Hemoglobin: Structure
... variations have become part of the biology by random changes in the genetic material. This process, known as genetic drift, can result in the appearance of features that are not part of an adaptive system. These random, or stochastic (means random) processes add a measure of uncertainty and complexi ...
... variations have become part of the biology by random changes in the genetic material. This process, known as genetic drift, can result in the appearance of features that are not part of an adaptive system. These random, or stochastic (means random) processes add a measure of uncertainty and complexi ...
Chapter 4 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... highest in the spring and fall. The data point for 2004 represents the cases only to Sept. 4, 2004, when this graph was prepared. Which of the following predictions appear(s) most likely? a. The total 2004 cases of WNV will increase but the downward trend will continue. b. It is probable that WNV ca ...
... highest in the spring and fall. The data point for 2004 represents the cases only to Sept. 4, 2004, when this graph was prepared. Which of the following predictions appear(s) most likely? a. The total 2004 cases of WNV will increase but the downward trend will continue. b. It is probable that WNV ca ...
Human Genetics
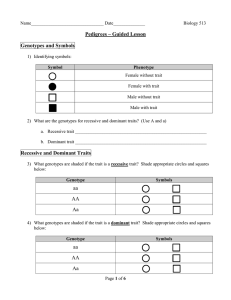
... Pedigree Charts • Another model for understanding inheritance is a pedigree chart. – Each level represents a new generation. • Lines connect offspring to parents – Males are squares and females are circles. – Blank squares or circles usually represent individuals who do not carry a recessive trait ...
... Pedigree Charts • Another model for understanding inheritance is a pedigree chart. – Each level represents a new generation. • Lines connect offspring to parents – Males are squares and females are circles. – Blank squares or circles usually represent individuals who do not carry a recessive trait ...
Laboratory #4: Pedigree Exercises Single
... (or variant) will have a different DNA sequence and is considered mutant. Depending on the different alleles being studied, the wild-type (or normal allele) can either be recessive or dominant. An individual human has two copies of each gene, with one copy coming from the mother and the other coming ...
... (or variant) will have a different DNA sequence and is considered mutant. Depending on the different alleles being studied, the wild-type (or normal allele) can either be recessive or dominant. An individual human has two copies of each gene, with one copy coming from the mother and the other coming ...
Child Development
... “lay physics” (magic & Baillargeon) beginning of representational thought (words & gestures) ...
... “lay physics” (magic & Baillargeon) beginning of representational thought (words & gestures) ...
EXPLORING GENETICS OF ADAPTATION AND SPECIATION BY
... This week in lab we will take a genetic approach towards understanding how adaptations and reproductive isolation evolve. We will be working with two familiar Mimulus wildflower species, M. lewisii and M. cardinalis, that are adapted to different pollinators and are reproductively isolated from each ...
... This week in lab we will take a genetic approach towards understanding how adaptations and reproductive isolation evolve. We will be working with two familiar Mimulus wildflower species, M. lewisii and M. cardinalis, that are adapted to different pollinators and are reproductively isolated from each ...
Hox
... Codes for a DNA binding segment (aa sequence) in the transcription factor. The transcription factors activate structural genes. Structural genes produce structures appropriate for that location. Mutations in Hox genes result in inappropriate structures for that location. ...
... Codes for a DNA binding segment (aa sequence) in the transcription factor. The transcription factors activate structural genes. Structural genes produce structures appropriate for that location. Mutations in Hox genes result in inappropriate structures for that location. ...
Chapter 4 Modern Human Variation and Adaptation Historical Views
... identify an individual’s race from skeletal remains. ...
... identify an individual’s race from skeletal remains. ...
Mitosis
... 15. What organelle captures sunlight in plants? _________________________. 16. What pigment gives green plants their color? ___________________. 17. Most plants appear green because chlorophyll does not absorb _______________ light. 18. What gas is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis? _______ ...
... 15. What organelle captures sunlight in plants? _________________________. 16. What pigment gives green plants their color? ___________________. 17. Most plants appear green because chlorophyll does not absorb _______________ light. 18. What gas is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis? _______ ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 10, Part 2 Notes: Genetic Variation
... 15. Because there is variation in this population, if a new predator is introduced into the environment that kills light-colored mice but not dark-colored mice, natural selection can occur. This will result in dark-colored mice surviving and reproducing better than the white colored mice. In the nex ...
... 15. Because there is variation in this population, if a new predator is introduced into the environment that kills light-colored mice but not dark-colored mice, natural selection can occur. This will result in dark-colored mice surviving and reproducing better than the white colored mice. In the nex ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 9. A white woman with fair skin, blond hair, and blue eyes and a black man with dark brown skin, dark hair, and brown eyes have fraternal twins. One twin has blond hair, brown eyes, and light skin, and the other has dark hair, brown eyes, and dark skin. What Mendelian law does this real-life case il ...
