10529_2013_1416_MOESM1_ESM
... culture containing 20 µg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 3 days. The strains of exconjugants were spread on MS agar plates containing apramycin. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 5 days. E. coli–Streptomyces shuttle plasmid pKC1139 has a temperature-sensitive replicon from Strepto ...
... culture containing 20 µg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 3 days. The strains of exconjugants were spread on MS agar plates containing apramycin. The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 5 days. E. coli–Streptomyces shuttle plasmid pKC1139 has a temperature-sensitive replicon from Strepto ...
Rate of Evolution
... • Although phylogenies based on molecular evidence reflect the relative time of divergence ‐ g cannot be used to establish how or when specific characters evolved. • Taxonomic groups are recognized by presence of unique morphological traits by which all known members can be identified. ...
... • Although phylogenies based on molecular evidence reflect the relative time of divergence ‐ g cannot be used to establish how or when specific characters evolved. • Taxonomic groups are recognized by presence of unique morphological traits by which all known members can be identified. ...
Brooker Chapter 16 - Volunteer State Community College
... It is commonly expressed as the number of new mutations in a given gene per generation It is in the range of 10-5 to 10-9 per generation ...
... It is commonly expressed as the number of new mutations in a given gene per generation It is in the range of 10-5 to 10-9 per generation ...
Article Fitness Trade-Offs Determine the Role of the Molecular
... To evaluate the fitness cost associated with groE overexpression, we performed an evolution experiment under two conditions: 1) Populations evolving under very strong genetic drift imposed by frequent single-colony bottlenecks, and 2) populations evolving under mild genetic drift imposed by serial t ...
... To evaluate the fitness cost associated with groE overexpression, we performed an evolution experiment under two conditions: 1) Populations evolving under very strong genetic drift imposed by frequent single-colony bottlenecks, and 2) populations evolving under mild genetic drift imposed by serial t ...
Monstrous Mutations
... Each group should attain the proper materials and prepare itself to represent the characteristic produced by the letter of the mutation selected from the paper bag. 5. Each group should begin the activity at the specified location in Figure A. The goals of each group are to: A. Gather the food (nin ...
... Each group should attain the proper materials and prepare itself to represent the characteristic produced by the letter of the mutation selected from the paper bag. 5. Each group should begin the activity at the specified location in Figure A. The goals of each group are to: A. Gather the food (nin ...
Evidence for Natural Selection MRSA
... Faced with the super-evolutionary abilities of bacteria, the situation might seem hopeless — and indeed it is dire. However, there are some simple precautions we can each put into action. Taking antibiotics only for serious bacterial infections and completing your full course of antibiotics as instr ...
... Faced with the super-evolutionary abilities of bacteria, the situation might seem hopeless — and indeed it is dire. However, there are some simple precautions we can each put into action. Taking antibiotics only for serious bacterial infections and completing your full course of antibiotics as instr ...
Isolation of Cell Nuclei from Animal Tissues by the Citrate Method
... Addition of DNAzol to the nuclear pellet before suspending the pellet in water results in the formation of a clump that is difficult to dissolve. ...
... Addition of DNAzol to the nuclear pellet before suspending the pellet in water results in the formation of a clump that is difficult to dissolve. ...
Genetic variations and Gene RearrangementsMutation
... gas, methyl-methane sulfonate (MMS) and ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS). ...
... gas, methyl-methane sulfonate (MMS) and ethyl methane sulfonate (EMS). ...
Evolutionary rescue by beneficial mutations in
... Hutchinson [1] famously referred to ‘the ecological theater and the evolutionary play’ to emphasize that natural selection occurs in an environmental context. But, the metaphor works equally well if ‘ecological’ and ‘evolutionary’ are transposed: evolution provides the phenotypic setting that determ ...
... Hutchinson [1] famously referred to ‘the ecological theater and the evolutionary play’ to emphasize that natural selection occurs in an environmental context. But, the metaphor works equally well if ‘ecological’ and ‘evolutionary’ are transposed: evolution provides the phenotypic setting that determ ...
Evolutionary rescue by beneficial mutations in environments that
... Hutchinson [1] famously referred to ‘the ecological theater and the evolutionary play’ to emphasize that natural selection occurs in an environmental context. But, the metaphor works equally well if ‘ecological’ and ‘evolutionary’ are transposed: evolution provides the phenotypic setting that determ ...
... Hutchinson [1] famously referred to ‘the ecological theater and the evolutionary play’ to emphasize that natural selection occurs in an environmental context. But, the metaphor works equally well if ‘ecological’ and ‘evolutionary’ are transposed: evolution provides the phenotypic setting that determ ...
Estimation of the upper limit of the mutation rate and mean
... In brief, mutations are assumed to be strictly deleterious for the fitness trait studied, and a variable proportion of them are assumed to have a pleiotropic advantageous effect on another fitness trait, generating overdominance on global fitness. Using diffusion approximations and transition matrix meth ...
