companies step up fx hedging after big moves in
... Hedging (covered in Module 3 of the CFA Institute Investment FoundationsTM course of study) is a common risk management strategy used to limit exposure to fluctuations in the exchange rates. Foreign exchange transactions take place in the spot market or in the forward market. ...
... Hedging (covered in Module 3 of the CFA Institute Investment FoundationsTM course of study) is a common risk management strategy used to limit exposure to fluctuations in the exchange rates. Foreign exchange transactions take place in the spot market or in the forward market. ...
Economic and Strategy Viewpoint
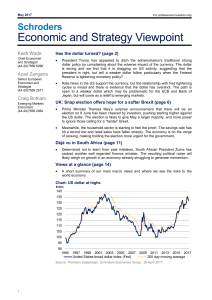
... Has the dollar become a major drag on the US? Looking at the current account deficit the answer would be no: the deficit remains around 1.5% of GDP and has been relatively stable since 2014. If we strip out oil and only look at trade, the deficit is larger at 2.8% of GDP, but again has been relative ...
... Has the dollar become a major drag on the US? Looking at the current account deficit the answer would be no: the deficit remains around 1.5% of GDP and has been relatively stable since 2014. If we strip out oil and only look at trade, the deficit is larger at 2.8% of GDP, but again has been relative ...
SEP 19, 2015 - Chuck Coppes
... Federal Reserve’s next steps will be suddenly has shifted from when it will raise rates to when it will offer more stimulus. Mind you, no one believes the U.S. central bank is about to start printing money again anytime soon. However, there is talk that faced with a slowing global economy and a dome ...
... Federal Reserve’s next steps will be suddenly has shifted from when it will raise rates to when it will offer more stimulus. Mind you, no one believes the U.S. central bank is about to start printing money again anytime soon. However, there is talk that faced with a slowing global economy and a dome ...
內生變數
... enormous, and it has ballooned in recent years. • New technologies, such as Internet links, are used among the major foreign exchange trading centers (London, New York, Tokyo, Frankfurt, and Singapore). • The integration of financial centers implies that there can be no significant arbitrage. – The ...
... enormous, and it has ballooned in recent years. • New technologies, such as Internet links, are used among the major foreign exchange trading centers (London, New York, Tokyo, Frankfurt, and Singapore). • The integration of financial centers implies that there can be no significant arbitrage. – The ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES EXPERIENCE OF AND LESSONS FROM EXCHANGE RATE
... “managed floating with no preannounced path for the exchange rate,” a category that may sound like a float but which typically entails sufficient de facto targeting and intervention that it should probably be classified as an intermediate regime. That leaves 40 countries that the IMF classifies as i ...
... “managed floating with no preannounced path for the exchange rate,” a category that may sound like a float but which typically entails sufficient de facto targeting and intervention that it should probably be classified as an intermediate regime. That leaves 40 countries that the IMF classifies as i ...
Diapositiva 1 - Manufacturing Circle
... a) They are generally not well hedged against a currency risk; b) A strengthening of the exchange rate may result in the loss of competitiveness of the traded goods sector and the ensuing effect could become permanent, even if the exchange rate subsequently returns to its previous level. 3. Foreign ...
... a) They are generally not well hedged against a currency risk; b) A strengthening of the exchange rate may result in the loss of competitiveness of the traded goods sector and the ensuing effect could become permanent, even if the exchange rate subsequently returns to its previous level. 3. Foreign ...
CE Mark - KV Institute of Management and Information Studies
... The Bogor Goals were created by the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) in Bogor, Indonesia in 1994, with the intention of increasing economic unity among Asian Pacific nations by increasing trade. The goals are to have free trade and investment in developed nations by 2010 and in developing na ...
... The Bogor Goals were created by the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) in Bogor, Indonesia in 1994, with the intention of increasing economic unity among Asian Pacific nations by increasing trade. The goals are to have free trade and investment in developed nations by 2010 and in developing na ...
