Non-thermal equilibrium two-phase flow for melt migration and ascent
... We test the theory for a simple 1D case of sudden temperature difference between fluid and solid and vary fluid fractions and differential velocities between fluid and solid to obtain the requisites for the maximum Fourier coefficient and the time increments for numerical integration. The necessary ...
... We test the theory for a simple 1D case of sudden temperature difference between fluid and solid and vary fluid fractions and differential velocities between fluid and solid to obtain the requisites for the maximum Fourier coefficient and the time increments for numerical integration. The necessary ...
Lecture Presentation Chp-10
... analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a).The tube is cantilevered out from a rigidly supported base. An electromechanical driver is use ...
... analyzed within a rotating reference frame. Useful flowmeters based on this effect are now widely used in the process industries. Consider a fluid flowing through the U-shaped tube shown in Figure 10.13(a).The tube is cantilevered out from a rigidly supported base. An electromechanical driver is use ...
form_sheet_final_che..
... Print this document on a single sheet of paper and bring it to the exam; there will be no spare sheets at the exam. You are allowed to add information on the side of the sheet you printed on; the reverse side should be blank ...
... Print this document on a single sheet of paper and bring it to the exam; there will be no spare sheets at the exam. You are allowed to add information on the side of the sheet you printed on; the reverse side should be blank ...
Fluid Flow
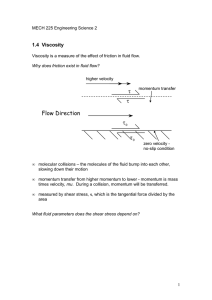
... The top plate drags the fluid particles in the top fluid layer, which then drag the particles in the adjacent lower layer, which then drag the particles in the next lowest layer, and so on—thus giving rise to momentum transfer ...
... The top plate drags the fluid particles in the top fluid layer, which then drag the particles in the adjacent lower layer, which then drag the particles in the next lowest layer, and so on—thus giving rise to momentum transfer ...
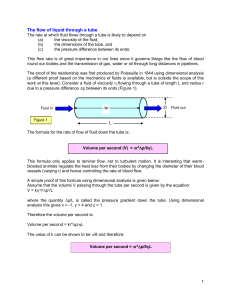
Derive from first principles the Poiseuille equation for
... pressure and does not depend upon the absolute magnitude of the pressure itself. In other words, even if the pressure in the tube is very large, there will be no motion of the fluid if there is no difference in pressure between the two ends and the motion will be in the direction of the positive pre ...
... pressure and does not depend upon the absolute magnitude of the pressure itself. In other words, even if the pressure in the tube is very large, there will be no motion of the fluid if there is no difference in pressure between the two ends and the motion will be in the direction of the positive pre ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear force to the area on which it acts is known as the shear stress. The rate at which the fluid deforms co ...
... A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear force to the area on which it acts is known as the shear stress. The rate at which the fluid deforms co ...
FLUID MECHANICS FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERS
... A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear force to the area on which it acts is known as the shear stress. The rate at which the fluid deforms co ...
... A fluid is defined as a substance that deforms continuously whilst acted upon by any force tangential to the area on which it acts. Such a force is termed a shear force, and the ratio of the shear force to the area on which it acts is known as the shear stress. The rate at which the fluid deforms co ...
Fluid thread breakup
Fluid thread breakup is the process by which a single mass of fluid breaks into several smaller fluid masses. The process is characterized by the elongation of the fluid mass forming thin, thread-like regions between larger nodules of fluid. The thread-like regions continue to thin until they break, forming individual droplets of fluid.Thread breakup occurs where two fluids or a fluid in a vacuum form a free surface with surface energy. If more surface area is present than the minimum required to contain the volume of fluid, the system has an excess of surface energy. A system not at the minimum energy state will attempt to rearrange so as to move toward the lower energy state, leading to the breakup of the fluid into smaller masses to minimize the system surface energy by reducing the surface area. The exact outcome of the thread breakup process is dependent on the surface tension, viscosity, density, and diameter of the thread undergoing breakup.