AMA3100 - PolyU EIE
... multiplicative inverses, system of linear congruences, discrete logarithms, and error correcting codes. 2. Combinatorics This part covers combinatorial probability, Knapsack problem, and pigeonhole principle, and binomial coefficients. Optional overview of advanced topics such as linear programming ...
... multiplicative inverses, system of linear congruences, discrete logarithms, and error correcting codes. 2. Combinatorics This part covers combinatorial probability, Knapsack problem, and pigeonhole principle, and binomial coefficients. Optional overview of advanced topics such as linear programming ...
Ideas for Progress: Mathematics, Range 16–19
... model real-world and mathematical problems that contain verbal and symbolic representations of money ...
... model real-world and mathematical problems that contain verbal and symbolic representations of money ...
Mathematical Modeling of Human Body System in a
... disorders and inter-ventions and mathematical modeling of human body system towards future algorithmic medicine. Method: Instead of more common task-splitting cooperation between two or three institutions and a sizeable number of individual scholars, a stratified “massive brain” and load-sharing app ...
... disorders and inter-ventions and mathematical modeling of human body system towards future algorithmic medicine. Method: Instead of more common task-splitting cooperation between two or three institutions and a sizeable number of individual scholars, a stratified “massive brain” and load-sharing app ...
(pdf)
... In the second part we will explore issues in Monte Carlo simulation. With applications ranging from molecular dynamics to statistical parameter estimation, Monte Carlo is one of the most important tools in modern scientific computing. We will introduce some of the basic tools like Markov chain Monte ...
... In the second part we will explore issues in Monte Carlo simulation. With applications ranging from molecular dynamics to statistical parameter estimation, Monte Carlo is one of the most important tools in modern scientific computing. We will introduce some of the basic tools like Markov chain Monte ...
Functional Analysis
... Degree competences to which the subject contributes Specific: 8. Ability to solve problems from academic, technical, financial and social fields through mathematical methods. 9. CE-4. Have the ability to use computational tools as an aid to mathematical processes. 10. CE-3. Have the knowledge of spe ...
... Degree competences to which the subject contributes Specific: 8. Ability to solve problems from academic, technical, financial and social fields through mathematical methods. 9. CE-4. Have the ability to use computational tools as an aid to mathematical processes. 10. CE-3. Have the knowledge of spe ...
A prospective on mathematics and artificial
... its own body of knowledge using such mathematical foundations as category theory. Formulating patterns in problem solving [1] opens new approaches to reasoning about models and toward more automated formulation and reformulation, given problem information, which could be incomplete. Automated theore ...
... its own body of knowledge using such mathematical foundations as category theory. Formulating patterns in problem solving [1] opens new approaches to reasoning about models and toward more automated formulation and reformulation, given problem information, which could be incomplete. Automated theore ...
SSTEM _1200 Megan Anakin - ISCAR 2014 Presentations
... No shared object No possibility of boundary crossing ...
... No shared object No possibility of boundary crossing ...
Department of Economics EC 2019 Sampling and Inference
... Main Purpose: To deepen and consolidate knowledge of probability and statistics, with a focus on sampling and inference, as they pertain to Econometrics. ...
... Main Purpose: To deepen and consolidate knowledge of probability and statistics, with a focus on sampling and inference, as they pertain to Econometrics. ...
LMS Northern Meeting: Abstracts of Communications
... material into protein containers (viral capsids) arranged with icosahedral symmetry, they maximize container volume while minimizing the portion of the genomic sequence needed to code for the capsid. From a mathematical point of view, this implies that techniques from group theory can be used to pre ...
... material into protein containers (viral capsids) arranged with icosahedral symmetry, they maximize container volume while minimizing the portion of the genomic sequence needed to code for the capsid. From a mathematical point of view, this implies that techniques from group theory can be used to pre ...
Lecture 1 -- Welcome - The WA Franke College of Business
... What is Economics? A large subject — How do we approach it? Heilbroner’s analogy: think of the economy as an unexplored continent. ...
... What is Economics? A large subject — How do we approach it? Heilbroner’s analogy: think of the economy as an unexplored continent. ...
Modeling and Variation in Secondary Mathematics
... Journal Entry: Modeling and Variation in Secondary Mathematics A revised set of standards and principles for school mathematics has just been released by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. For this journal you must read the sections in this document that address Mathematical Modeling a ...
... Journal Entry: Modeling and Variation in Secondary Mathematics A revised set of standards and principles for school mathematics has just been released by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics. For this journal you must read the sections in this document that address Mathematical Modeling a ...
