Study Guide – Test Two Organismal Biology Deoxyribonucleic Acid
... If repair enzymes cannot fix the error, a dividing cell can pass the error to its decendants Any change in a cell’s DNA sequence A mutation sometimes changes the structure of its encoded protein so much that the protein can no longer do its job Some effects of this are inherited diseases such as: o ...
... If repair enzymes cannot fix the error, a dividing cell can pass the error to its decendants Any change in a cell’s DNA sequence A mutation sometimes changes the structure of its encoded protein so much that the protein can no longer do its job Some effects of this are inherited diseases such as: o ...
Genetics Review
... 2. Dominance operates in females only. 3. Reciprocal crosses produce different results. 4. ‘Criss-cross’ inheritance pattern: father to daughter to grandson, etc ...
... 2. Dominance operates in females only. 3. Reciprocal crosses produce different results. 4. ‘Criss-cross’ inheritance pattern: father to daughter to grandson, etc ...
Ch 15: Sex Determination & Sex Linkage
... a group of linked genes • BUT Mendel’s principle of independent assortment still holds true • It is the chromosome that assorts independently!! – Mendel missed this because 6 of the 7 traits he studied were on different chromosomes. ...
... a group of linked genes • BUT Mendel’s principle of independent assortment still holds true • It is the chromosome that assorts independently!! – Mendel missed this because 6 of the 7 traits he studied were on different chromosomes. ...
Introduction to Genetics
... A hybrid parent contains one dominant allele and one recessive allele. For example, a round hybrid parent would be (Rr). R is the allele for round while r is the allele for wrinkled. Mendel discovered that when he crossed two hybrid parents 75% of the offspring expressed the dominant trait (round) w ...
... A hybrid parent contains one dominant allele and one recessive allele. For example, a round hybrid parent would be (Rr). R is the allele for round while r is the allele for wrinkled. Mendel discovered that when he crossed two hybrid parents 75% of the offspring expressed the dominant trait (round) w ...
Down Syndrome: A Complex Disease
... Hypothesis: combinations of mutations embedded in particular haplotypes, in trisomic individuals, disturb the supramolecular structure of a vital protein and modulate the predisposition of an individual to a single or several types of CHD. ...
... Hypothesis: combinations of mutations embedded in particular haplotypes, in trisomic individuals, disturb the supramolecular structure of a vital protein and modulate the predisposition of an individual to a single or several types of CHD. ...
the Study Guide for Mr. Brown`s Level 1- Biology Unit 4
... Do you know the following?: 10.4. - In sexually reproducing organisms, each offspring contains a mix of characteristics inherited from both parents. Genetic information is stored in genes that are located on chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on ...
... Do you know the following?: 10.4. - In sexually reproducing organisms, each offspring contains a mix of characteristics inherited from both parents. Genetic information is stored in genes that are located on chromosomes inside the cell nucleus. Most organisms have two genes for each trait, one on ...
Wed 12-2 Computers Lab (40 points if all correct or 0 if not) Open up
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
... RNA is transcribed from DNA by enzymes called RNA polymerases and is generally further processed by other enzymes. RNA is central to protein synthesis. Here, a type of RNA called messenger RNA carries information from DNA to structures called ribosomes. These ribosomes are made from proteins and rib ...
7.2.7 Describe the promoter as an example of non
... gene’s location. It is the binding site of RNA polymerase--the enzyme that constructs mRNA from the DNA template during Transcription. ...
... gene’s location. It is the binding site of RNA polymerase--the enzyme that constructs mRNA from the DNA template during Transcription. ...
Sunken Lesson Animal Growth and Heredity
... makes an exact copy of its chromosomes • During mitosis, the chromosomes pull apart, and the cell membrane pinches in at the middle • Two new cells are formed that are identical to the parent cell ...
... makes an exact copy of its chromosomes • During mitosis, the chromosomes pull apart, and the cell membrane pinches in at the middle • Two new cells are formed that are identical to the parent cell ...
Genome_annotation
... list," would include protein-coding genes, non–proteincoding genes, transcriptional regulatory elements, and sequences that mediate chromosome structure and dynamics; undoubtedly, additional, yet-to-bedefined types of functional sequences will also need to be included.” ...
... list," would include protein-coding genes, non–proteincoding genes, transcriptional regulatory elements, and sequences that mediate chromosome structure and dynamics; undoubtedly, additional, yet-to-bedefined types of functional sequences will also need to be included.” ...
Gene Cloning 2
... – For example, a foreign gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid and this recombinant DNA molecule is returned to a bacterial cell. – Every time this cell reproduces, the recombinant plasmid is replicated as well and passed on to its descendents. – Under suitable conditions, the bacterial clone wi ...
... – For example, a foreign gene is inserted into a bacterial plasmid and this recombinant DNA molecule is returned to a bacterial cell. – Every time this cell reproduces, the recombinant plasmid is replicated as well and passed on to its descendents. – Under suitable conditions, the bacterial clone wi ...
Molecular Evolution - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... therefore do not affect the fitness of the organism •Such neutral changes are not influenced by natural selection and therefore accumulate at a rate roughly equal to the mutation rate •If adaptive changes are few compared to neutral changes, differences between taxa can be used to date lineage separ ...
... therefore do not affect the fitness of the organism •Such neutral changes are not influenced by natural selection and therefore accumulate at a rate roughly equal to the mutation rate •If adaptive changes are few compared to neutral changes, differences between taxa can be used to date lineage separ ...
Introduction to Biology
... “ Once the entire sequence was replicated, it was reconverted into RNA by enzymatic means. Viral propagation and replication were accomplished by throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and ...
... “ Once the entire sequence was replicated, it was reconverted into RNA by enzymatic means. Viral propagation and replication were accomplished by throwing the virus into a predesigned protein soup that contained all the polymerases and other enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and ...
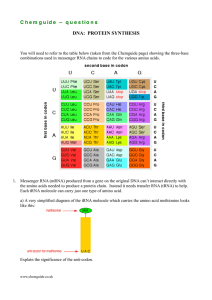
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Dr. Wade Berrettini`s Powerpoint presentation
... ADVANCES in DNA TECHNOLOGY ~1,000,000 SNP CHIPs provide the ability to obtain a genotype at 1 SNP every ~ 3000 base pairs in the genome, allowing determination of most common SNPs. Allele-specific fluorescently-tagged DNA fragments (known as oligonucleotides) are mounted on the slide. The oligonucl ...
... ADVANCES in DNA TECHNOLOGY ~1,000,000 SNP CHIPs provide the ability to obtain a genotype at 1 SNP every ~ 3000 base pairs in the genome, allowing determination of most common SNPs. Allele-specific fluorescently-tagged DNA fragments (known as oligonucleotides) are mounted on the slide. The oligonucl ...
aren`t completely dominant
... In males, EVERY gene on their X chromosome is expressed. The Y doesn’t have the same genes. In females this is not the case because they have another copy on their other X chromosome to overcome it. ...
... In males, EVERY gene on their X chromosome is expressed. The Y doesn’t have the same genes. In females this is not the case because they have another copy on their other X chromosome to overcome it. ...
Practice Exam 3
... b. epistasis; polygenic inheritance c. polygenic inheritance: epistasis d. epistasis; pleiotrophy 17.) Crossing over is important because: a. it causes segregation b. it aligns the chromosomes at metaphase II of meiosis c. it creates new combinations of alleles on homologous chromosomes d. it causes ...
... b. epistasis; polygenic inheritance c. polygenic inheritance: epistasis d. epistasis; pleiotrophy 17.) Crossing over is important because: a. it causes segregation b. it aligns the chromosomes at metaphase II of meiosis c. it creates new combinations of alleles on homologous chromosomes d. it causes ...
Genes & Development
... Wilson and Morgan were very good friends HOMEWORK: go online to devbio website and read material at website 4.1 Quiz on Monday! ...
... Wilson and Morgan were very good friends HOMEWORK: go online to devbio website and read material at website 4.1 Quiz on Monday! ...
DNA Review Questions
... 7. Why is the single-strand binding protein needed in DNA replication? 8. With few exceptions, all nuclei of eukaryotes contain A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found B. All of the information needed for growing the whole organism C. All of the chromosomes except sex ...
... 7. Why is the single-strand binding protein needed in DNA replication? 8. With few exceptions, all nuclei of eukaryotes contain A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found B. All of the information needed for growing the whole organism C. All of the chromosomes except sex ...
The Two Percent Difference
... Bio-anthropology is an extremely integral part of anthropology, and also a very controversial one. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), known as the building block of life, is the basis of the controversy among bio-anthropologists and all people because of two things; it explains that homo sapiens are simi ...
... Bio-anthropology is an extremely integral part of anthropology, and also a very controversial one. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), known as the building block of life, is the basis of the controversy among bio-anthropologists and all people because of two things; it explains that homo sapiens are simi ...
Genetics and Personality
... Contains between 30,000 and 40,000 genes All are located on 23 pairs of chromosomes The body contains roughly 100 trillion copies of the human genome The Human Genome Project ...
... Contains between 30,000 and 40,000 genes All are located on 23 pairs of chromosomes The body contains roughly 100 trillion copies of the human genome The Human Genome Project ...
Gene

A gene is a locus (or region) of DNA that encodes a functional RNA or protein product, and is the molecular unit of heredity. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as the gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye colour or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that comprise life.Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence, leading to different variants, known as alleles, in the population. These alleles encode slightly different versions of a protein, which cause different phenotype traits. Colloquial usage of the term ""having a gene"" (e.g., ""good genes,"" ""hair colour gene"") typically refers to having a different allele of the gene. Genes evolve due to natural selection or survival of the fittest of the alleles.The concept of a gene continues to be refined as new phenomena are discovered. For example, regulatory regions of a gene can be far removed from its coding regions, and coding regions can be split into several exons. Some viruses store their genome in RNA instead of DNA and some gene products are functional non-coding RNAs. Therefore, a broad, modern working definition of a gene is any discrete locus of heritable, genomic sequence which affect an organism's traits by being expressed as a functional product or by regulation of gene expression.