Name
... Sex-linked traits are traits whose genes are found on the sex chromosomes (X or Y). Most sexlinked traits are found on the X chromosome; in fact, since they’re only found on the X chromosome we can guess that they are found on the fourth “leg” that the X has instead of 3 legs on the Y. Further, sex- ...
... Sex-linked traits are traits whose genes are found on the sex chromosomes (X or Y). Most sexlinked traits are found on the X chromosome; in fact, since they’re only found on the X chromosome we can guess that they are found on the fourth “leg” that the X has instead of 3 legs on the Y. Further, sex- ...
Founder Effect Exercise
... Founder Effect Occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated f from the th restt off the th population l ti Alleles that were uncommon in the original g population might be common in the new population. ...
... Founder Effect Occurs when a small sample of a population settles in a location separated f from the th restt off the th population l ti Alleles that were uncommon in the original g population might be common in the new population. ...
TALL - Forest Hills School District
... control ________each trait and that __________ one factor must be able to _______ HIDE the other. ...
... control ________each trait and that __________ one factor must be able to _______ HIDE the other. ...
Natural selection
... of a phenotype to subsequent generations. Changes in the relative success of different phenotypes in a population leads to change in allele frequencies. ...
... of a phenotype to subsequent generations. Changes in the relative success of different phenotypes in a population leads to change in allele frequencies. ...
Biological Diversity Study Guide
... • Please note: this is only a GUIDE. Additional review may be required. ...
... • Please note: this is only a GUIDE. Additional review may be required. ...
LECTURE 34
... one genome, and A’A’ represent genes on chromosomes from a second genome. A and A’ represent homologous genes but the chromosomes bearing A and A’ do not have sufficient homology to pair at meiosis. A and A (and A’ and A’) are on homologous chromosomes, whereas A and A’ are on homeologous chromosome ...
... one genome, and A’A’ represent genes on chromosomes from a second genome. A and A’ represent homologous genes but the chromosomes bearing A and A’ do not have sufficient homology to pair at meiosis. A and A (and A’ and A’) are on homologous chromosomes, whereas A and A’ are on homeologous chromosome ...
How well does a Punnett square predict the actual ratios?
... Student Accomodations: (ELL, SPED) I would want all of my students to perform this laba activity. I would select a partner for my ELL, SPED students who would be able to assist them if needed. ELL and SPED need to graph only one set of data. Assessments: Lab activity will be graded. See lab report r ...
... Student Accomodations: (ELL, SPED) I would want all of my students to perform this laba activity. I would select a partner for my ELL, SPED students who would be able to assist them if needed. ELL and SPED need to graph only one set of data. Assessments: Lab activity will be graded. See lab report r ...
Challenges of integrating conventional breeding and biotechnology
... ‘art’ because, essentially most of the selection for improved genetic type has been based on empirical selection of observed phenotypes and statistical analysis of observational plot data, rather than for the specific, desirable underlying genetic factors, the genes known to improve those traits. T ...
... ‘art’ because, essentially most of the selection for improved genetic type has been based on empirical selection of observed phenotypes and statistical analysis of observational plot data, rather than for the specific, desirable underlying genetic factors, the genes known to improve those traits. T ...
An effect of the DGAT1 gene polymorphism on breeding
... 10434, resulting in lysine for alanine substitution (K232A) has been shown to be associated with milk production traits. In particular, the lysine encoding allele (allele K) is associated with increased fat content of milk compared to the alanine aminoacid residue (allele A) at position 232 [Winter ...
... 10434, resulting in lysine for alanine substitution (K232A) has been shown to be associated with milk production traits. In particular, the lysine encoding allele (allele K) is associated with increased fat content of milk compared to the alanine aminoacid residue (allele A) at position 232 [Winter ...
Research Note Identification of a co
... Leaf rust, caused by Puccinia triticina (Pt), is an important disease of wheat worldwide. New leaf rust resistance loci from diverse germplasm including wild relatives of wheat are continuously being identified. Many leaf rust resistance genes produce similar infection types and therefore are diffic ...
... Leaf rust, caused by Puccinia triticina (Pt), is an important disease of wheat worldwide. New leaf rust resistance loci from diverse germplasm including wild relatives of wheat are continuously being identified. Many leaf rust resistance genes produce similar infection types and therefore are diffic ...
Allele interactions: Terms used to specify interactions between
... in domestic dogs, a third gene is implicated, the K locus, whose genetic characteristics predict a previously unrecognized component of the melanocortin pathway. We identify the K locus as β -defensin (CBD103) and show that its protein product binds with high affinity to the Mc1r and has a simple an ...
... in domestic dogs, a third gene is implicated, the K locus, whose genetic characteristics predict a previously unrecognized component of the melanocortin pathway. We identify the K locus as β -defensin (CBD103) and show that its protein product binds with high affinity to the Mc1r and has a simple an ...
EXERCISE 4: Principles of Heredity: Human Genetics Learning
... 1. What is the significance of the Hardy-Weinberg principle? ...
... 1. What is the significance of the Hardy-Weinberg principle? ...
Statistical models for trisomic phenotypes.
