2005 Biology: Describe the transfer of genetic information (90163)
... significance of the outcome in identifying the parent genotype. Eg the white offspring show that the unknown genotype of the red plant must have included a white allele which combined with the white plants alleles to create the white plant. OR discusses fact that a heterozygous genotype can be deter ...
... significance of the outcome in identifying the parent genotype. Eg the white offspring show that the unknown genotype of the red plant must have included a white allele which combined with the white plants alleles to create the white plant. OR discusses fact that a heterozygous genotype can be deter ...
genes associated with production and health in farm animals
... maps that pinpoint the structure (DNA nucleotide sequences) and, more importantly, the location of genes on specific chromosomes. The coverage on these maps is now sufficient to allow researchers to conduct quantitative trait loci (QTL) linkage analyses. QTL linkage analyses involve using a genomic sc ...
... maps that pinpoint the structure (DNA nucleotide sequences) and, more importantly, the location of genes on specific chromosomes. The coverage on these maps is now sufficient to allow researchers to conduct quantitative trait loci (QTL) linkage analyses. QTL linkage analyses involve using a genomic sc ...
Meiosis pre test
... B. Crossing-over which results in genetic recombination C. mutation D. Chromosome switching ...
... B. Crossing-over which results in genetic recombination C. mutation D. Chromosome switching ...
Inheritance - PGS Science
... A sample of seeds were exposed to radiation. Some seeds then had more than the normal number of chromosomes and grew into plants which gave higher yields. Example 2 A new variety of tomato is produced by crossing suitable parent plants. The new variety has tomatoes that are yellow in colour and much ...
... A sample of seeds were exposed to radiation. Some seeds then had more than the normal number of chromosomes and grew into plants which gave higher yields. Example 2 A new variety of tomato is produced by crossing suitable parent plants. The new variety has tomatoes that are yellow in colour and much ...
Chapter 2 Patterns of Inheritance Chapter 2 Patterns of Inheritance
... are reciprocal crosses. Mendel's reciprocal cross in which he pollinated a white flower with pollen from a purple-flowered plant produced the same result (all purple flowers) in the F1 (Figure 2-5 ). He concluded that it makes no difference which way the cross is made. If one pure-breeding parent is ...
... are reciprocal crosses. Mendel's reciprocal cross in which he pollinated a white flower with pollen from a purple-flowered plant produced the same result (all purple flowers) in the F1 (Figure 2-5 ). He concluded that it makes no difference which way the cross is made. If one pure-breeding parent is ...
PGLO - jvbiologyk
... Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientists can use a process called ...
... Genetic transformation involves the insertion of some new DNA into the E. coli cells. In addition to one large chromosome, bacteria often contain one or more small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA usually contains genes for more than one trait. Scientists can use a process called ...
Patterns of Inheritance in Maize written by JD Hendrix
... Contemporary understanding: A segment on a DNA molecule, usually at a specific location (locus) on a chromosome, characterized by its nucleotide sequence. Genes play three notable roles: to encode the amino acid sequences of proteins, to encode the nucleotide sequences of tRNA or rRNA, and to regula ...
... Contemporary understanding: A segment on a DNA molecule, usually at a specific location (locus) on a chromosome, characterized by its nucleotide sequence. Genes play three notable roles: to encode the amino acid sequences of proteins, to encode the nucleotide sequences of tRNA or rRNA, and to regula ...
Metabolic functions of duplicate genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... deletion mutants on 5 conditions ...
... deletion mutants on 5 conditions ...
Pedigree Chart Activity
... provided pedigree charts or redraw them. If you create a poster, it cannot be larger than 12x18. If it is I will return it ungraded. Use of color and creativity will add points only if the project is neat, complete, and shows strong content. The goal is for you to learn how to use pedigrees to predi ...
... provided pedigree charts or redraw them. If you create a poster, it cannot be larger than 12x18. If it is I will return it ungraded. Use of color and creativity will add points only if the project is neat, complete, and shows strong content. The goal is for you to learn how to use pedigrees to predi ...
Tall
... Who is the “father” of genetics? A. Robert Hooke B. Charles Darwin C. Gregor Mendel D. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek ...
... Who is the “father” of genetics? A. Robert Hooke B. Charles Darwin C. Gregor Mendel D. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek ...
PLEIOTROPY AND GENETIC HETEROGENEITY
... can affect a single phenotype. This is easy to understand in terms of a character such as eye color, in which there are complex metabolic pathways with numerous enzymatic steps, each encoded by one or more gene products. Genetic heterogeneity is the term used to refer to a given condition that may b ...
... can affect a single phenotype. This is easy to understand in terms of a character such as eye color, in which there are complex metabolic pathways with numerous enzymatic steps, each encoded by one or more gene products. Genetic heterogeneity is the term used to refer to a given condition that may b ...
slides - UBC Botany
... between 0 and 1 are equally likely. Fixation or loss, however, are more likely. ...
... between 0 and 1 are equally likely. Fixation or loss, however, are more likely. ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND POPULATION ASPECTS OF BEHAVIOR
... validation of such a hypothesis presents formidable difficulties (Monod and Jacob, 1961). Perhaps, however, there is more than coincidence in the fact that these authors, whose concern is with transmission of information back and forth between cytoplasm and gene, and Miller (1963), whose interest is ...
... validation of such a hypothesis presents formidable difficulties (Monod and Jacob, 1961). Perhaps, however, there is more than coincidence in the fact that these authors, whose concern is with transmission of information back and forth between cytoplasm and gene, and Miller (1963), whose interest is ...
