Chromosomal Genetics and Pathology (Dr
... “A reversible process whereby a gamete-specific modification in the parental generation can sometimes lead to functional differences between maternal and paternal genomes in diploid cells of the offspring.” germline erasure of existing imprints acquisition of imprint by gamete according to sex ...
... “A reversible process whereby a gamete-specific modification in the parental generation can sometimes lead to functional differences between maternal and paternal genomes in diploid cells of the offspring.” germline erasure of existing imprints acquisition of imprint by gamete according to sex ...
classes of mutation
... Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. ...
... Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. ...
2013 Training Power Point
... the Trp synthesis pathway are clustered on the same chromosome in what is called the Trp Operon If the amino acid tryptophan (Trp) is added to a culture of E coli , the bacteria soon stop producing the five enzymes needed to synthesize Trp from intermediates produced during the respiration of glucos ...
... the Trp synthesis pathway are clustered on the same chromosome in what is called the Trp Operon If the amino acid tryptophan (Trp) is added to a culture of E coli , the bacteria soon stop producing the five enzymes needed to synthesize Trp from intermediates produced during the respiration of glucos ...
Molecular Methods for Evolutionary Genetics
... polymorphism in a single protein enabled the first molecular evidence of genetic variation. In the 1980s, the advent of DNA sequencing revealed that the amount of genetic variation at a single locus was far greater than expected. Since 2000, the expansion of DNA sequencing to encompass whole genomes ...
... polymorphism in a single protein enabled the first molecular evidence of genetic variation. In the 1980s, the advent of DNA sequencing revealed that the amount of genetic variation at a single locus was far greater than expected. Since 2000, the expansion of DNA sequencing to encompass whole genomes ...
Activity 2.16 Reebops
... Each chromosome has a separate molecule of DNA, so a cell with eight chromosomes has eight molecules of DNA. A gene is a segment on a DNA molecule. Different genes may be very different lengths. Each gene codes for a certain protein molecule, which is then made in the cell cytoplasm. The proteins pr ...
... Each chromosome has a separate molecule of DNA, so a cell with eight chromosomes has eight molecules of DNA. A gene is a segment on a DNA molecule. Different genes may be very different lengths. Each gene codes for a certain protein molecule, which is then made in the cell cytoplasm. The proteins pr ...
013368718X_CH11_159
... For the following questions, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words 18. The units that determine the inheritance of biological characteristics are 19. A form of a gene is a(n) ...
... For the following questions, complete each statement by writing the correct word or words 18. The units that determine the inheritance of biological characteristics are 19. A form of a gene is a(n) ...
Eye and hair color
... • If you stood up, you received all of those genetic, physical features from your parents or grandparents. • We look the way we do because of our inherited traits ...
... • If you stood up, you received all of those genetic, physical features from your parents or grandparents. • We look the way we do because of our inherited traits ...
ppt
... TAL effectors (Transcription Activator-Like Effectors ) are proteins that are injected into plant cells by Xanthomonas bacterial. They enter the nucleus, bind to effectorspecific promoter sequences, and activate the expression of individual plant genes, which can either benefit the bacterium or trig ...
... TAL effectors (Transcription Activator-Like Effectors ) are proteins that are injected into plant cells by Xanthomonas bacterial. They enter the nucleus, bind to effectorspecific promoter sequences, and activate the expression of individual plant genes, which can either benefit the bacterium or trig ...
Ch 8 Review - Priory Haiku
... d. Tay-Sachs disease In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. ______ 5. sickle cell anemia a. determine the different ABO blood types ______ 6. Huntington’s disease b. caused by a mutated allele that results in a ______ 7. gene therapy defectiv ...
... d. Tay-Sachs disease In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. ______ 5. sickle cell anemia a. determine the different ABO blood types ______ 6. Huntington’s disease b. caused by a mutated allele that results in a ______ 7. gene therapy defectiv ...
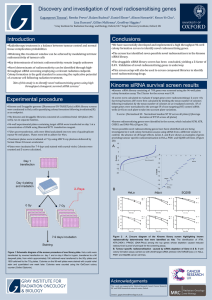
View Poster - Target Discovery Institute
... Surviving fractions (SF) were first calculated by dividing the mean number of colonies following irradiation by the mean number of colonies in un-irradiated controls. SF of target genes were normalised to the average SF of non-targeting (NT) control siRNA wells (n=8) on each plate to take into accou ...
... Surviving fractions (SF) were first calculated by dividing the mean number of colonies following irradiation by the mean number of colonies in un-irradiated controls. SF of target genes were normalised to the average SF of non-targeting (NT) control siRNA wells (n=8) on each plate to take into accou ...
6 Principles of Gene Regulation
... In vitro transcription: quantification of the mRNA Result: some promoters exhibit superhelicitydependent transcription in vivo: Addition of gyrase inhibitors Analyses of gyr or topA mutants ...
... In vitro transcription: quantification of the mRNA Result: some promoters exhibit superhelicitydependent transcription in vivo: Addition of gyrase inhibitors Analyses of gyr or topA mutants ...
