LUX MIDDLE SCHOOL 8 grade Science Mendel Laws and Probability
... We can use the probability to predict the probability of given genetic traits appearing in the offspring of particular parents. Punnett squares can also be used to obtain these results. When gametes are formed, the pair of genes that determine a particular trait separate and one gene goes to each ga ...
... We can use the probability to predict the probability of given genetic traits appearing in the offspring of particular parents. Punnett squares can also be used to obtain these results. When gametes are formed, the pair of genes that determine a particular trait separate and one gene goes to each ga ...
Exercise 1 - EuPathDB Workshop
... c. Does the P. falciparum DHFR-TS (or AMA1) gene contain any single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)? (hint: SNPs are represented graphically in the genomic context section and also in a table called “SNP Overview”). ...
... c. Does the P. falciparum DHFR-TS (or AMA1) gene contain any single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)? (hint: SNPs are represented graphically in the genomic context section and also in a table called “SNP Overview”). ...
1. Data Distributions
... and the white had two white genes. We will call those parent plants the first generation, . When two flowers bred, the offspring received one gene from each parent. If the offspring inherited one red and one white gene, the genes combined to produce a pink flower. Now given Mendel’s work, as describ ...
... and the white had two white genes. We will call those parent plants the first generation, . When two flowers bred, the offspring received one gene from each parent. If the offspring inherited one red and one white gene, the genes combined to produce a pink flower. Now given Mendel’s work, as describ ...
what is mutation?
... *** In reality it is impossible to detect whether a particular mutation occurred spontaneously or was induced. ...
... *** In reality it is impossible to detect whether a particular mutation occurred spontaneously or was induced. ...
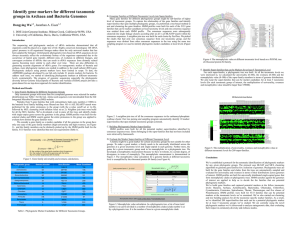
Gregor Mendel Between 1856 and 1863, Gregor Mendel, an
... dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles, or traits, mask (hide) recessive alleles. In this case, the yellow is dominant, and the green is recessive. So the purebred parents made offspring that had green and yellow alleles, but only the yellow showed because it was dominant. When the F1 generation br ...
... dominant or recessive. Dominant alleles, or traits, mask (hide) recessive alleles. In this case, the yellow is dominant, and the green is recessive. So the purebred parents made offspring that had green and yellow alleles, but only the yellow showed because it was dominant. When the F1 generation br ...
Horizontal Transfer of DNA From GM Crops to Bacteria and to
... fragments of the DNA which have specific plasmid sequences removed, such as the origin of replication. If the bacterial origin of replication was not included, the excised DNA could not form a replicating plasmid and therefore would behave as any other fragment of the maize genome. In organisms wher ...
... fragments of the DNA which have specific plasmid sequences removed, such as the origin of replication. If the bacterial origin of replication was not included, the excised DNA could not form a replicating plasmid and therefore would behave as any other fragment of the maize genome. In organisms wher ...
SHH - Faculty Bennington College
... end up being destroyed - the one that make their proper connections with their target cells cause those cells to secrete growth factors which block initiation of the programmed cell death pathway eliminates the extra tissue between digits during finger and toe formation (so we don’t end up with webb ...
... end up being destroyed - the one that make their proper connections with their target cells cause those cells to secrete growth factors which block initiation of the programmed cell death pathway eliminates the extra tissue between digits during finger and toe formation (so we don’t end up with webb ...
Construction and genetic characterization of temperature-sensitive mutant alleles of the yeast actin gene.
... actl-2/actl-3) were tested at 37°C, growth was either extremely slow or absent, indicating that no significant complementation occurs among the three act) alleles and thus formally placing them in the same complementation group. To establish that this single complementation group represents the sing ...
... actl-2/actl-3) were tested at 37°C, growth was either extremely slow or absent, indicating that no significant complementation occurs among the three act) alleles and thus formally placing them in the same complementation group. To establish that this single complementation group represents the sing ...
PCR Applications
... 2) Refer to the last paragraph prior to this section where the sense strand DNA sequences from 5’to 3’ are given for taster and non-taster alleles. Recall that the sense strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA codons except that thymine in DNA replaced with uracil in RNAUsing the given informat ...
... 2) Refer to the last paragraph prior to this section where the sense strand DNA sequences from 5’to 3’ are given for taster and non-taster alleles. Recall that the sense strand of DNA has the same sequence as mRNA codons except that thymine in DNA replaced with uracil in RNAUsing the given informat ...
1 Protein Synthesis and Gene Expression
... sequences. They are important in biotechnology because they allow scientists to make precise cuts in DNA. Plasmid – Small, circular piece of bacterial DNA that exists separate from the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids are important because they can act as a ferry to carry a gene into a cell. ...
... sequences. They are important in biotechnology because they allow scientists to make precise cuts in DNA. Plasmid – Small, circular piece of bacterial DNA that exists separate from the bacterial chromosome. Plasmids are important because they can act as a ferry to carry a gene into a cell. ...
PDF
... multiple lines of evidence have implicated both genetic and environmental factors.3 Studies aimed at identifying the genes that contribute to interindividual blood pressure variation have been limited to candidate genes; the results have proven informative but not always consistent.4 Investigations ...
