Document
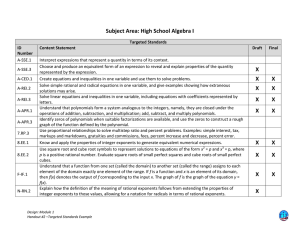
... p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. If f is a funct ...
... p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. If f is a funct ...
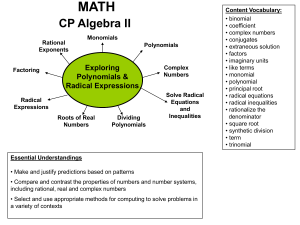
Lesson 3.4 – Zeros of Polynomial Functions Rational Zero Theorem
... Step 1:Find your p’s and q’s and list all possible roots. Step 2:Number of roots/zeros is based on highest degree. Use synthetic division to find your first root. If that does not work, USE YOUR CALCULATOR!!! Remember your multiplicity ideas as well. If the polynomial crosses the x axis, the multipl ...
... Step 1:Find your p’s and q’s and list all possible roots. Step 2:Number of roots/zeros is based on highest degree. Use synthetic division to find your first root. If that does not work, USE YOUR CALCULATOR!!! Remember your multiplicity ideas as well. If the polynomial crosses the x axis, the multipl ...
Unit 4 Lesson 1 Day 5
... a + b is a root of the polynomial where a and b are rational and is irrational, then a - b is also a root. Complex Conjugate Roots Theorem: If P is a polynomial in one variable with real coefficients and a + bi is a root of P, then a – bi must also be a root of P. In other words, these types of root ...
... a + b is a root of the polynomial where a and b are rational and is irrational, then a - b is also a root. Complex Conjugate Roots Theorem: If P is a polynomial in one variable with real coefficients and a + bi is a root of P, then a – bi must also be a root of P. In other words, these types of root ...
Florian Enescu, Fall 2010 Polynomials: Lecture notes Week 9. 1
... corresponding to them has the sign of −v, and terms corresponding to real roots which have also sign equal to the sign of −v. In conclusion, the above sum has sign exactly the sign of −v, and we know that −v 6= 0, so the sum cannot be zero. Contradiction! Therefore our w must belong inside or on the ...
... corresponding to them has the sign of −v, and terms corresponding to real roots which have also sign equal to the sign of −v. In conclusion, the above sum has sign exactly the sign of −v, and we know that −v 6= 0, so the sum cannot be zero. Contradiction! Therefore our w must belong inside or on the ...
Root of unity
In mathematics, a root of unity, occasionally called a de Moivre number, is any complex number that gives 1 when raised to some positive integer power n. Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, and are especially important in number theory, the theory of group characters, and the discrete Fourier transform.In field theory and ring theory the notion of root of unity also applies to any ring with a multiplicative identity element. Any algebraically closed field has exactly n nth roots of unity, if n is not divisible by the characteristic of the field.