Development and Apoptosis
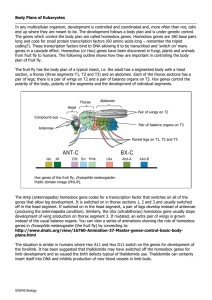
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
11-4 Meiosis - wvhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... NOTES: 14.1-14.2 - HUMAN HEREDITY; PEDIGREES Human Genes: ● The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive and Dominant Alleles: • Some common genetic disorders are -This means that you nee ...
... NOTES: 14.1-14.2 - HUMAN HEREDITY; PEDIGREES Human Genes: ● The human genome is the complete set of genetic information -it determines characteristics such as eye color and how proteins function within cells Recessive and Dominant Alleles: • Some common genetic disorders are -This means that you nee ...
DNA- Experiments and People
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
Human Genetics and Molecular Biology Review Packet
... genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in sunlight is in the form of ultraviolet (uv) radiation. This uv energy can change the ch ...
... genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in sunlight is in the form of ultraviolet (uv) radiation. This uv energy can change the ch ...
Decode the following message.
... removed from a DNA sequence at single point. • An deletion of one base pair causes a shift in the reading frame = One or more amino acids changed Base Pair Removed ...
... removed from a DNA sequence at single point. • An deletion of one base pair causes a shift in the reading frame = One or more amino acids changed Base Pair Removed ...
Nutrigenomics? Epigenetics? The must-know
... all antioxidants are good’ has turned out to be quite simply wrong and yet this theory has driven mega-consumption of synthetic vitamin supplements without there being adequate evidence for their benefit, unless a frank deficiency exists. Research over the past decade has clearly shown that ‘free ra ...
... all antioxidants are good’ has turned out to be quite simply wrong and yet this theory has driven mega-consumption of synthetic vitamin supplements without there being adequate evidence for their benefit, unless a frank deficiency exists. Research over the past decade has clearly shown that ‘free ra ...
Behavior Genetics and Evolutionary Psychology
... Segments within DNA consist of genes that make proteins to determine our development. • complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes has two strands-forming a “double helix”—held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...
... Segments within DNA consist of genes that make proteins to determine our development. • complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes has two strands-forming a “double helix”—held together by bonds between pairs of nucleotides ...
Evolution process by which species change over time
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...
... DNA Evidence of Evolution • DNA is an organisms genetic material that is responsible for its characteristics and traits • Scientists have found common DNA sequencing or DNA strands in many species indicating they came from a common ancestor • Humans and Chimps have 99% similar DNA, alike in genetic ...
In heterozygote, one allele may conceal the
... existed in two forms, one dominant and the other recessive - These factor are now called genes, a word coined by Wilhelm Johannsen (1909) -Each of reproductive cell (or gamete) contain only one copy of a gene for each trait. A particular gamete could have either the recessive or dominant allele for ...
... existed in two forms, one dominant and the other recessive - These factor are now called genes, a word coined by Wilhelm Johannsen (1909) -Each of reproductive cell (or gamete) contain only one copy of a gene for each trait. A particular gamete could have either the recessive or dominant allele for ...
2nd Nine Weeks Exam Review Unit 5
... The mold Aspergillus flavus grows on grain. A. flavus produces a toxin that binds to the DNA in the bodies of animals that eat the grain. The binding of the toxin to DNA blocks transcription, so it directly interferes with the ability of an animal cell to do which of the following? A. Transport gluc ...
... The mold Aspergillus flavus grows on grain. A. flavus produces a toxin that binds to the DNA in the bodies of animals that eat the grain. The binding of the toxin to DNA blocks transcription, so it directly interferes with the ability of an animal cell to do which of the following? A. Transport gluc ...
Module 4 PowerPoint Slides - The Cancer 101 Curriculum
... Mutations detected by a positive test may never lead to disease. Existing tests look for more common gene mutations, many disease-causing mutations may ...
... Mutations detected by a positive test may never lead to disease. Existing tests look for more common gene mutations, many disease-causing mutations may ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
... The purpose of translation is to convert the information in the mRNA into an amino acid sequence, which will form a protein. Translation takes place in a cell’s cytoplasm, after the mRNA has exited the nucleus. Translation depends on “translating” three-letter groups of nucleotides in the mRNA, call ...
... The purpose of translation is to convert the information in the mRNA into an amino acid sequence, which will form a protein. Translation takes place in a cell’s cytoplasm, after the mRNA has exited the nucleus. Translation depends on “translating” three-letter groups of nucleotides in the mRNA, call ...
basic similarities among sign
... are already fruitful in linguistics (especially for coding macromolecules), in analysis of temporal processes in oral speech and musics (these bio-literals also have the temporal interpretations), in architecture, technics and other areas where signs have the spatial morphology (biology is very deep ...