... In brief, mutations are assumed to be strictly deleterious for the fitness trait studied, and a variable proportion of them are assumed to have a pleiotropic advantageous effect on another fitness trait, generating overdominance on global fitness. Using diffusion approximations and transition matrix meth ...
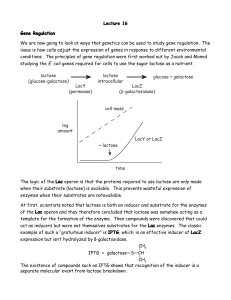
Lecture 16 Gene Regulation
... The logic of the Lac operon is that the proteins required to use lactose are only made when their substrate (lactose) is available. This prevents wasteful expression of enzymes when their substrates are notavailable. At first, scientists noted that lactose is both an inducer and substrate for the en ...
... The logic of the Lac operon is that the proteins required to use lactose are only made when their substrate (lactose) is available. This prevents wasteful expression of enzymes when their substrates are notavailable. At first, scientists noted that lactose is both an inducer and substrate for the en ...
1 - marric
... Birth defects (mutation affecting sex cell), or No observable problem within the cell. 2. Explain the following types of gene mutations: a. Insertion – addition of an extra nucleotide – results in a frameshift mutation b. Deletion - removal of an original nucleotide – results in a frameshift mutatio ...
... Birth defects (mutation affecting sex cell), or No observable problem within the cell. 2. Explain the following types of gene mutations: a. Insertion – addition of an extra nucleotide – results in a frameshift mutation b. Deletion - removal of an original nucleotide – results in a frameshift mutatio ...
The experiments provide ne~~~den~~~~t the r&rate clewage pathway... of carbon for the synthesis of $tty ack& k‘l...
... beets by E, van Lippman (MB). The first biocbemj~~ ~nv~st~g~~i~nof the stereoisomersof hy~~oxyc~t~atewas conducted by Marri.us and Ma& (1941). Using the methyfene b&e test for de~yd~o~~ase activity, these authors demonstrated that race&c bydroxy~trat~ is. attacked by what was presumed to be isocitra ...
... beets by E, van Lippman (MB). The first biocbemj~~ ~nv~st~g~~i~nof the stereoisomersof hy~~oxyc~t~atewas conducted by Marri.us and Ma& (1941). Using the methyfene b&e test for de~yd~o~~ase activity, these authors demonstrated that race&c bydroxy~trat~ is. attacked by what was presumed to be isocitra ...
Bacteriophages use an expanded genetic code on
... mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis. Termination at the amber codon or incorporation of 3iodotyrosine or a canonical amino acid results in different masses for the directly informative peptides. For some proteins, read-through of the amber as any amino acid may also result in an additional C ...
... mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis. Termination at the amber codon or incorporation of 3iodotyrosine or a canonical amino acid results in different masses for the directly informative peptides. For some proteins, read-through of the amber as any amino acid may also result in an additional C ...
MUTATIONS
... A frameshift mutation causes the reading of codons to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could ...
... A frameshift mutation causes the reading of codons to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could ...
Genetic Markers of E. coli
... Endonuclease I is a 12kDa periplasmic protein encoded by the gene endA that degrades double-stranded DNA. The E. coli genotype endA1 refers to a mutation in the wildtype endA gene, which produces an inactive form of the nuclease. E. coli strains with this mutation are referred to as End A negative ( ...
... Endonuclease I is a 12kDa periplasmic protein encoded by the gene endA that degrades double-stranded DNA. The E. coli genotype endA1 refers to a mutation in the wildtype endA gene, which produces an inactive form of the nuclease. E. coli strains with this mutation are referred to as End A negative ( ...
Mutation
... apply and produce less damaging effects. The most widely used chemical mutagen is ethyle methane sulfonate (EMS). It is an alkaline agent. Chemical mutagens are usually less drastic in their effects than ionizing radiations, producing more gene mutations and fewer chromosome disruptions. Procedure ...
... apply and produce less damaging effects. The most widely used chemical mutagen is ethyle methane sulfonate (EMS). It is an alkaline agent. Chemical mutagens are usually less drastic in their effects than ionizing radiations, producing more gene mutations and fewer chromosome disruptions. Procedure ...
Mad Mutation
... • Review student ideas as a whole class. Be sure to define “mutation” and give examples how they can: have no effect, be harmful (cancer, sickle cell anemia), or be beneficial (increasing genetic diversity, sickle cell malaria resistance). Explain point mutations sometimes have no effect because th ...
... • Review student ideas as a whole class. Be sure to define “mutation” and give examples how they can: have no effect, be harmful (cancer, sickle cell anemia), or be beneficial (increasing genetic diversity, sickle cell malaria resistance). Explain point mutations sometimes have no effect because th ...
No Slide Title
... induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase activity and arginase activity in the absence (-cit) or presence (+cit) of citr ...
... induces the production of urea cycle enzymes. Four genes (citA, citB, citC, citD) affecting the activity or regulation of the enzymes were analyzed by assaying the wild-type and mutant strains for argininosuccinate lyase activity and arginase activity in the absence (-cit) or presence (+cit) of citr ...
A new genetic screening test for Marfan syndrome
... enough microfibrils, excess TGF-β growth factors are activated and elasticity in many tissues is decreased, leading to overgrowth and instability of tissues and the signs and symptoms of MFS. Individuals with MFS have a 50% chance of transmitting the mutation to their offspring. Approximately 75% of ...
... enough microfibrils, excess TGF-β growth factors are activated and elasticity in many tissues is decreased, leading to overgrowth and instability of tissues and the signs and symptoms of MFS. Individuals with MFS have a 50% chance of transmitting the mutation to their offspring. Approximately 75% of ...
E. coli
... To do this they used indicator plates, similar to MacConkey’s agar plates. •These contain peptone (milk or meat peptides), bile salts to keep organisms that are normally not in the gut from growing, lactose (or some other sugar), a dye like neutral red which is red under acidic conditions. •When Lac ...
... To do this they used indicator plates, similar to MacConkey’s agar plates. •These contain peptone (milk or meat peptides), bile salts to keep organisms that are normally not in the gut from growing, lactose (or some other sugar), a dye like neutral red which is red under acidic conditions. •When Lac ...
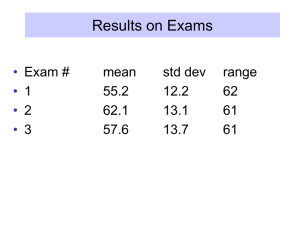
Lecture slides
... Use descriptive titles, captions on tables and figures so that they are self-explanatory Always include axis labels in graphs Write in a formal style (never use first person, instead say, for instance, ``the author'') Format tabular material in proper tables with grid ...
... Use descriptive titles, captions on tables and figures so that they are self-explanatory Always include axis labels in graphs Write in a formal style (never use first person, instead say, for instance, ``the author'') Format tabular material in proper tables with grid ...
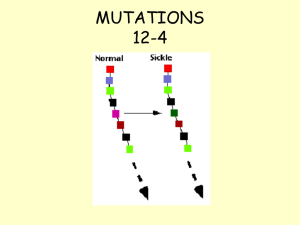
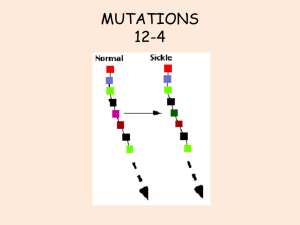
MUTATIONS 12-4 - Somers Public School District
... Segment breaks off and joins a different non-homologous chromosome ...
... Segment breaks off and joins a different non-homologous chromosome ...
E. coli long-term evolution experiment

The E. coli long-term evolution experiment is an ongoing study in experimental evolution led by Richard Lenski that has been tracking genetic changes in 12 initially identical populations of asexual Escherichia coli bacteria since 24 February 1988. The populations reached the milestone of 50,000 generations in February 2010 and 60,000 in April 2014.Since the experiment's inception in 1988, Lenski and his colleagues have reported a wide array of genetic changes. Some changes have occurred in all 12 populations and others have only appeared in one or a few populations. For example, all 12 populations experienced improvement in fitness that decelerated over time and some of populations evolved detrimental effects such as defects in DNA repair, causing mutator phenotypes. One of the significant adaptions occurred in one strain of E. coli. In general, this bacteria is known to not being able to use citrate in an aerobic environment as an energy source, even though it could use citrate under anaerobic conditions because it already has the machinery to process citrate. This strain, though ancestrally unable to do so initially, was able to transport citrate for use as an energy source after a duplication mutation that was involved in the gene for the citrate transporter protein used in anaerobic growth. Even though all the ancestors already had a complete citric acid cycle, and thus could metabolize citrate internally for energy during aerobic growth, none of the 12 populations had a transporter protein for citrate since the beginning, which was the only barrier to being able to use citrate for energy in oxygen-rich conditions. Earlier independent studies had already reported E.Coli strains from agricultural or clinical settings that already had the ability to use citrate under aerobic conditions.A genomic study was done to investigate the history of the adaption using clones to isolate the number of mutations needed to develop the trait. It concluded that multiple mutations (at least two or more) such as duplication mutations were needed to allow the transport of citrate for use in energy. For the trait to develop and stick in a population, it needed multiple mutations at three main phases: potentiation (makes a trait possible), actualization (makes the trait manifest), and refinement (makes it effective).