Functional genomics
... Inactivation of Gsk3 by AKT causes accumulation of b-catenin in Alveolar Macrophages Multi-step Regulation of Transcription by Pitx2 Presenilin action in Notch and Wnt signaling ...
... Inactivation of Gsk3 by AKT causes accumulation of b-catenin in Alveolar Macrophages Multi-step Regulation of Transcription by Pitx2 Presenilin action in Notch and Wnt signaling ...
15 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 2. Describe the contributions that Walter Sutton, Theodor Boveri, and Thomas Hunt Morgan made to current understanding of chromosomal inheritance. a. Sutton i. Demonstrated Mendel's laws in grasshoppers ii. Suggested meiotic separation accounted for Mendel's laws b. Boveri i. Studied sea urchins ii. ...
... 2. Describe the contributions that Walter Sutton, Theodor Boveri, and Thomas Hunt Morgan made to current understanding of chromosomal inheritance. a. Sutton i. Demonstrated Mendel's laws in grasshoppers ii. Suggested meiotic separation accounted for Mendel's laws b. Boveri i. Studied sea urchins ii. ...
file 1 – dna replication – cell cycle – mitosis and meiosis
... zb striated). The gene P1 (pericarp color), determine the colour of pericarp dark red (P1 dark; p1 pale), These genes are on the same chromosome and they are 5 mapunits distant. Which phenotypical classes are expected in the progeny and with which frequencies? ...
... zb striated). The gene P1 (pericarp color), determine the colour of pericarp dark red (P1 dark; p1 pale), These genes are on the same chromosome and they are 5 mapunits distant. Which phenotypical classes are expected in the progeny and with which frequencies? ...
Huntington`s disease: Understanding a mutation - LENS
... Describe DNA in terms of structure and function Describe the process of DNA replication and the role that enzymes have in this process Describe the process of protein synthesis and the role of DNA and enzymes in the production of proteins Describe the role of DNA in gene expression and the determ ...
... Describe DNA in terms of structure and function Describe the process of DNA replication and the role that enzymes have in this process Describe the process of protein synthesis and the role of DNA and enzymes in the production of proteins Describe the role of DNA in gene expression and the determ ...
Gene expression: Transcription
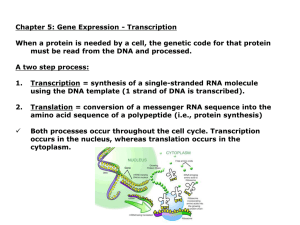
... Chapter 5: Gene Expression - Transcription When a protein is needed by a cell, the genetic code for that protein must be read from the DNA and processed. A two step process: ...
... Chapter 5: Gene Expression - Transcription When a protein is needed by a cell, the genetic code for that protein must be read from the DNA and processed. A two step process: ...
Slide 1
... Introns – these intervening (non-coding) sequences must be cut out Exons – Coding sequences that encode for a specific protein No clear understanding why introns must be removed Only the mature (“edited”) mRNA moves to the cytoplasm ...
... Introns – these intervening (non-coding) sequences must be cut out Exons – Coding sequences that encode for a specific protein No clear understanding why introns must be removed Only the mature (“edited”) mRNA moves to the cytoplasm ...
Meiosis - mvhs
... containing the same sets of genes – One chromosome from each parent – Don’t necessarily contain identical genetic material – Ex. You get one chromosome #4 from mom and one chromosome #4 from dad ...
... containing the same sets of genes – One chromosome from each parent – Don’t necessarily contain identical genetic material – Ex. You get one chromosome #4 from mom and one chromosome #4 from dad ...
Answers-pg-294 - WordPress.com
... Statement: This nucleus can fit 300 solenoid structures side by side within it. 3. DNA wraps tightly around the histone complex because of polar and ionic interactions. The histones are positively charged and the DNA is negatively charged. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: DNA-packing Strategies P ...
... Statement: This nucleus can fit 300 solenoid structures side by side within it. 3. DNA wraps tightly around the histone complex because of polar and ionic interactions. The histones are positively charged and the DNA is negatively charged. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: DNA-packing Strategies P ...
