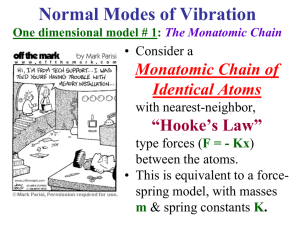
Digital Image Correlation Strain Analysis of Geometric Stress
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
... In a plate of uniform cross section the stress concentration factor is 1. Stress is evenly displaced across the cross section of the material and yields uniformly when highly stressed. In a non-uniform cross section, e.g. a plate with a circular hole, stress concentration increases by a factor of 2. ...
Lesson 11.1 properties of solutions
... that contains more dissolved substance than a saturated solution does. How does this happen? For example, the solubility of sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3 in water at 100∘C is 231 g/100mL. But at room temperature it is only 50 g/100mL. Suppose you prepare a solution saturated with sodium thiosulfate at ...
... that contains more dissolved substance than a saturated solution does. How does this happen? For example, the solubility of sodium thiosulfate, Na2S2O3 in water at 100∘C is 231 g/100mL. But at room temperature it is only 50 g/100mL. Suppose you prepare a solution saturated with sodium thiosulfate at ...
Balance this equation:
... The Law of Conservation of Mass does not apply to reactions involving combustion or explosion of matter. The oil companies make gasoline in a way that it gets used up so that we are always required to replenish it. The atoms (mass) of gasoline are converted into energy by the engine according to E = ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass does not apply to reactions involving combustion or explosion of matter. The oil companies make gasoline in a way that it gets used up so that we are always required to replenish it. The atoms (mass) of gasoline are converted into energy by the engine according to E = ...
Chapter 13 Solutions - Mosinee School District
... If the surface was rough, the block would spend energy overcoming a retarding friction force as it moved toward the equilibrium position, causing it to arrive at that position with a lower speed than that computed above. Computing a number value for this lower speed requires knowledge of the coeffic ...
... If the surface was rough, the block would spend energy overcoming a retarding friction force as it moved toward the equilibrium position, causing it to arrive at that position with a lower speed than that computed above. Computing a number value for this lower speed requires knowledge of the coeffic ...
4 Constitutive Equations
... constants which in turn depend on the actual definition of the stress rate (and thus on the deformation). Because of the properties of the rate of deformation tensor (cf. Section 2.5) hypoelastic constitutive laws do not strictly reflect the path independence of elasticity. Moreover, the derivation ...
... constants which in turn depend on the actual definition of the stress rate (and thus on the deformation). Because of the properties of the rate of deformation tensor (cf. Section 2.5) hypoelastic constitutive laws do not strictly reflect the path independence of elasticity. Moreover, the derivation ...
Публикация доступна для обсуждения в рамках
... of equilibrium with respect to the component B to the cathode direction in comparison with the value of Eeq in the GaAs−H2O system he was offered to introduce a correction for reversibility into the potential-determining reaction of uniform (pseudoselective) destruction of compound, taking into acco ...
... of equilibrium with respect to the component B to the cathode direction in comparison with the value of Eeq in the GaAs−H2O system he was offered to introduce a correction for reversibility into the potential-determining reaction of uniform (pseudoselective) destruction of compound, taking into acco ...
Morphology and Composition Control of Nanostructures in Aqueous Systems
... over 1.5 year. Through similar approach, ZnO nanowires were also doped by n-type carriers. Heavily-doped ZnO nanowires could be a solution to flexible TCO materials. Nanowires often suffer from challenges in being integrated with other functional parts for device fabrication, whereas 2D membrane str ...
... over 1.5 year. Through similar approach, ZnO nanowires were also doped by n-type carriers. Heavily-doped ZnO nanowires could be a solution to flexible TCO materials. Nanowires often suffer from challenges in being integrated with other functional parts for device fabrication, whereas 2D membrane str ...
Spinodal decomposition

Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism for the rapid unmixing of a mixture of liquids or solids from one thermodynamic phase, to form two coexisting phases. As an example, consider a hot mixture of water and an oil. At high temperatures the oil and the water may mix to form a single thermodynamic phase in which water molecules are surrounded by oil molecules and vice versa. The mixture is then suddenly cooled to a temperature at which thermodynamic equilibrium favours an oil-rich phase coexisting with a water-rich phase. Spinodal decomposition then occurs when the mixture is such that there is essentially no barrier to nucleation of the new oil-rich and water-rich phases. In other words, the oil and water molecules immediately start to cluster together into microscopic water-rich and oil-rich clusters throughout the liquid. These clusters then rapidly grow and coalesce until there is a single macroscopic oil-rich cluster, the oil-rich phase, and a single water-rich cluster, the water-rich phase.Spinodal decomposition can be contrasted with nucleation and growth. There the initial formation of the microscopic clusters involves a large free energy barrier, and so can be very slow, and may occur as little as once in the initial phase, not throughout the phase, as happens in spinodal decomposition.Spinodal decomposition is of interest for two primary reasons. In the first place, it is one of the few phase transformations in solids for which there is any plausible quantitative theory. The reason for this is the inherent simplicity of the reaction. Since there is no thermodynamic barrier to the reaction inside of the spinodal region, the decomposition is determined solely by diffusion. Thus, it can be treated purely as a diffusional problem, and many of the characteristics of the decomposition can be described by an approximate analytical solution to the general diffusion equation.In contrast, theories of nucleation and growth have to invoke the thermodynamics of fluctuations. And the diffusional problem involved in the growth of the nucleus is far more difficult to solve, because it is unrealistic to linearize the diffusion equation.From a more practical standpoint, spinodal decomposition provides a means of producing a very finely dispersed microstructure that can significantly enhance the physical properties of the material.