... examples of disomic homozygosity, defined as homozygosity by descent of the two alleles inherited from the parent in whom the nondisjunction event occurred (i.e., the nondisjoining parent). Thus, a subset of the DS population (i.e., those affected with a specific phenotypic trait) can be screened fo ...
... examples of disomic homozygosity, defined as homozygosity by descent of the two alleles inherited from the parent in whom the nondisjunction event occurred (i.e., the nondisjoining parent). Thus, a subset of the DS population (i.e., those affected with a specific phenotypic trait) can be screened fo ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology
... normal counterpart, genetic tests use labeled DNA probes that can detect and distinguish the complementary base sequences found in the disease-causing alleles. Genetic tests are now available for diagnosing hundreds of disorders. ...
... normal counterpart, genetic tests use labeled DNA probes that can detect and distinguish the complementary base sequences found in the disease-causing alleles. Genetic tests are now available for diagnosing hundreds of disorders. ...
Chapter 10
... 6. Evolution by genetic drift proceeds faster in small than in large populations. 7. Since the allele frequency in each deme changes, eventually becoming 0 or 1, the frequency of heterozygotes declines to zero in each deme and in the metapopulation as a whole. 8. Mildly advantageous or disadvantageo ...
... 6. Evolution by genetic drift proceeds faster in small than in large populations. 7. Since the allele frequency in each deme changes, eventually becoming 0 or 1, the frequency of heterozygotes declines to zero in each deme and in the metapopulation as a whole. 8. Mildly advantageous or disadvantageo ...
Human Genetics
... allele from his mother, he will have the disorder; while a female has to receive the allele from both parents to be affected Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... allele from his mother, he will have the disorder; while a female has to receive the allele from both parents to be affected Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Recitation Section 11 Answer Key Bacterial Genetics
... a. two pieces of DNA in the two strains interact with each other b. two pieces of DNA in the two strains are identical to each other c. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains can interact d. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains are var ...
... a. two pieces of DNA in the two strains interact with each other b. two pieces of DNA in the two strains are identical to each other c. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains can interact d. products of expression of the gene(s) of interest in the two strains are var ...
Genomic Consequences of Background Effects on scalloped Mutant
... homeotic phenotype (Gibson et al. 1999), while modifiers of an Egfr gain-of-function allele suggest that the architecture of this photoreceptor determination phenotype was more likely due to many alleles of small effects (Dworkin et al. 2003). We ask here whether microarrays are a fine enough tool t ...
... homeotic phenotype (Gibson et al. 1999), while modifiers of an Egfr gain-of-function allele suggest that the architecture of this photoreceptor determination phenotype was more likely due to many alleles of small effects (Dworkin et al. 2003). We ask here whether microarrays are a fine enough tool t ...
Analyzing Copy Number Variation in the Human Genome
... *- effectively independent individuals equal to number of trios ** - 39 healthy controls, 16 with karyotype abnormalities *** - accounting for only those sites that showed in 2 or more individuals ...
... *- effectively independent individuals equal to number of trios ** - 39 healthy controls, 16 with karyotype abnormalities *** - accounting for only those sites that showed in 2 or more individuals ...
Tool for Visualisation the Gene Loci of Multple Genes
... gene loci can be represented at a single time. We consider the array express data set. Some of the chromosome gene loci are not been inputted in the data set. To address these problems, we have found out a visualization tool which can graphically represent all the disease causing genes for a particu ...
... gene loci can be represented at a single time. We consider the array express data set. Some of the chromosome gene loci are not been inputted in the data set. To address these problems, we have found out a visualization tool which can graphically represent all the disease causing genes for a particu ...
Guo, Ming: Biological Pathways - A pathway to explore diseases mechanism
... The methods abovementioned aim at inferring pathway representation directly from the gene expression data of each gene. All these approaches implicitly assume each gene as target for enrichment. The gene set approach, on the other hand, treats the known functionally related genes together as a group ...
... The methods abovementioned aim at inferring pathway representation directly from the gene expression data of each gene. All these approaches implicitly assume each gene as target for enrichment. The gene set approach, on the other hand, treats the known functionally related genes together as a group ...
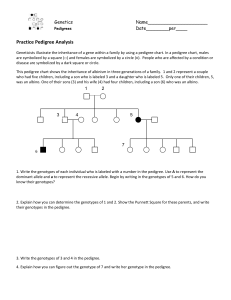
Introduction
... 1. Write the genotypes of each individual who is labeled with a number in the pedigree. Use A to represent the dominant allele and a to represent the recessive allele. Begin by writing in the genotypes of 5 and 6. How do you ...
... 1. Write the genotypes of each individual who is labeled with a number in the pedigree. Use A to represent the dominant allele and a to represent the recessive allele. Begin by writing in the genotypes of 5 and 6. How do you ...
X-linked genes - Effingham County Schools
... usually die in infancy or early childhood • Certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), are caused by translocations of chromosomes © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... usually die in infancy or early childhood • Certain cancers, including chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), are caused by translocations of chromosomes © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Inheritance of Anthocyanin Pigmentation in Rice
... two dominant complemetary genes and another independent recessive gene. ...
... two dominant complemetary genes and another independent recessive gene. ...