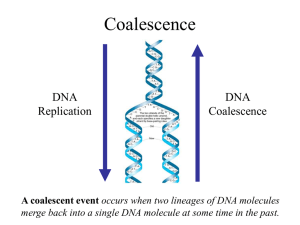
This is a test - DNALC Lab Center
... Once an Alu inserts at a chromosome locus, it can copy itself for transposition, but there is no evidence that it is ever excised or lost from a chromosome locus. So, each Alu insertion is stable through evolutionary time. Each is the "fossil" of a unique transposition event that occurred only once ...
... Once an Alu inserts at a chromosome locus, it can copy itself for transposition, but there is no evidence that it is ever excised or lost from a chromosome locus. So, each Alu insertion is stable through evolutionary time. Each is the "fossil" of a unique transposition event that occurred only once ...
Neurospora genetic nomenclature
... Mutant genes that are recognized by their expression in the perithecia of heterozygous crosses are immediately known to be dominant (e.g, R, Asm). Recessive sexual-phase mutations are less likely to be detected because they must be present in both parents of a cross in order to be expressed. Many of ...
... Mutant genes that are recognized by their expression in the perithecia of heterozygous crosses are immediately known to be dominant (e.g, R, Asm). Recessive sexual-phase mutations are less likely to be detected because they must be present in both parents of a cross in order to be expressed. Many of ...
Nomenclature I
... Genetic Nomenclature for Mice, which states: “A locus is a point in the genome, identified by a marker, which can be mapped by some means. It does not necessarily correspond to a gene; it could, for example, be an anonymous non-coding DNA segment or a cytogenetic feature. A single gene may have seve ...
... Genetic Nomenclature for Mice, which states: “A locus is a point in the genome, identified by a marker, which can be mapped by some means. It does not necessarily correspond to a gene; it could, for example, be an anonymous non-coding DNA segment or a cytogenetic feature. A single gene may have seve ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... elegans sex determination, is testable by studying other nematodes. A study of more distantly related species, for which genetic tools are available that are comparable with those of C. elegans, can answer the question of how complex signaling pathways might have evolved. ...
... elegans sex determination, is testable by studying other nematodes. A study of more distantly related species, for which genetic tools are available that are comparable with those of C. elegans, can answer the question of how complex signaling pathways might have evolved. ...
Chapter 15 The Techniques of Molecular Genetics
... If it is used for reproducing the DNA fragment, it is called a "cloning vector". If it is used for expressing certain gene in the DNA fragment, it is called an "expression vector". ...
... If it is used for reproducing the DNA fragment, it is called a "cloning vector". If it is used for expressing certain gene in the DNA fragment, it is called an "expression vector". ...
Gregor Mendel “The Father of Genetics”
... Ex: Gene: height Alleles: tall, dwarf Genes are inherited in pairs, one allele from each parent Homozygous: identical alleles Heterozygous: different alleles In a hybrid, only the dominant allele (T) will be expressed (or seen). The other allele is recessive (t). Alleles segregate (separate) from ea ...
... Ex: Gene: height Alleles: tall, dwarf Genes are inherited in pairs, one allele from each parent Homozygous: identical alleles Heterozygous: different alleles In a hybrid, only the dominant allele (T) will be expressed (or seen). The other allele is recessive (t). Alleles segregate (separate) from ea ...
Split hand/foot malformations with microdeletions at chromosomes
... or hypoplasia (or both) of the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals. Numerous human gene defects can cause SHFMs. For example, the SHFM1 gene is associated with deletions of varying extent on chromosome 7q21eq22 [1], whereas SHFM2 is associated with genes localized at Xq26eq26.16 [2]. Previous re ...
... or hypoplasia (or both) of the phalanges, metacarpals, and metatarsals. Numerous human gene defects can cause SHFMs. For example, the SHFM1 gene is associated with deletions of varying extent on chromosome 7q21eq22 [1], whereas SHFM2 is associated with genes localized at Xq26eq26.16 [2]. Previous re ...
