Jiang Lab Progress
... plants from each of the three Katahdin plants (control Katahdin, Katahdin containing one RB gene, Katahdin containing multiple copies of RB gene) are sampled under each of the three time points (2, 5, and 10 hours after inoculation). Eight RNA samples will be isolated from these four plants. Challen ...
... plants from each of the three Katahdin plants (control Katahdin, Katahdin containing one RB gene, Katahdin containing multiple copies of RB gene) are sampled under each of the three time points (2, 5, and 10 hours after inoculation). Eight RNA samples will be isolated from these four plants. Challen ...
Lec3
... Humans between 1400 and 1750 (from estimates of 20 to 25 thousand genes) polymorphic loci Considering 2 alleles per locus this yields 31400 to 31750 different genotypes Populations are far more genetically diverse than almost anyone imagined ...
... Humans between 1400 and 1750 (from estimates of 20 to 25 thousand genes) polymorphic loci Considering 2 alleles per locus this yields 31400 to 31750 different genotypes Populations are far more genetically diverse than almost anyone imagined ...
Brooker Chapter 4
... 50% of the normal protein is enough to accomplish the protein’s cellular function The normal gene is “up-regulated” to compensate for the lack of function of the defective allele ...
... 50% of the normal protein is enough to accomplish the protein’s cellular function The normal gene is “up-regulated” to compensate for the lack of function of the defective allele ...
Chapter 15
... between the G/g and L/l allele pairs in the FEMALE ONLY…why? The male was chosen to be double homozygous recessive on purpose so that crossing over does not matter because the same gametes form either way. Thus, from this experiment one can determine the frequency of crossing over in a SINGLE INDIVI ...
... between the G/g and L/l allele pairs in the FEMALE ONLY…why? The male was chosen to be double homozygous recessive on purpose so that crossing over does not matter because the same gametes form either way. Thus, from this experiment one can determine the frequency of crossing over in a SINGLE INDIVI ...
Test Review Genetics08-09
... between the phenotypes of the parents. Example: When red snapdragons are crossed with white snapdragons all the offspring have pink flowers 41. ______:The alleles for A and B blood types are codominant, and both are expressed in the phenotype 42. ______:A single gene may affect phenotype in many way ...
... between the phenotypes of the parents. Example: When red snapdragons are crossed with white snapdragons all the offspring have pink flowers 41. ______:The alleles for A and B blood types are codominant, and both are expressed in the phenotype 42. ______:A single gene may affect phenotype in many way ...
Modes of Inheritance
... genetic basis (carried by genes on chromosomes) • Genetic Disorders are classified in 4 categories ...
... genetic basis (carried by genes on chromosomes) • Genetic Disorders are classified in 4 categories ...
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs)
... RFLP can arise due to VNTR's VNTR are variable number tandem repeat. First example found in myoglobin gene. Short sequence of 33 base pairs (other examples vary from 15-100 bp) is repeated a variable number of times. Direct repeat - highly polymorphic - many allele morphs Figure 14-4 (7th) Use this ...
... RFLP can arise due to VNTR's VNTR are variable number tandem repeat. First example found in myoglobin gene. Short sequence of 33 base pairs (other examples vary from 15-100 bp) is repeated a variable number of times. Direct repeat - highly polymorphic - many allele morphs Figure 14-4 (7th) Use this ...
genes - School
... If your mother was the only girl and has seven brothers and your father is one of seven boys, you are more likely to have a boy. ...
... If your mother was the only girl and has seven brothers and your father is one of seven boys, you are more likely to have a boy. ...
Chapter 11 Section 2 Notes 11-2 Probability and Punnett Squares
... The principles of _________________can be used to __________________ the outcomes of _________________________ crosses. Checkpoint: What is the probability that a tossed coin will come up tails twice in a row? ...
... The principles of _________________can be used to __________________ the outcomes of _________________________ crosses. Checkpoint: What is the probability that a tossed coin will come up tails twice in a row? ...
geneflow - International Food Safety Consultancy
... > by only one gene. They then add complexity, or, as Ives says, "more > realism." That is, they consider a crop that is more different genetically > and a wild population that is small or varies in size. > The researchers are quick to point out that the models do not distinguish > between crops deve ...
... > by only one gene. They then add complexity, or, as Ives says, "more > realism." That is, they consider a crop that is more different genetically > and a wild population that is small or varies in size. > The researchers are quick to point out that the models do not distinguish > between crops deve ...