... are already fruitful in linguistics (especially for coding macromolecules), in analysis of temporal processes in oral speech and musics (these bio-literals also have the temporal interpretations), in architecture, technics and other areas where signs have the spatial morphology (biology is very deep ...
1. Which of the following genotype below shows a pure dominant
... 14. cDNA can be cloned into vectors to create a cDNA library. In analyzing cDNA clones. It is often difficult to find clones that are full length, that is, extend to the 5’ end of the mRNA. Why is this so? 15. Acridine dyes induce frames shift mutations. Is such a mutation likely to be more detrimen ...
... 14. cDNA can be cloned into vectors to create a cDNA library. In analyzing cDNA clones. It is often difficult to find clones that are full length, that is, extend to the 5’ end of the mRNA. Why is this so? 15. Acridine dyes induce frames shift mutations. Is such a mutation likely to be more detrimen ...
Mendel notes chp 4
... ii. Also taught and did research in natural science iii. Such a good substitute teacher that they sent him to get his bachelors degree at age 29 where he learned the statistics he used in genetics iv. Crossed and catalogued more than 24,034 plants b. Mendel’s Experimentsi. Single traits that have 2 ...
... ii. Also taught and did research in natural science iii. Such a good substitute teacher that they sent him to get his bachelors degree at age 29 where he learned the statistics he used in genetics iv. Crossed and catalogued more than 24,034 plants b. Mendel’s Experimentsi. Single traits that have 2 ...
Final Exam Study Guide Ms. Thomas Spring 2011
... 13. Draw and label a DNA nucleotide. 14. Draw and label the major parts of a flower. Describe the function of each part. 15. Draw and label the stages of meiosis. 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are prese ...
... 13. Draw and label a DNA nucleotide. 14. Draw and label the major parts of a flower. Describe the function of each part. 15. Draw and label the stages of meiosis. 16. Draw the following cycles and define each process within the cycle: a. Water b. Carbon c. Nitrogen 17. How many chromosomes are prese ...
Transcription and Translation Reproduction is one of the basic
... the human genome. In addition, some genes are transcribed to produce other forms of RNA other than mRNA. Most genes only occur at one position on one chromosome type, so they are referred to as unique or single-copy genes. Originally, estimates for the number of genes were much higher. This predicti ...
... the human genome. In addition, some genes are transcribed to produce other forms of RNA other than mRNA. Most genes only occur at one position on one chromosome type, so they are referred to as unique or single-copy genes. Originally, estimates for the number of genes were much higher. This predicti ...
Slide 1
... However, most behavioral traits are polygenic: They are influenced by a large number of genes. Furthermore: Pleiotropy,1 gene influencing several different behavioral phenotypes is also common in the control of behavior. This makes it more difficult to have systematic experimental control. ...
... However, most behavioral traits are polygenic: They are influenced by a large number of genes. Furthermore: Pleiotropy,1 gene influencing several different behavioral phenotypes is also common in the control of behavior. This makes it more difficult to have systematic experimental control. ...
USC3002_2008.Lect5 - Department of Mathematics
... There you have them, Mendel's huge contributions to the world of science. A very smart cookie. His work has stood the test of time, even as the discovery & understanding of chromosomes & genes has developed in the 140 years after he published his findings. New discoveries have found "exceptions" to ...
... There you have them, Mendel's huge contributions to the world of science. A very smart cookie. His work has stood the test of time, even as the discovery & understanding of chromosomes & genes has developed in the 140 years after he published his findings. New discoveries have found "exceptions" to ...
frontiers of genetics chap13
... B. Regulation of Genes in Eukaryotes 1. Transcription factors- proteins that regulate transcription by binding to those promoters or to RNA polymerases; are activated and deactivated by chemical signals in the cell 2. Gene expression- the transcription and translation of genes into proteins ...
... B. Regulation of Genes in Eukaryotes 1. Transcription factors- proteins that regulate transcription by binding to those promoters or to RNA polymerases; are activated and deactivated by chemical signals in the cell 2. Gene expression- the transcription and translation of genes into proteins ...
What is the probability that an offspring will have black fur?
... dominant a genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor recessive a genetic factor that is hidden by the presence of a dominant factor gene a section of DNA that has information about a specific trait of an organism law of segregation the two factors for each trait segregate or separate from ea ...
... dominant a genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor recessive a genetic factor that is hidden by the presence of a dominant factor gene a section of DNA that has information about a specific trait of an organism law of segregation the two factors for each trait segregate or separate from ea ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.