Imprinted gene expression in hybrids: perturbed
... Recent studies in humans have uncovered that SNPs may induce pronounced changes in locus-specific DNA methylation levels (Hellman and Chess, 2010). Whether polymorphic loss of imprinting also results from genetic diversity remains unknown. However, singlenucleotide mutations were shown to prevent bi ...
... Recent studies in humans have uncovered that SNPs may induce pronounced changes in locus-specific DNA methylation levels (Hellman and Chess, 2010). Whether polymorphic loss of imprinting also results from genetic diversity remains unknown. However, singlenucleotide mutations were shown to prevent bi ...
Structure and evolution of plant disease resistance genes
... plant pathogens, including bacteria, virus, fungi and nematodes, have been isolated from different plant species. Sequence analysis of the predicted proteins of these cloned disease resistance genes reveals that common motifs occur in resistance genes of diverse origin and pathogen specificity. Five ...
... plant pathogens, including bacteria, virus, fungi and nematodes, have been isolated from different plant species. Sequence analysis of the predicted proteins of these cloned disease resistance genes reveals that common motifs occur in resistance genes of diverse origin and pathogen specificity. Five ...
Gene Section ASNS (asparagine synthetase) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... 540 aa N-terminally truncated proteins that differ in sequence between amino acids 312-322 and 332-339. Transcript AK302242 encodes a 478 aa isoform that is further truncated at the N-terminus. ...
... 540 aa N-terminally truncated proteins that differ in sequence between amino acids 312-322 and 332-339. Transcript AK302242 encodes a 478 aa isoform that is further truncated at the N-terminus. ...
Classical / Mendelian Genetics
... and CW (white). These two alleles exhibit incomplete dominance and the phenotype of a heterozygous snapdragon (CRCW) is pink. If you were to cross a red snapdragon with a white snapdragon, what would be the colour distribution of the F2 generation? ...
... and CW (white). These two alleles exhibit incomplete dominance and the phenotype of a heterozygous snapdragon (CRCW) is pink. If you were to cross a red snapdragon with a white snapdragon, what would be the colour distribution of the F2 generation? ...
Structural maintenance of chromosome complexes and bone
... estrogen-responsive genes, pointing out a possible collaboration between it and ESR1. Furthermore, depletion of the cohesin subunit SMC3 significantly impaired the estrogenregulated transcriptome.43 Taken together, these findings suggest that cohesin modifies the higher-order structure of chromatin ...
... estrogen-responsive genes, pointing out a possible collaboration between it and ESR1. Furthermore, depletion of the cohesin subunit SMC3 significantly impaired the estrogenregulated transcriptome.43 Taken together, these findings suggest that cohesin modifies the higher-order structure of chromatin ...
PTC Assessment - Student Version
... Q3: A light receptor, like a taste receptor, is used to sense a particular signal and then transmit that information to the brain. How might changes to amino acid sequence effect a light receptor? [LS1(911)FAF+POC-2b] ...
... Q3: A light receptor, like a taste receptor, is used to sense a particular signal and then transmit that information to the brain. How might changes to amino acid sequence effect a light receptor? [LS1(911)FAF+POC-2b] ...
t - nslc.wustl.edu
... mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose further that mutation is such a rare occurrence that in any time unit it is only likely for at most ...
... mutating per unit time (only neutral mutations are allowed). This model assumes that when a nucleotide site mutates it is equally likely to mutate to any of the three other nucleotide states. Suppose further that mutation is such a rare occurrence that in any time unit it is only likely for at most ...
Slide 1
... commonly used to modify metal uptake, root -to- shoot translocation, and distribution at the cellular, tissue, and organ levels. Such alterations are focus to enhance crops for higher mineral levels. Biofortification aims at an efficient micronutrient uptake mainly from poor soils, and an efficient ...