Heredity
... Recessive allele – a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring – an organism can carry the recessive trait and not show it is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present represented with a lowercase letter Hybrid Organism – has two different alleles ...
... Recessive allele – a trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring – an organism can carry the recessive trait and not show it is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present represented with a lowercase letter Hybrid Organism – has two different alleles ...
Natural selection
... Homology = similarity in characteristics that result from common ancestry – Ex. Vertebrate forelimbs ...
... Homology = similarity in characteristics that result from common ancestry – Ex. Vertebrate forelimbs ...
F: Acronyms and Glossary
... Introns: DNA sequences interrupting the protein-coding DNA sequences of a gene that are transcribed into mRNA, but are spliced out of the rnRNA before the rnRNA is translated into protein. Compare exons. Karyotype: A photomicrograph of an individual’s chromosomes arranged in a standard format showin ...
... Introns: DNA sequences interrupting the protein-coding DNA sequences of a gene that are transcribed into mRNA, but are spliced out of the rnRNA before the rnRNA is translated into protein. Compare exons. Karyotype: A photomicrograph of an individual’s chromosomes arranged in a standard format showin ...
Genetics Exam Study Guide
... 16. What is a dihybrid cross? Do you know how to set one up? How to figure out the possible gamete combinations from a parent’s genotype? 17. What is polygenic inheritance? How does this lead to continuous variation, and what is continuous variation? 18. What is pleiotropy? ...
... 16. What is a dihybrid cross? Do you know how to set one up? How to figure out the possible gamete combinations from a parent’s genotype? 17. What is polygenic inheritance? How does this lead to continuous variation, and what is continuous variation? 18. What is pleiotropy? ...
DNA Powerpoint Notes
... the complementary bases on the DNA chain. 3. FORM _______________________________________: The nucleotides join as the sugars and phosphates bond to form a new backbone. This process occurs due to the enzyme ___________________ which also checks for ___________________ as it goes. ...
... the complementary bases on the DNA chain. 3. FORM _______________________________________: The nucleotides join as the sugars and phosphates bond to form a new backbone. This process occurs due to the enzyme ___________________ which also checks for ___________________ as it goes. ...
Conference title
... Multiple contigs may belong to same gene Unannotated sequences (novel coding, UTR, junk?) ...
... Multiple contigs may belong to same gene Unannotated sequences (novel coding, UTR, junk?) ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... – Important in maintaining the shape of cells and organisms. – Collagen Regulatory proteins – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
... – Important in maintaining the shape of cells and organisms. – Collagen Regulatory proteins – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
7.1 Identification of specific DNA motifs. Note: For this exercise use
... 7.2 Find genes that have one of these BamHI sites within 250 nucleotides upstream of their start. In the section 7.1 you found BamHI sites, but now you are looking for genes that have one of these sites located within 250 nucleotides upstream of their start. Hint: You can achieve this by running a ...
... 7.2 Find genes that have one of these BamHI sites within 250 nucleotides upstream of their start. In the section 7.1 you found BamHI sites, but now you are looking for genes that have one of these sites located within 250 nucleotides upstream of their start. Hint: You can achieve this by running a ...
Transcription and Translation
... How many bases specify one amino acid? • Reading frame – the correct frame to read the aa’s in • Example – read sentence one letter off • Remove one, two or three bases… • Only by removing three bases is the reading frame unchanged A: Therefore, a codon must be three bases. ...
... How many bases specify one amino acid? • Reading frame – the correct frame to read the aa’s in • Example – read sentence one letter off • Remove one, two or three bases… • Only by removing three bases is the reading frame unchanged A: Therefore, a codon must be three bases. ...
transcriptiontranslation lecture
... Ch. 17: From Gene to Protein Mendel’s work revealed that proteins are the link between genotype and phenotype Tall vs. dwarf height in pea plants was due to a ...
... Ch. 17: From Gene to Protein Mendel’s work revealed that proteins are the link between genotype and phenotype Tall vs. dwarf height in pea plants was due to a ...
Mendelian Genetics
... established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization). » BI2. e. Students know why approximately half of an individual’s DNA sequence come ...
... established at fertilization. As a basis for understanding this concept: » BI2. d. Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization). » BI2. e. Students know why approximately half of an individual’s DNA sequence come ...
Transcription and Translation
... How many bases specify one amino acid? • Reading frame – the correct frame to read the aa’s in • Example – read sentence one letter off • Remove one, two or three bases… • Only by removing three bases is the reading frame unchanged A: Therefore, a codon must be three bases. ...
... How many bases specify one amino acid? • Reading frame – the correct frame to read the aa’s in • Example – read sentence one letter off • Remove one, two or three bases… • Only by removing three bases is the reading frame unchanged A: Therefore, a codon must be three bases. ...
... extracting a significant quantity of genomic DNA, undergoing restriction digestions prior to blotting and probing. This is time consuming and often involves the use of 32P. Since its discovery, PCR has spawned a multitude of variations that have been accepted in many forms of biology and medicine. A ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.