Section 1: Mendelʼs Work * Gregor Mendel was a young priest from
... MULTIPLE ALLELES. These are like different flavors of pudding. Theyʼre all pudding, but there are more than two flavors. * Although a gene may have more than two forms, a human can only carry a pair, or two alleles in each gene because a gene is made of chromosomes and chromosomes always come in pai ...
... MULTIPLE ALLELES. These are like different flavors of pudding. Theyʼre all pudding, but there are more than two flavors. * Although a gene may have more than two forms, a human can only carry a pair, or two alleles in each gene because a gene is made of chromosomes and chromosomes always come in pai ...
Genes Within Populations
... A bit more about genetic drift • In small populations the allele frequencies may change drastically by chance alone • Since these changes occur randomly, as if the frequencies were drifting, we call it genetic drift • There are two related causes of decreases in a population’s size – founder effec ...
... A bit more about genetic drift • In small populations the allele frequencies may change drastically by chance alone • Since these changes occur randomly, as if the frequencies were drifting, we call it genetic drift • There are two related causes of decreases in a population’s size – founder effec ...
GeneticsProblemsFall08
... 1) In tomatoes, tall stature (T) is dominant over dwarf stature (t). If you cross a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous dwarf plant in the parental generation, what would the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F1 progeny (offspring) be? If the F1s were crossed, what would the genotypic and p ...
... 1) In tomatoes, tall stature (T) is dominant over dwarf stature (t). If you cross a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous dwarf plant in the parental generation, what would the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of the F1 progeny (offspring) be? If the F1s were crossed, what would the genotypic and p ...
PRINCIPLES OF BEEF CATTLE GENETICS
... have 19 and humans have 23. While the nucleus of each body cell of cattle contains 30 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 60, there are perhaps thousands of pairs of genes. ...
... have 19 and humans have 23. While the nucleus of each body cell of cattle contains 30 pairs of chromosomes, a total of 60, there are perhaps thousands of pairs of genes. ...
File
... The effect of the t allele is hidden by the T allele and hence the t allele is said to be a recessive allele. Genotype ...
... The effect of the t allele is hidden by the T allele and hence the t allele is said to be a recessive allele. Genotype ...
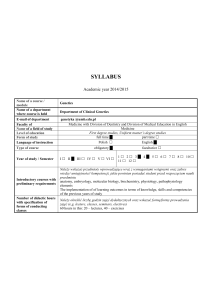
SYLABUS
... recognize genetic syndromes ; to understand the objectives, principles and stages of genetic counseling and the role of psychological factors in occurrence of the crisis in parents of children diagnosed with genetic syndrome; tips of coping with the diagnosis of genetically determined disorders in c ...
... recognize genetic syndromes ; to understand the objectives, principles and stages of genetic counseling and the role of psychological factors in occurrence of the crisis in parents of children diagnosed with genetic syndrome; tips of coping with the diagnosis of genetically determined disorders in c ...
Leukaemia Section t(9;21)(q34;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0921q34q22ID1483.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/44413 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Anomalies/t0921q34q22ID1483.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/44413 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
Unit Plan Part 1
... Objective(s) As a result of this unit, students will be able to: 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution Describe Darwin’s contribution to science. 2. Evolution is a change in the relative Identify indicators of evolution in a population. frequency of alleles in a population Relate allele frequencies ...
... Objective(s) As a result of this unit, students will be able to: 1. Darwin’s theory of evolution Describe Darwin’s contribution to science. 2. Evolution is a change in the relative Identify indicators of evolution in a population. frequency of alleles in a population Relate allele frequencies ...
Multilocus Genetics
... LOD Score Method • A linkage distance is estimated, and given that estimate, the probability of a given birth sequence is calculated. That value is then divided by the probability of a given birth sequence assuming that the genes are unlinked. The log of this value is calculated, and that value is ...
... LOD Score Method • A linkage distance is estimated, and given that estimate, the probability of a given birth sequence is calculated. That value is then divided by the probability of a given birth sequence assuming that the genes are unlinked. The log of this value is calculated, and that value is ...
Joint analysis of the influence of CYP11B1 and DGAT1 genetic
... deduced from the genotypes of the sons. With offspring from heterozygous sires, alleles of maternal descent could only be determined unequivocally if the sons were homozygous. Therefore, a maximum likelihood procedure was applied for estimating allele frequencies: p̂ = ...
... deduced from the genotypes of the sons. With offspring from heterozygous sires, alleles of maternal descent could only be determined unequivocally if the sons were homozygous. Therefore, a maximum likelihood procedure was applied for estimating allele frequencies: p̂ = ...