Work Booklet - Brooks Composite High School
... Store in cool, dry place away from acids. Do not store in metal containers. Use in well-ventilated area. ...
... Store in cool, dry place away from acids. Do not store in metal containers. Use in well-ventilated area. ...
Solution
... You decide to carry out this reaction in your flask. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is K and the reaction is known to be endothermic. Assume that you start with only gas A in your flask and you let the system come to equilibrium. Now, you place your flask in the refrigerator (i.e. you su ...
... You decide to carry out this reaction in your flask. The equilibrium constant for this reaction is K and the reaction is known to be endothermic. Assume that you start with only gas A in your flask and you let the system come to equilibrium. Now, you place your flask in the refrigerator (i.e. you su ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... 7. Which hydroxides are strong bases? Sr(OH)2, KOH, NaOH, Ba(OH)2 (a). KOH, Ba(OH)2 (b). KOH, NaOH (c). KOH, NaOH, Ba(OH)2 (d) Sr(OH)2, KOH, NaOH and Ba(OH)2 8. A neutralization reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide produces __________. (a). water and a salt (b). hydrogen gas (c). precipita ...
... 7. Which hydroxides are strong bases? Sr(OH)2, KOH, NaOH, Ba(OH)2 (a). KOH, Ba(OH)2 (b). KOH, NaOH (c). KOH, NaOH, Ba(OH)2 (d) Sr(OH)2, KOH, NaOH and Ba(OH)2 8. A neutralization reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide produces __________. (a). water and a salt (b). hydrogen gas (c). precipita ...
NUCLEATION PRIMARY SECONDARY (induced by crystals
... It is assumed that a free liquid drop automatically takes the shape that minimizes the free energy of the entire system. A surface with cluster contact angle of zero is known as wetting while a surface with cluster contact of more than 90° is known as non-wetting [Ada97]. When the contact angle is b ...
... It is assumed that a free liquid drop automatically takes the shape that minimizes the free energy of the entire system. A surface with cluster contact angle of zero is known as wetting while a surface with cluster contact of more than 90° is known as non-wetting [Ada97]. When the contact angle is b ...
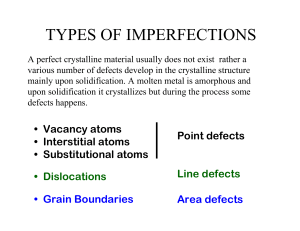
TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS
... Remarks regarding interstitial solid solutions: •The atomic radius of an interstitial atom must be substantially smaller than that of the host atom. •Metallic materials that have relatively high atomic packing factors crystal structures, the interstitial positions are relatively small. •Normally th ...
... Remarks regarding interstitial solid solutions: •The atomic radius of an interstitial atom must be substantially smaller than that of the host atom. •Metallic materials that have relatively high atomic packing factors crystal structures, the interstitial positions are relatively small. •Normally th ...
Test - Regents
... • 98.93% of the carbon atoms have a mass of 12.00 atomic mass units. • 1.07% of the carbon atoms have a mass of 13.00 atomic mass units. 66 In the space provided in your answer booklet, show a correct numerical setup for calculating the average atomic mass of carbon. [1] 67 Describe, in terms of sub ...
... • 98.93% of the carbon atoms have a mass of 12.00 atomic mass units. • 1.07% of the carbon atoms have a mass of 13.00 atomic mass units. 66 In the space provided in your answer booklet, show a correct numerical setup for calculating the average atomic mass of carbon. [1] 67 Describe, in terms of sub ...
Physical Setting/Chemistry Examination
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... c. XeF2 is nonpolar. Both Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the linear geometry they offset each other. XeF4 is nonpolar. All Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the square planar geometry they offset each other. XeO3 is polar. The Xe–O bond dipoles are the same size, and t ...
... c. XeF2 is nonpolar. Both Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the linear geometry they offset each other. XeF4 is nonpolar. All Xe–F bond dipoles are the same size, but due to the square planar geometry they offset each other. XeO3 is polar. The Xe–O bond dipoles are the same size, and t ...
Nearest-Neighbor Distribution Functions for Impenetrable Particles
... different P" nearest-neighbor distributions associated with the four G(4,x) choices. These results were calculated using 800 x values, uniformly distributed between x = 1 and that particular x which led to a value of P" 1000 times smaller than its initial value. Results were found to be very nearly ...
... different P" nearest-neighbor distributions associated with the four G(4,x) choices. These results were calculated using 800 x values, uniformly distributed between x = 1 and that particular x which led to a value of P" 1000 times smaller than its initial value. Results were found to be very nearly ...
Test - Angelfire
... with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or external keyboards. Students may have more than one calculator available during the examina ...
... with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or external keyboards. Students may have more than one calculator available during the examina ...
solid metal
... heterogeneous mixture vary within the sample (oil and water). The properties of a homogeneous mixture are constant (salt solution). A pure substance may be either a compound (water) or an element (gold). Left to right: oil and water; NaCl solution; H2O; and gold nugget. ...
... heterogeneous mixture vary within the sample (oil and water). The properties of a homogeneous mixture are constant (salt solution). A pure substance may be either a compound (water) or an element (gold). Left to right: oil and water; NaCl solution; H2O; and gold nugget. ...
Exam 1
... The best description of the effect of a catalyst on a chemical reaction is that it A. lowers the activation energy of the forward reaction without changing the activation energy of the reverse reaction. B. lowers the activation energy of the forward reaction and raises the activation energy of the r ...
... The best description of the effect of a catalyst on a chemical reaction is that it A. lowers the activation energy of the forward reaction without changing the activation energy of the reverse reaction. B. lowers the activation energy of the forward reaction and raises the activation energy of the r ...
Spinodal decomposition

Spinodal decomposition is a mechanism for the rapid unmixing of a mixture of liquids or solids from one thermodynamic phase, to form two coexisting phases. As an example, consider a hot mixture of water and an oil. At high temperatures the oil and the water may mix to form a single thermodynamic phase in which water molecules are surrounded by oil molecules and vice versa. The mixture is then suddenly cooled to a temperature at which thermodynamic equilibrium favours an oil-rich phase coexisting with a water-rich phase. Spinodal decomposition then occurs when the mixture is such that there is essentially no barrier to nucleation of the new oil-rich and water-rich phases. In other words, the oil and water molecules immediately start to cluster together into microscopic water-rich and oil-rich clusters throughout the liquid. These clusters then rapidly grow and coalesce until there is a single macroscopic oil-rich cluster, the oil-rich phase, and a single water-rich cluster, the water-rich phase.Spinodal decomposition can be contrasted with nucleation and growth. There the initial formation of the microscopic clusters involves a large free energy barrier, and so can be very slow, and may occur as little as once in the initial phase, not throughout the phase, as happens in spinodal decomposition.Spinodal decomposition is of interest for two primary reasons. In the first place, it is one of the few phase transformations in solids for which there is any plausible quantitative theory. The reason for this is the inherent simplicity of the reaction. Since there is no thermodynamic barrier to the reaction inside of the spinodal region, the decomposition is determined solely by diffusion. Thus, it can be treated purely as a diffusional problem, and many of the characteristics of the decomposition can be described by an approximate analytical solution to the general diffusion equation.In contrast, theories of nucleation and growth have to invoke the thermodynamics of fluctuations. And the diffusional problem involved in the growth of the nucleus is far more difficult to solve, because it is unrealistic to linearize the diffusion equation.From a more practical standpoint, spinodal decomposition provides a means of producing a very finely dispersed microstructure that can significantly enhance the physical properties of the material.