same shape and size are called: Homologous Chromosomes • Homologous Chromosomes carry the same genes but can have different forms or alleles of these genes. • For Example: Both chro ...
... PROBABILITY & GENETICS • Diploid Organisms have 2 copies of each numbers chromosome. • Remember, chromosomes of the same shape and size are called: Homologous Chromosomes • Homologous Chromosomes carry the same genes but can have different forms or alleles of these genes. • For Example: Both chro ...
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2012
... Body: Increased endothelin-1 (ET-1) and decreased bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type 2 (BMPR2) signaling pathways have been shown to be implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). However, little is known about the interaction between these two signaling path ...
... Body: Increased endothelin-1 (ET-1) and decreased bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor type 2 (BMPR2) signaling pathways have been shown to be implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). However, little is known about the interaction between these two signaling path ...
Text S1. Supporting Information Supporting Information Figure
... the length of the sequenced region. Although some regions have been sequenced in multiple studies (for example, UL55 (gB)), for the purposes of this figure, we show the data from the study that sequenced the largest region. The data used to construct this figure are from [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, ...
... the length of the sequenced region. Although some regions have been sequenced in multiple studies (for example, UL55 (gB)), for the purposes of this figure, we show the data from the study that sequenced the largest region. The data used to construct this figure are from [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12, ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse