Outliers - University of Notre Dame
... Descriptive statistics. It is always a good idea to start with descriptive statistics of your data. Besides the built-in command summarize, the user-written commands fre and extremes can be helpful here. (To save space I am only printing out a few of the frequencies.) ...
... Descriptive statistics. It is always a good idea to start with descriptive statistics of your data. Besides the built-in command summarize, the user-written commands fre and extremes can be helpful here. (To save space I am only printing out a few of the frequencies.) ...
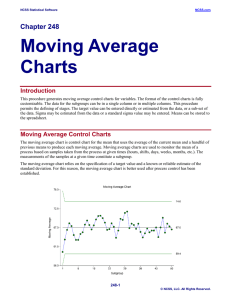
Moving Average Charts
... The calculation of E(R) requires the knowledge of the underlying distribution of the xij’s. Making the assumption that the xij’s follow the normal distribution with constant mean and variance, the values for d2 are derived through the use of numerical integration. It is important to note that the no ...
... The calculation of E(R) requires the knowledge of the underlying distribution of the xij’s. Making the assumption that the xij’s follow the normal distribution with constant mean and variance, the values for d2 are derived through the use of numerical integration. It is important to note that the no ...
document
... • So the estimated mean FEV for males is ̂ and the estimated mean FEV for females is ̂ + ̂ • When we conduct the hypothesis test of the null hypothesis =0 what are we testing? • What other test have we learned that tests the same thing? Run that test. ...
... • So the estimated mean FEV for males is ̂ and the estimated mean FEV for females is ̂ + ̂ • When we conduct the hypothesis test of the null hypothesis =0 what are we testing? • What other test have we learned that tests the same thing? Run that test. ...
Introduction to Econometrics - San Francisco State University
... De…nition 5 A random variable is a function which assigns a real number to each outcome in the sample space. Formally, X : ! R is the notation of a function (named X), which maps the sample space into the real numbers R. From the above de…nition, note that if X is a random variable and g ( ) is some ...
... De…nition 5 A random variable is a function which assigns a real number to each outcome in the sample space. Formally, X : ! R is the notation of a function (named X), which maps the sample space into the real numbers R. From the above de…nition, note that if X is a random variable and g ( ) is some ...
the manuscript.
... including ad exposure intensity, user demographics, retailer customer categories, and two years of past sales history. Covariates struggle to predict sales in the campaign because purchases at the retailer are occasional, unpredictable and highly variable in amount conditional on purchase. The contr ...
... including ad exposure intensity, user demographics, retailer customer categories, and two years of past sales history. Covariates struggle to predict sales in the campaign because purchases at the retailer are occasional, unpredictable and highly variable in amount conditional on purchase. The contr ...
r 2
... Simple Linear Regression Regression models are used to test if a relationship exists between variables; that is, to use one variable to predict another. However, there is some random error that cannot be predicted. ...
... Simple Linear Regression Regression models are used to test if a relationship exists between variables; that is, to use one variable to predict another. However, there is some random error that cannot be predicted. ...
Interaction (statistics)
In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more variables, and describes a situation in which the simultaneous influence of two variables on a third is not additive. Most commonly, interactions are considered in the context of regression analyses.The presence of interactions can have important implications for the interpretation of statistical models. If two variables of interest interact, the relationship between each of the interacting variables and a third ""dependent variable"" depends on the value of the other interacting variable. In practice, this makes it more difficult to predict the consequences of changing the value of a variable, particularly if the variables it interacts with are hard to measure or difficult to control.The notion of ""interaction"" is closely related to that of ""moderation"" that is common in social and health science research: the interaction between an explanatory variable and an environmental variable suggests that the effect of the explanatory variable has been moderated or modified by the environmental variable.