Lesson 8.2
... ◦ With linear growth, the debt grows by a constant monetary value (e.g. number of guilders) each period, whereas with exponential growth, the debt grows by the same percentage each period. ...
... ◦ With linear growth, the debt grows by a constant monetary value (e.g. number of guilders) each period, whereas with exponential growth, the debt grows by the same percentage each period. ...
Mathematical Modeling – Introduction and early examples
... number of nickels and y= number of dimes. The natural next step is to create a system of two equations with two unknowns: the first one describing the fact that there are 11 coins all together: x + y = 11 and the second one describing the fact that the value of x many coins worth 5 cents each and th ...
... number of nickels and y= number of dimes. The natural next step is to create a system of two equations with two unknowns: the first one describing the fact that there are 11 coins all together: x + y = 11 and the second one describing the fact that the value of x many coins worth 5 cents each and th ...
Tools for Mathematics Reasoning
... every time one does mathematics. A formal proof by deductive logic is a cornerstone of the foundation of mathematics. However, even for mathematicians, it is not possible or desirable to start from first principles (axioms) every time a problem is tackled. In most cases, previous proofs are accepted ...
... every time one does mathematics. A formal proof by deductive logic is a cornerstone of the foundation of mathematics. However, even for mathematicians, it is not possible or desirable to start from first principles (axioms) every time a problem is tackled. In most cases, previous proofs are accepted ...
y varies directly as x. y varies inversely as x. x varies
... 21) The annual simple interest on an investment is directly proportional to the amount invested. By investing $2500 in a certain bond issue, you obtained an interest payment of $187.50 at the end of 1 year. Find a mathematical model that gives the interest I for this bond issue at the end of 1 year ...
... 21) The annual simple interest on an investment is directly proportional to the amount invested. By investing $2500 in a certain bond issue, you obtained an interest payment of $187.50 at the end of 1 year. Find a mathematical model that gives the interest I for this bond issue at the end of 1 year ...
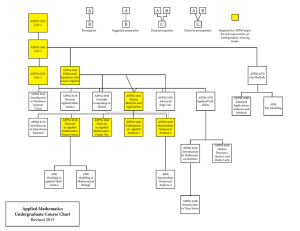
MATHEMATICS COURSE OFFERINGS Prerequisites Tree Diagram
... Prerequisites Tree Diagram (Revised 10/29/2014) 024 Elementary Algebra Topics (or CLM test score 65-94) PHYS 114 Physics I with Calculus 110 Precalculus (or CLM test score 95-120) CRWT 102 Critical Reading & Writing II 121 Calculus I ...
... Prerequisites Tree Diagram (Revised 10/29/2014) 024 Elementary Algebra Topics (or CLM test score 65-94) PHYS 114 Physics I with Calculus 110 Precalculus (or CLM test score 95-120) CRWT 102 Critical Reading & Writing II 121 Calculus I ...
Differential Equations: A Universal Language
... Models contagious disease in a specific population over ...
... Models contagious disease in a specific population over ...
Mathematical economics
Mathematical economics is the application of mathematical methods to represent theories and analyze problems in economics. By convention, the applied methods refer to those beyond simple geometry, such as differential and integral calculus, difference and differential equations, matrix algebra, mathematical programming, and other computational methods. An advantage claimed for the approach is its allowing formulation of theoretical relationships with rigor, generality, and simplicity.It is argued that mathematics allows economists to form meaningful, testable propositions about wide-ranging and complex subjects which could less easily be expressed informally. Further, the language of mathematics allows economists to make specific, positive claims about controversial or contentious subjects that would be impossible without mathematics. Much of economic theory is currently presented in terms of mathematical economic models, a set of stylized and simplified mathematical relationships asserted to clarify assumptions and implications.Broad applications include: optimization problems as to goal equilibrium, whether of a household, business firm, or policy maker static (or equilibrium) analysis in which the economic unit (such as a household) or economic system (such as a market or the economy) is modeled as not changing comparative statics as to a change from one equilibrium to another induced by a change in one or more factors dynamic analysis, tracing changes in an economic system over time, for example from economic growth.Formal economic modeling began in the 19th century with the use of differential calculus to represent and explain economic behavior, such as utility maximization, an early economic application of mathematical optimization. Economics became more mathematical as a discipline throughout the first half of the 20th century, but introduction of new and generalized techniques in the period around the Second World War, as in game theory, would greatly broaden the use of mathematical formulations in economics.This rapid systematizing of economics alarmed critics of the discipline as well as some noted economists. John Maynard Keynes, Robert Heilbroner, Friedrich Hayek and others have criticized the broad use of mathematical models for human behavior, arguing that some human choices are irreducible to mathematics.