i + 1
... we also need to understand the “performance” of an algorithm: How well does a network or a component that uses a particular algorithm perform, as perceived by the user? performance analysis is concerned with metrics like delay, throughput, loss rates, etc metrics of the designer and of the theoretic ...
... we also need to understand the “performance” of an algorithm: How well does a network or a component that uses a particular algorithm perform, as perceived by the user? performance analysis is concerned with metrics like delay, throughput, loss rates, etc metrics of the designer and of the theoretic ...
Adaptive routing
... » A node gathers information on the status of each link to each neighbour, e.g. bit rate, delay time reliability, number of queued packets » The node builds a link state packet for each link, containing the above information » A node receiving link state packets forwards them to all its neighbours e ...
... » A node gathers information on the status of each link to each neighbour, e.g. bit rate, delay time reliability, number of queued packets » The node builds a link state packet for each link, containing the above information » A node receiving link state packets forwards them to all its neighbours e ...
PPT - TIME.mk
... Each router must do the following: A. Discover its neighbors, learn their network address. B. Measure the delay or cost to each of its neighbors. C. Construct a packet telling all it has just learned. D. Send this packet to all other routers. E. Compute the shortest path to every other router. ...
... Each router must do the following: A. Discover its neighbors, learn their network address. B. Measure the delay or cost to each of its neighbors. C. Construct a packet telling all it has just learned. D. Send this packet to all other routers. E. Compute the shortest path to every other router. ...
- ShareStudies.com
... • Flow control (adjacent nodes) • Error detection /correction (retransmission / correction) • Half-duplex / full-duplex communication (can nodes on both ends of a link transmit at the same time?) ...
... • Flow control (adjacent nodes) • Error detection /correction (retransmission / correction) • Half-duplex / full-duplex communication (can nodes on both ends of a link transmit at the same time?) ...
Brief Announcement: Network-Destabilizing Attacks
... The Internet is composed of smaller networks, called Autonomous Systems (ASes) (e.g., AT&T, Bank of America, Google, etc.). ASes use the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to learn how to reach distant ASes on the Internet via announcements from their neighboring ASes. Each BGP announcement contains a li ...
... The Internet is composed of smaller networks, called Autonomous Systems (ASes) (e.g., AT&T, Bank of America, Google, etc.). ASes use the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to learn how to reach distant ASes on the Internet via announcements from their neighboring ASes. Each BGP announcement contains a li ...
union бг ве дзжй ¡ ¡ , where the root node is defined and #" .
... online and offline, and the corresponding routing table updates. Tools such as traceroute are usually used to obtain the topology information. However, they rely on the cooperation of internal routers, which has become less attractive as the traffic load and size of the Internet grow. Duffield et al ...
... online and offline, and the corresponding routing table updates. Tools such as traceroute are usually used to obtain the topology information. However, they rely on the cooperation of internal routers, which has become less attractive as the traffic load and size of the Internet grow. Duffield et al ...
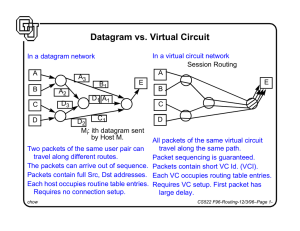
Datagram vs. Virtual Circuit
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
... Find the shortest paths form a given source node to all other nodes by developing paths in order of increasing path length. Let the set of nodes in a network be N. 1. start with a source node S in node set M. Let the nodes not in M be M’. 2. Let L with the set of links connecting M and M’. l Among t ...
Switching and Routing
... • We can allow multiple messages to share the link by having multiple virtual channels: – Each virtual channel has one buffer with the related flow control mechanism. – The switch can use some scheduling algorithm to select flits in different buffer for forwarding. – With virtual channel, the train ...
... • We can allow multiple messages to share the link by having multiple virtual channels: – Each virtual channel has one buffer with the related flow control mechanism. – The switch can use some scheduling algorithm to select flits in different buffer for forwarding. – With virtual channel, the train ...
Chapter 12 Routing
... • Pairs of routers (BGP peers) exchange routing info over semipermanent TCP conctns: BGP sessions • Note that BGP sessions do not correspond to physical links. • When AS2 advertises a prefix to AS1, AS2 is promising it will forward any datagrams destined to that prefix towards the prefix. — AS2 can ...
