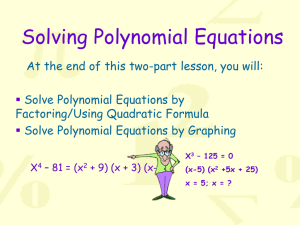
algebra ii - MooreMath23
... 2) Always use PLACEHOLDERS for missing coefficients of a descending order polynomial (Example: If x4 – 3x2 + 4x + 6 is given, use 1+ 0 – 3 + 4 + 6 on the first line 3) Remove the variables for this style of division on the first line 4) The Leading Coefficient drops directly to the solution line to ...
... 2) Always use PLACEHOLDERS for missing coefficients of a descending order polynomial (Example: If x4 – 3x2 + 4x + 6 is given, use 1+ 0 – 3 + 4 + 6 on the first line 3) Remove the variables for this style of division on the first line 4) The Leading Coefficient drops directly to the solution line to ...