Mendelism
... Named it nuclein since it derived from the nucleus In 1914 Robert Feulgen discovered a test for it fuchsin dye stained DNA In 1920s Phoebus Aaron Theodor Levene analyzed its composition and identified four nitrogenous bases— cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine—as well as deoxyribose sugar an ...
... Named it nuclein since it derived from the nucleus In 1914 Robert Feulgen discovered a test for it fuchsin dye stained DNA In 1920s Phoebus Aaron Theodor Levene analyzed its composition and identified four nitrogenous bases— cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine—as well as deoxyribose sugar an ...
Adenine - /ad·e·nine/ - One of four bases found in the nucleotides of
... such as hair color or blood type or even diseases. In an individual, one allele (the dominant form) may be expressed more than another form (the recessive one). Different alleles of DNA sequences when not located in genes do not produce variations in inherited characteristics or diseases. Mutations ...
... such as hair color or blood type or even diseases. In an individual, one allele (the dominant form) may be expressed more than another form (the recessive one). Different alleles of DNA sequences when not located in genes do not produce variations in inherited characteristics or diseases. Mutations ...
The molecular natural history of the human genome
... consists of sequences that are obviously associated with transposable-element activity, and a large fraction of the remaining noncoding DNA might be a product of such activity but too divergent to be recognized as such. So much for intelligent design. The numbers and ages of mobile elements in human ...
... consists of sequences that are obviously associated with transposable-element activity, and a large fraction of the remaining noncoding DNA might be a product of such activity but too divergent to be recognized as such. So much for intelligent design. The numbers and ages of mobile elements in human ...
Ncbi
... 3. Go to the NCBI home page and under the Resources (on the left,) click on “Genetics and Medicine” and then scroll down and click on “Genes and Disease”. 4. Choose a disease category that interests you and read the synopsis. 5. Scroll down, choose a disease and read the synopsis. What disease did y ...
... 3. Go to the NCBI home page and under the Resources (on the left,) click on “Genetics and Medicine” and then scroll down and click on “Genes and Disease”. 4. Choose a disease category that interests you and read the synopsis. 5. Scroll down, choose a disease and read the synopsis. What disease did y ...
A Mathematical Model for Solving Four Point Test Cross in Genetics
... between two genes during meiosis. A centimorgan (cM) is a unit that describes a recombination frequency of 1%. In this way we can measure the genetic distance between two loci, based upon their recombination frequency. Double crossovers (or even numbers of crossovers) would turn into no recombinatio ...
... between two genes during meiosis. A centimorgan (cM) is a unit that describes a recombination frequency of 1%. In this way we can measure the genetic distance between two loci, based upon their recombination frequency. Double crossovers (or even numbers of crossovers) would turn into no recombinatio ...
biology Ch. 13 Notes Part b Evolution
... ✍ Homologous structures, both anatomical and molecular, can be used to determine the branching sequence of such a tree. ✍ Genetic Code: (A, T, C, G) is a homology shared by all species because they date to the deep ancestral past. ✍ Characteristics that evolved more __________ are shared only ...
... ✍ Homologous structures, both anatomical and molecular, can be used to determine the branching sequence of such a tree. ✍ Genetic Code: (A, T, C, G) is a homology shared by all species because they date to the deep ancestral past. ✍ Characteristics that evolved more __________ are shared only ...
Sickle cell / mutations
... 2. Unlike popular misconceptions about people with green skin or extra body parts, a mutation is simply a change in the nucleotide sequence, or base pair sequence, of DNA. Most mutations are either neutral (they have no effect) or harmful, but occasionally mutations can actually cause a helpful chan ...
... 2. Unlike popular misconceptions about people with green skin or extra body parts, a mutation is simply a change in the nucleotide sequence, or base pair sequence, of DNA. Most mutations are either neutral (they have no effect) or harmful, but occasionally mutations can actually cause a helpful chan ...
Overview of Drosophila development
... cellularization of the embryo has occurred by this stage and it turns out that the ...
... cellularization of the embryo has occurred by this stage and it turns out that the ...