... 9. A white woman with fair skin, blond hair, and blue eyes and a black man with dark brown skin, dark hair, and brown eyes have fraternal twins. One twin has blond hair, brown eyes, and light skin, and the other has dark hair, brown eyes, and dark skin. What Mendelian law does this real-life case il ...
Mitosis
... 15. What organelle captures sunlight in plants? _________________________. 16. What pigment gives green plants their color? ___________________. 17. Most plants appear green because chlorophyll does not absorb _______________ light. 18. What gas is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis? _______ ...
... 15. What organelle captures sunlight in plants? _________________________. 16. What pigment gives green plants their color? ___________________. 17. Most plants appear green because chlorophyll does not absorb _______________ light. 18. What gas is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis? _______ ...
7.013 Problem Set 1 Solutions
... In a different and very cute species of owl, Harry notices that members of this species emit two different noises which he names “loud” and “quiet”, and that they have either smooth or rough eyelids. Harry sees a tank of very young owls, with no indication of who the parents were. a) Assuming all of ...
... In a different and very cute species of owl, Harry notices that members of this species emit two different noises which he names “loud” and “quiet”, and that they have either smooth or rough eyelids. Harry sees a tank of very young owls, with no indication of who the parents were. a) Assuming all of ...
Genome Analysis
... Human genome is the largest genome to be extensively sequenced The genomic landscape shows marked variation in the distribution of a number of features, including genes, transposable elements, GC content, CpG islands and recombination rate Hundreds of human genes appear likely to have resulted fr ...
... Human genome is the largest genome to be extensively sequenced The genomic landscape shows marked variation in the distribution of a number of features, including genes, transposable elements, GC content, CpG islands and recombination rate Hundreds of human genes appear likely to have resulted fr ...
Suppressors
... I. Suppression – a mutation in one gene alleviates the defect of a mutation in another gene—“low-copy” suppressor. II. Suppression – overexpression of a wild-type copy of a gene alleviates the defect of a mutation in another gene—“high-copy suppressor”. In this case the wild-type allele of a gene is ...
... I. Suppression – a mutation in one gene alleviates the defect of a mutation in another gene—“low-copy” suppressor. II. Suppression – overexpression of a wild-type copy of a gene alleviates the defect of a mutation in another gene—“high-copy suppressor”. In this case the wild-type allele of a gene is ...
Genetics problems - University of Toronto Mississauga
... 1. A sexually reproducing organism is heterozygous for two genes located on different chromosomes, one for ear shape and one for toe length. Its genotype is AaBb. Which of the following genotypes is most probable in a gamete from this organism? a. AB b. AaBb c. Aa d. Bb e. A 2. Pseudohypertrophic mu ...
... 1. A sexually reproducing organism is heterozygous for two genes located on different chromosomes, one for ear shape and one for toe length. Its genotype is AaBb. Which of the following genotypes is most probable in a gamete from this organism? a. AB b. AaBb c. Aa d. Bb e. A 2. Pseudohypertrophic mu ...
Genotype, Phenotype, Purebred Breeding, and Crossbreeding
... What are examples of animals that are purebred and crossbred? • Animals are considered pure bred when they meet all the ...
... What are examples of animals that are purebred and crossbred? • Animals are considered pure bred when they meet all the ...
Presentation
... If one parent gives the offspring an allele that says a plant should have green seeds and the other parent contributes an allele that says the offspring should have yellow seeds, one of them will mask the other one. ...
... If one parent gives the offspring an allele that says a plant should have green seeds and the other parent contributes an allele that says the offspring should have yellow seeds, one of them will mask the other one. ...
Practice Exam
... 15. (6) Two pure lines of plants are crossed, one with yellow petals and one with red. The F1 are all orange. When the F1 are selfed, the resulting F2 are: 285 orange, 80 yellow and 115 red. You form a hypothesis that this ratio can be accounted for by recessive epistasis of r (red) on Y (orange) an ...
... 15. (6) Two pure lines of plants are crossed, one with yellow petals and one with red. The F1 are all orange. When the F1 are selfed, the resulting F2 are: 285 orange, 80 yellow and 115 red. You form a hypothesis that this ratio can be accounted for by recessive epistasis of r (red) on Y (orange) an ...
Worksheet 1
... Set up a Punnett Square for bent/straight pinky and widow’s peak/straight hairline. What is the probability that a child resulting from a cross of your genetic traits would have a straight pinky and a widow’s peak? ...
... Set up a Punnett Square for bent/straight pinky and widow’s peak/straight hairline. What is the probability that a child resulting from a cross of your genetic traits would have a straight pinky and a widow’s peak? ...