... multiple lines of evidence have implicated both genetic and environmental factors.3 Studies aimed at identifying the genes that contribute to interindividual blood pressure variation have been limited to candidate genes; the results have proven informative but not always consistent.4 Investigations ...
(DOCX, Unknown)
... D) topoisomerase E) helicase 53) Which of the following investigators was/were responsible for the following discovery? In DNA from any species, the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine. A) Frederick Griffith B) Alfred Hershey and M ...
... D) topoisomerase E) helicase 53) Which of the following investigators was/were responsible for the following discovery? In DNA from any species, the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine. A) Frederick Griffith B) Alfred Hershey and M ...
THE LAC OPERON
... experiment with E coli bacteria . They researched the Lac operon model we will study. They proposed that genes with related functions are grouped together as units called operons. There are others such as the tryptophan operon etc. ...
... experiment with E coli bacteria . They researched the Lac operon model we will study. They proposed that genes with related functions are grouped together as units called operons. There are others such as the tryptophan operon etc. ...
Plankton of Bamfield Inlet
... interested in. PCR mimics DNA replication in a test-tube, and it specifically makes copies of one selected region. This amplification of a piece of the genome, often copied millions of times, results in the remainder of the genome becoming background noise to an almost pure sample of copies of the a ...
... interested in. PCR mimics DNA replication in a test-tube, and it specifically makes copies of one selected region. This amplification of a piece of the genome, often copied millions of times, results in the remainder of the genome becoming background noise to an almost pure sample of copies of the a ...
Section 18.4
... to the next through genes contained on the two sets of chromosomes that a person receives from their parents. ...
... to the next through genes contained on the two sets of chromosomes that a person receives from their parents. ...
Lecture3- Molecular Biology-1(2013).
... tRNA (transfer RNA) Function: Translation process (from mRNA to protein synthesis) It transfers amino acids to the growing protein chain ...
... tRNA (transfer RNA) Function: Translation process (from mRNA to protein synthesis) It transfers amino acids to the growing protein chain ...
Gregor Mendel 1822-1884
... • Recessive trait- a trait that is apparent only when two recessive alleles for the same characteristic are inherited • Genes- a segment of DNA that carries hereditary instructions and is passed from parent to offspring • Alleles- multiple forms of the same gene • Genotype- an organisms inherited co ...
... • Recessive trait- a trait that is apparent only when two recessive alleles for the same characteristic are inherited • Genes- a segment of DNA that carries hereditary instructions and is passed from parent to offspring • Alleles- multiple forms of the same gene • Genotype- an organisms inherited co ...
Biology STAAR EOC Fall 2011
... TEK 4A: Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (Supporting Standard) 1. Create a Venn diagram or Double Bubble (Thinking Map) comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (include cell organelles). TEK 4B: Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasi ...
... TEK 4A: Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (Supporting Standard) 1. Create a Venn diagram or Double Bubble (Thinking Map) comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (include cell organelles). TEK 4B: Investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasi ...
mendel intro
... pairs every time you want to mention the allele, so we shorten it. We’ll usually use one letter for each gene, like the letter R. Then, the different alleles are represented by the R being either upper-case R or lowercase r. ...
... pairs every time you want to mention the allele, so we shorten it. We’ll usually use one letter for each gene, like the letter R. Then, the different alleles are represented by the R being either upper-case R or lowercase r. ...
How Relevant is the Escherichia coli UvrABC Model for Excision
... DNA helicases operate in eukaryotic nucleotide excision. In addition, a striking sequence conservation is noted between human and yeast repair proteins. But no eukaryotic homologs of the UvrABC proteins have been identified. In this Commentary the parallels and differences between the prokaryotic an ...
... DNA helicases operate in eukaryotic nucleotide excision. In addition, a striking sequence conservation is noted between human and yeast repair proteins. But no eukaryotic homologs of the UvrABC proteins have been identified. In this Commentary the parallels and differences between the prokaryotic an ...
Gill: Gene Regulation II
... Epigenomics is not Epigenetics Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype, caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence There are objections to the use of the term epigenetic to describe chemical modification of histone, since it ...
... Epigenomics is not Epigenetics Epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype, caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence There are objections to the use of the term epigenetic to describe chemical modification of histone, since it ...
Determining the Role of Wnt Signaling in Zebrafish
... plays a key role in relaying external signals to internal pathway components4. Preliminary research has suggested that β-catenin increases in relative cytoplasmic concentration after maturation, and my findings from last summer showed that this change is not the result of migration from cytoskeleton ...
... plays a key role in relaying external signals to internal pathway components4. Preliminary research has suggested that β-catenin increases in relative cytoplasmic concentration after maturation, and my findings from last summer showed that this change is not the result of migration from cytoskeleton ...
Keystone2011poster
... The sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of rRNA molecules demonstrated that all organisms could be placed on a single tree of life. Highly conserved, homologous 16S rRNA genes' presence in all organismal lineages makes them the only universal marker that has been adopted by biologist. Unfortunately ...
... The sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of rRNA molecules demonstrated that all organisms could be placed on a single tree of life. Highly conserved, homologous 16S rRNA genes' presence in all organismal lineages makes them the only universal marker that has been adopted by biologist. Unfortunately ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.