5-1 outline answers genetics Mendel and his peas
... 5. For the second generation, Mendel cross-pollinated two hybrids with purple flowers. About 75 percent of the second-generation plants had purple flowers. These plants had at least one dominant factor. Twenty-five percent of the secondgeneration plants had white flowers. These plants had the same t ...
... 5. For the second generation, Mendel cross-pollinated two hybrids with purple flowers. About 75 percent of the second-generation plants had purple flowers. These plants had at least one dominant factor. Twenty-five percent of the secondgeneration plants had white flowers. These plants had the same t ...
MGY428- Genomes
... The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains 125 Mbp of DNA. This includes a small number of retrotransposons and about 25,000 functional genes. The maize (corn) genome contains 20 times more DNA (2.4 Gbp) 50% of the corn genome is made up of retrotransposons. Most of the 250 Gbp of DNA in the genome ...
... The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains 125 Mbp of DNA. This includes a small number of retrotransposons and about 25,000 functional genes. The maize (corn) genome contains 20 times more DNA (2.4 Gbp) 50% of the corn genome is made up of retrotransposons. Most of the 250 Gbp of DNA in the genome ...
Identification of Quantitative Trait Loci That Affect Aggressive
... testing, and behavioral testing was performed in the home room. With the exception of a weekly cage change, the mice were not handled until after the completion of all behavioral tests. Animals were housed in temperature-controlled rooms with a 14/10 hr light /dark cycle (lights on at 5:00 A.M.). Th ...
... testing, and behavioral testing was performed in the home room. With the exception of a weekly cage change, the mice were not handled until after the completion of all behavioral tests. Animals were housed in temperature-controlled rooms with a 14/10 hr light /dark cycle (lights on at 5:00 A.M.). Th ...
Document
... Fill in the blank with the word or phrase that best complete the following sentence. ...
... Fill in the blank with the word or phrase that best complete the following sentence. ...
Redalyc.An evolutionary frame of work to study physiological
... their ‘optimal’, it may take several to many generations to attain that optimal in response to selection (Roff 1997). Population structure can affect phenotypic evolution in several ways. First, it ultimately determines how many alleles may be ‘immersed’ in the population’s gene pool, setting an upp ...
... their ‘optimal’, it may take several to many generations to attain that optimal in response to selection (Roff 1997). Population structure can affect phenotypic evolution in several ways. First, it ultimately determines how many alleles may be ‘immersed’ in the population’s gene pool, setting an upp ...
GENE GENE INTERACTION DOMINANCE
... pairs seem to be identical in function ,either dominant gene or both dominant gene together give the same effect. Such genes are called duplicate genes and the type of epistasis is called dominant epistasis. ...
... pairs seem to be identical in function ,either dominant gene or both dominant gene together give the same effect. Such genes are called duplicate genes and the type of epistasis is called dominant epistasis. ...
validation of reference genes for real
... The geNorm software ranked the least variable genes as; UBC = GAPDH < Act < WARS < SDH < TBP < 18S < 28S (see Fig. 1 for full names). Alpha-tubulin and cyclophilin were down-regulated by IB and so were not included in the geNorm analysis, although this response warrants further study. The optimal no ...
... The geNorm software ranked the least variable genes as; UBC = GAPDH < Act < WARS < SDH < TBP < 18S < 28S (see Fig. 1 for full names). Alpha-tubulin and cyclophilin were down-regulated by IB and so were not included in the geNorm analysis, although this response warrants further study. The optimal no ...
Understanding mismarks
... To analyze the reason why some black Labs have only a few white hairs on their chests or undersides, while others have white spots or patches, it is best to first understand that all Labs are white (the condition of having no melanin). The gene loci for color control both the color of the pigment as ...
... To analyze the reason why some black Labs have only a few white hairs on their chests or undersides, while others have white spots or patches, it is best to first understand that all Labs are white (the condition of having no melanin). The gene loci for color control both the color of the pigment as ...
as a PDF
... In recent times it has been repeatedly observed that haplotypes surrounding rare alleles of a gene are quite large [1-9]. Sharing of large genomic areas can be used as a method to map disease genes: Identity By Descent (IBD) Mapping [4,10]. An empirical question is whether haplotype sharing can be o ...
... In recent times it has been repeatedly observed that haplotypes surrounding rare alleles of a gene are quite large [1-9]. Sharing of large genomic areas can be used as a method to map disease genes: Identity By Descent (IBD) Mapping [4,10]. An empirical question is whether haplotype sharing can be o ...
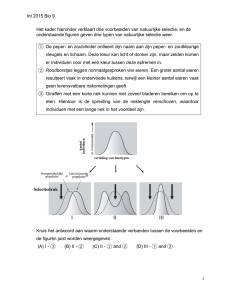
int_2015_Bio_9
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
... Directional selection (I): a mode of natural selection in which a single phenotype is favored, causing the allele frequency to continuously shift in one direction. The genetic variance of the population shifts toward a new phenotype when exposed to environmental changes. In the case of such selectio ...
Gene Section IGK@ (Immunoglobulin Kappa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... somatic mutations during the B cell differentiation in the lymph nodes, which will considerably increase their diversity. These somatic mutations can be analysed using IMGT/V-QUEST tool. ...
... somatic mutations during the B cell differentiation in the lymph nodes, which will considerably increase their diversity. These somatic mutations can be analysed using IMGT/V-QUEST tool. ...