... • Pairs of routers (BGP peers) exchange routing info over semipermanent TCP conctns: BGP sessions • Note that BGP sessions do not correspond to physical links. • When AS2 advertises a prefix to AS1, AS2 is promising it will forward any datagrams destined to that prefix towards the prefix. — AS2 can ...
Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks
... •Probabilistic selection of next hop from several advertisement can reduce the problem •Restricting the structure of the topology can eliminate the problem by eliminating advertisement. For example nodes can arrange itself in square, triangular, etc., So that every node can derive its neighbors ...
... •Probabilistic selection of next hop from several advertisement can reduce the problem •Restricting the structure of the topology can eliminate the problem by eliminating advertisement. For example nodes can arrange itself in square, triangular, etc., So that every node can derive its neighbors ...
PWave: A Multi-source Multi-sink Anycast Routing
... only support single-sink configuration (i.e., unicast routing) with no direct and easy extension to support multi-source, multi-sink anycast routing. In this paper we propose a novel framework – referred to as PWave to support multisource, multi-sink anycast routing that is inherent in WSNs. Inspir ...
... only support single-sink configuration (i.e., unicast routing) with no direct and easy extension to support multi-source, multi-sink anycast routing. In this paper we propose a novel framework – referred to as PWave to support multisource, multi-sink anycast routing that is inherent in WSNs. Inspir ...
PDF
... Sensing Unit: Sensing units are usually composed of two subunits: sensors and analog to digital converters (ADCs). Sensor is a device which is used to translate physical phenomena to electrical signals. Processing Unit: The processing unit mainly provides intelligence to the sensor node. The process ...
... Sensing Unit: Sensing units are usually composed of two subunits: sensors and analog to digital converters (ADCs). Sensor is a device which is used to translate physical phenomena to electrical signals. Processing Unit: The processing unit mainly provides intelligence to the sensor node. The process ...
Chapter 4b
... N = set of routers = { u, v, w, x, y, z } E = set of links ={ (u,v), (u,x), (v,x), (v,w), (x,w), (x,y), (w,y), (w,z), (y,z) } Remark: Graph abstraction is useful in other network contexts Example: P2P, where N is set of peers and E is set of TCP connections Network Layer ...
... N = set of routers = { u, v, w, x, y, z } E = set of links ={ (u,v), (u,x), (v,x), (v,w), (x,w), (x,y), (w,y), (w,z), (y,z) } Remark: Graph abstraction is useful in other network contexts Example: P2P, where N is set of peers and E is set of TCP connections Network Layer ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... The AntNet algorithm is a dynamic distributed hybrid routing algorithm that consist both the instances of reactive and pro-active routing protocols. That is, the route setup process is a reactive process and the route maintenance, route improvement process is based on the proactive mechanisms. AntNe ...
... The AntNet algorithm is a dynamic distributed hybrid routing algorithm that consist both the instances of reactive and pro-active routing protocols. That is, the route setup process is a reactive process and the route maintenance, route improvement process is based on the proactive mechanisms. AntNe ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... Object: The interface and behavior of a model is defined using Objects. Objects interact by exchanging tokens. These tokens flow from output places of one object to input places of another object through links. ARTIFEX also includes large number of library models that makes design of complex network ...
... Object: The interface and behavior of a model is defined using Objects. Objects interact by exchanging tokens. These tokens flow from output places of one object to input places of another object through links. ARTIFEX also includes large number of library models that makes design of complex network ...
Utility-Maximizing Data Dissemination in Socially Selfish
... selfishness of the users. In real-world networks, e.g., civilian networks [8], [15], users have social ties at various strength levels. Naturally, a user would prefer helping others with whom there is a strong social tie, and less so for nodes with weak social ties. Such social selfishness of users ...
... selfishness of the users. In real-world networks, e.g., civilian networks [8], [15], users have social ties at various strength levels. Naturally, a user would prefer helping others with whom there is a strong social tie, and less so for nodes with weak social ties. Such social selfishness of users ...
ppt
... and quickly turn to an alternate path when congestion or failure happens to the current path. A clique of N overlay nodes; Probe N2 edges to get latency; Run link-state routing algorithm to find the lowest cost routes; Not scale for N > 50. Routing underlay can provide: ...
... and quickly turn to an alternate path when congestion or failure happens to the current path. A clique of N overlay nodes; Probe N2 edges to get latency; Run link-state routing algorithm to find the lowest cost routes; Not scale for N > 50. Routing underlay can provide: ...