... commonly used to modify metal uptake, root -to- shoot translocation, and distribution at the cellular, tissue, and organ levels. Such alterations are focus to enhance crops for higher mineral levels. Biofortification aims at an efficient micronutrient uptake mainly from poor soils, and an efficient ...
Document
... and take blood samples of people 2. Do PCR and gel electrophoresis for 100s of SSRs spread throughout the genome 3. Do statistical analysis to determine which one SSR is the most likely to be linked to the trait locus, given the pedigree data we have. 4. Narrow in on the genes present in the genome ...
... and take blood samples of people 2. Do PCR and gel electrophoresis for 100s of SSRs spread throughout the genome 3. Do statistical analysis to determine which one SSR is the most likely to be linked to the trait locus, given the pedigree data we have. 4. Narrow in on the genes present in the genome ...
Nair, B.G. and H.S. Chhatpar
... a) were crossed with isogenic arg-1 and arg-10 strains in order to perform forced heterokaryons. A quantitative complementation analysis of photoinduction of carotenoids indicates that they fall into two complementation groups: wc-1 (7 mutants and wc-2 (4 mutants) (Russo and Innocenti, manuscript in ...
... a) were crossed with isogenic arg-1 and arg-10 strains in order to perform forced heterokaryons. A quantitative complementation analysis of photoinduction of carotenoids indicates that they fall into two complementation groups: wc-1 (7 mutants and wc-2 (4 mutants) (Russo and Innocenti, manuscript in ...
File
... determined by genes. (2) Where there are two or more forms (alleles) of the gene for a single trait, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others recessive. (3) In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene, one from each parent. These genes are segregated when ...
... determined by genes. (2) Where there are two or more forms (alleles) of the gene for a single trait, some forms of the gene may be dominant and others recessive. (3) In most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene, one from each parent. These genes are segregated when ...
Problems in Mendelian Genetics
... action of two different, non-allelic (and non-linked) genes. Each of these genes has two alleles, a dominant one which causes normal the production of the pigment controlled by the gene, and a recessive one which is defective, and causes none of that pigment to be produced. Thus, a normal eye-color ...
... action of two different, non-allelic (and non-linked) genes. Each of these genes has two alleles, a dominant one which causes normal the production of the pigment controlled by the gene, and a recessive one which is defective, and causes none of that pigment to be produced. Thus, a normal eye-color ...
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation
... Progressive, sometimes severe, scoliosis is a problem for many people with OI, and may aggravate respiratory problems. Surgery may be required to stabilize the spine. Medications and Other Experimental Therapies. Bisphosphonate drugs, which are currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration ...
... Progressive, sometimes severe, scoliosis is a problem for many people with OI, and may aggravate respiratory problems. Surgery may be required to stabilize the spine. Medications and Other Experimental Therapies. Bisphosphonate drugs, which are currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration ...
Problems in Mendelian Genetics
... action of two different, non-allelic (and non-linked) genes. Each of these genes has two alleles, a dominant one which causes normal the production of the pigment controlled by the gene, and a recessive one which is defective, and causes none of that pigment to be produced. Thus, a normal eye-color ...
... action of two different, non-allelic (and non-linked) genes. Each of these genes has two alleles, a dominant one which causes normal the production of the pigment controlled by the gene, and a recessive one which is defective, and causes none of that pigment to be produced. Thus, a normal eye-color ...
DNA Methylation Maintains Allele-specific KIR Gene Expression in
... methylation controls tissue-specific gene expression (14, 15). Consistent with this hypothesis, mammals methylate most cytosines that are part of the mini-palindrome, CpG. DNA methylation correlates with poor gene transcription of the inactive X chromosome of female cells, imprinted genes, transfect ...
... methylation controls tissue-specific gene expression (14, 15). Consistent with this hypothesis, mammals methylate most cytosines that are part of the mini-palindrome, CpG. DNA methylation correlates with poor gene transcription of the inactive X chromosome of female cells, imprinted genes, transfect ...