Εθνικό Σύστημα Διαπίστευσης ΑΕ
... *The use of the genetic analyser’s brand name/kit refers to a specific analytical method and the corresponding experimental protocol Site of assessment: Permanent laboratory premises, 52 Spaton Avenue, 15344, Gerakas, Attiki, Greece. Approved signatories: G. Nasioulas, A. Apessos, V. Mariatou-Metaxa ...
... *The use of the genetic analyser’s brand name/kit refers to a specific analytical method and the corresponding experimental protocol Site of assessment: Permanent laboratory premises, 52 Spaton Avenue, 15344, Gerakas, Attiki, Greece. Approved signatories: G. Nasioulas, A. Apessos, V. Mariatou-Metaxa ...
TGFBR2 - Loeys-Dietz syndrome Testing Indication
... with clinically evident disease. Genetic testing also allows for early identification and diagnosis of individuals at greatest risk prior to the expression of typical clinical manifestations and can be used for prenatal diagnosis. If a mutation is identified in an asymptomatic individual, regular an ...
... with clinically evident disease. Genetic testing also allows for early identification and diagnosis of individuals at greatest risk prior to the expression of typical clinical manifestations and can be used for prenatal diagnosis. If a mutation is identified in an asymptomatic individual, regular an ...
Procaryotic chromosome
... 2. Eukaryotic chromatin: Histones (octamer)+146bp DNA > Nucleosome core + H1 >chromatosome + Linker DNA (10--55200+) > beads on string > 30nm fiber > fiber loop (to 100bp) +nuclear matrix > chromosome 3. Jargons: centromere, kinetochore, telomere, hetero or euchromatin, CpG island and methylation 4. ...
... 2. Eukaryotic chromatin: Histones (octamer)+146bp DNA > Nucleosome core + H1 >chromatosome + Linker DNA (10--55200+) > beads on string > 30nm fiber > fiber loop (to 100bp) +nuclear matrix > chromosome 3. Jargons: centromere, kinetochore, telomere, hetero or euchromatin, CpG island and methylation 4. ...
Educator Materials
... o Genes are inherited. Genes are located on chromosomes. Chromosomes are inherited in pairs, one from each parent. Different versions of genes are called alleles. A single gene can have many alleles. o Genes affect phenotypes. Genes code for proteins, which are critical for thousands of functions ...
... o Genes are inherited. Genes are located on chromosomes. Chromosomes are inherited in pairs, one from each parent. Different versions of genes are called alleles. A single gene can have many alleles. o Genes affect phenotypes. Genes code for proteins, which are critical for thousands of functions ...
References - Proceedings of the Royal Society B
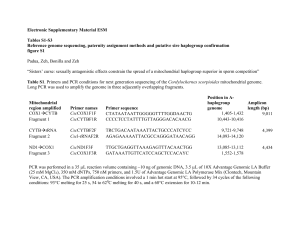
... Expand Long Template PCR kit (Roche). High-Tm, C. scorpioides-specific primers were designed by first amplifying an ~ 660-bp segment of the COX1 gene, using the highly conserved chelicerate forward1 (5'-TACTCTACTAATCATAAAGACATTGG – 3’) and reverse2 (5’ – GGATGGCCAAAAAATCAAAATAAATG – 3’) primers [1], ...
... Expand Long Template PCR kit (Roche). High-Tm, C. scorpioides-specific primers were designed by first amplifying an ~ 660-bp segment of the COX1 gene, using the highly conserved chelicerate forward1 (5'-TACTCTACTAATCATAAAGACATTGG – 3’) and reverse2 (5’ – GGATGGCCAAAAAATCAAAATAAATG – 3’) primers [1], ...
Ch 6 Test C
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
... Use the terms from the following list to complete the sentences below. Each term may be used only once. Some terms may not be used. ...
How to be a clinical geneticist
... DNA structure • The base pairs contained in one loop is what is called GENE • GENES are units of genetic information • They instruct the cell how to perform specific functions or create cell structures • Half of our chromosomes and genes come from a maternal egg – half from the sperm • All these 46 ...
... DNA structure • The base pairs contained in one loop is what is called GENE • GENES are units of genetic information • They instruct the cell how to perform specific functions or create cell structures • Half of our chromosomes and genes come from a maternal egg – half from the sperm • All these 46 ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.