(Textbook) Behavior in Organizations, 8ed (A. B. Shani)
... Internalization theory (also known as market imperfections theory) suggests that licensing has three major drawbacks: licensing may result in a firm’s giving away valuable technological know-how to a potential foreign competitor licensing does not give a firm the tight control over manufacturing, ...
... Internalization theory (also known as market imperfections theory) suggests that licensing has three major drawbacks: licensing may result in a firm’s giving away valuable technological know-how to a potential foreign competitor licensing does not give a firm the tight control over manufacturing, ...
DOLLARIZATION, THE FUNCTIONS OF A CENTRAL BANK AND
... collapses. If these real assets and/or nonperforming loans are marked to market, then the domestic banking system can be said to be “unsound”. Unless the banking system can be shored up by a lender of last resort either extending additional credits and/or buying up (at least temporarily) these asset ...
... collapses. If these real assets and/or nonperforming loans are marked to market, then the domestic banking system can be said to be “unsound”. Unless the banking system can be shored up by a lender of last resort either extending additional credits and/or buying up (at least temporarily) these asset ...
Chapter 1
... Growth tapered off in 2005 Central banks are reducing or removing policies that fuel rapid growth ...
... Growth tapered off in 2005 Central banks are reducing or removing policies that fuel rapid growth ...
12-Real
... nominal anchor right way? • Sudden stops of inflation (as done during Cruzado Plan) would have such problem: some prices at the peak and others at the bottom --> generating inflation pressure • This is an important component of the inertia behind Brazilian inflation – URV allowed prices to be fully ...
... nominal anchor right way? • Sudden stops of inflation (as done during Cruzado Plan) would have such problem: some prices at the peak and others at the bottom --> generating inflation pressure • This is an important component of the inertia behind Brazilian inflation – URV allowed prices to be fully ...
Four Goals for Higher Job-Rich Growth
... • An important expected effect of the rise of advanced manufacturing policies was that the costs of low-skilled labour may become less important, thus making off-shoring to low labour costs economies less attractive • Developed economies may benefit in terms of the location of production, but the di ...
... • An important expected effect of the rise of advanced manufacturing policies was that the costs of low-skilled labour may become less important, thus making off-shoring to low labour costs economies less attractive • Developed economies may benefit in terms of the location of production, but the di ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... The question is: Are these balance sheet effects large enough to make policymakers prefer a fixed exchange rate regime? Céspedes, Chang, and Velasco (2004) and Gertler, Gilchrist, and Natalucci (2003) address this question by analyzing the reaction of an emerging market model economy to an adverse e ...
... The question is: Are these balance sheet effects large enough to make policymakers prefer a fixed exchange rate regime? Céspedes, Chang, and Velasco (2004) and Gertler, Gilchrist, and Natalucci (2003) address this question by analyzing the reaction of an emerging market model economy to an adverse e ...
DDD381-caratula copia - Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú
... the rate of return of productive capital, which in time is reflected in the low interest rates and explained mainly by lagging technological progress. Although innovation is only one of the five possible sources of growth —the other four being a larger supply of labor; capital accumulation; an incre ...
... the rate of return of productive capital, which in time is reflected in the low interest rates and explained mainly by lagging technological progress. Although innovation is only one of the five possible sources of growth —the other four being a larger supply of labor; capital accumulation; an incre ...
Internationalization of the RMB and Historical Precedents
... the 1960s and 1970s, the Japanese and German governments were particularly worried about the possibility that if assets were made available to foreign residents, an inflow of capital would cause the currency to appreciate and render exporters less competitive on world markets. Again, this is also Ch ...
... the 1960s and 1970s, the Japanese and German governments were particularly worried about the possibility that if assets were made available to foreign residents, an inflow of capital would cause the currency to appreciate and render exporters less competitive on world markets. Again, this is also Ch ...
Chapter 5: Open Economy (A Long Run Model for Small Open
... and NX is positive (trade surplus). If output falls short of spending, we import the difference and NX is negative (trade ...
... and NX is positive (trade surplus). If output falls short of spending, we import the difference and NX is negative (trade ...
Aggregate Demand, International Trade
... • Aggregate demand increases, which pushes up both real GDP and the price level in the usual manner. • This effect is shown as the shift from Do to the D1 in the figure. In a closed economy, that single shift is the end of the story. • But in an open economy with international capital flows, we mus ...
... • Aggregate demand increases, which pushes up both real GDP and the price level in the usual manner. • This effect is shown as the shift from Do to the D1 in the figure. In a closed economy, that single shift is the end of the story. • But in an open economy with international capital flows, we mus ...
3460Chap12
... How to Measure Economic Exposure Economic exposure is the sensitivity of the future home currency value of the firm’s assets and liabilities and the firm’s operating cash flow to random changes in exchange rates. There exist statistical measurements of ...
... How to Measure Economic Exposure Economic exposure is the sensitivity of the future home currency value of the firm’s assets and liabilities and the firm’s operating cash flow to random changes in exchange rates. There exist statistical measurements of ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES SWISS EXCHANGE RATE POLICY IN THE 1930S.
... The initial response to the Great Depression varied greatly across countries. Switzerland, like some of the gold bloc countries (notably France), was affected later and less than others. To some extent, the relative favorable conditions in 1930 and 1931 reflected the impetus from strong capital inf ...
... The initial response to the Great Depression varied greatly across countries. Switzerland, like some of the gold bloc countries (notably France), was affected later and less than others. To some extent, the relative favorable conditions in 1930 and 1931 reflected the impetus from strong capital inf ...
Lecture 7: Factors Affect Current Account
... average growth rate before the crisis (significant estimated coefficient). However, growth tends to decline the year of the crisis (not significant). Countries more open to trade tend to grow faster after a currency crisis. Real exchange rate is not a good predictor of economic performance after a c ...
... average growth rate before the crisis (significant estimated coefficient). However, growth tends to decline the year of the crisis (not significant). Countries more open to trade tend to grow faster after a currency crisis. Real exchange rate is not a good predictor of economic performance after a c ...
Currency war

Currency war, also known as competitive devaluation, is a condition in international affairs where countries compete against each other to achieve a relatively low exchange rate for their own currency. As the price to buy a country's currency falls so too does the price of exports. Imports to the country become more expensive. So domestic industry, and thus employment, receives a boost in demand from both domestic and foreign markets. However, the price increase for imports can harm citizens' purchasing power. The policy can also trigger retaliatory action by other countries which in turn can lead to a general decline in international trade, harming all countries.Competitive devaluation has been rare through most of history as countries have generally preferred to maintain a high value for their currency. Countries have generally allowed market forces to work, or have participated in systems of managed exchanges rates. An exception occurred when currency war broke out in the 1930s. As countries abandoned the Gold Standard during the Great Depression, they used currency devaluations to stimulate their economies. Since this effectively pushes unemployment overseas, trading partners quickly retaliated with their own devaluations. The period is considered to have been an adverse situation for all concerned, as unpredictable changes in exchange rates reduced overall international trade.According to Guido Mantega, the Brazilian Minister for Finance, a global currency war broke out in 2010. This view was echoed by numerous other government officials and financial journalists from around the world. Other senior policy makers and journalists suggested the phrase ""currency war"" overstated the extent of hostility. With a few exceptions, such as Mantega, even commentators who agreed there had been a currency war in 2010 generally concluded that it had fizzled out by mid-2011.States engaging in possible competitive devaluation since 2010 have used a mix of policy tools, including direct government intervention, the imposition of capital controls, and, indirectly, quantitative easing. While many countries experienced undesirable upward pressure on their exchange rates and took part in the ongoing arguments, the most notable dimension of the 2010–11 episode was the rhetorical conflict between the United States and China over the valuation of the yuan. In January 2013, measures announced by Japan which were expected to devalue its currency sparked concern of a possible second 21st century currency war breaking out, this time with the principal source of tension being not China versus the US, but Japan versus the Eurozone. By late February, concerns of a new outbreak of currency war had been mostly allayed, after the G7 and G20 issued statements committing to avoid competitive devaluation. After the European Central Bank launched a fresh programme of quantitative easing in January 2015, there was once again an intensification of discussion about currency war.