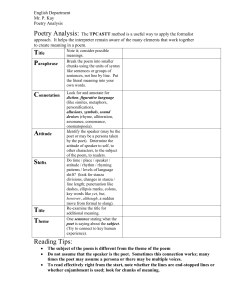
Poetry - WordPress.com
... Figurative language used to create particular mental images Metaphor Association of two completely different objects as being the same thing Meter Used to measure poetry, unit used is the metric “foot,” determined by a series of stressed and unstressed syllables, number of feet determines the me ...
... Figurative language used to create particular mental images Metaphor Association of two completely different objects as being the same thing Meter Used to measure poetry, unit used is the metric “foot,” determined by a series of stressed and unstressed syllables, number of feet determines the me ...
Glossary of Poetic Terms
... Poetic meters such as trochaic and dactylic that move or fall from a stressed to an unstressed syllable. The nonsense line, "Higgledy, piggledy," is dactylic, with the accent on the first syllable and the two syllables following falling off from that accent in each word. Trochaic meter is represente ...
... Poetic meters such as trochaic and dactylic that move or fall from a stressed to an unstressed syllable. The nonsense line, "Higgledy, piggledy," is dactylic, with the accent on the first syllable and the two syllables following falling off from that accent in each word. Trochaic meter is represente ...
Elements of poetry
... Free verse poetry is very conversational sounds like someone talking with you. A more modern type of poetry. ...
... Free verse poetry is very conversational sounds like someone talking with you. A more modern type of poetry. ...
File
... Onomatopoeia: words whose sound suggest their meaning (whirr, buzz) Rhyme: identical end sounds in a word (fan, ran) End rhyme: rhyme that occurs at the end of lines of poetry Internal Rhyme: rhymes within a line of poetry ...
... Onomatopoeia: words whose sound suggest their meaning (whirr, buzz) Rhyme: identical end sounds in a word (fan, ran) End rhyme: rhyme that occurs at the end of lines of poetry Internal Rhyme: rhymes within a line of poetry ...
Literary Terms for English IV AP
... Italian sonnet. Examples: Petrarch's "If it is not love, then what is it that I feel," and Frost's "Design." 62. Sonnet - A fourteen-line poem in iambic pentameter. The Shakespearean or English sonnet is arranged as three quatrains and a final couplet, rhyming abab cdcd efef gg. The Petrarchan or It ...
... Italian sonnet. Examples: Petrarch's "If it is not love, then what is it that I feel," and Frost's "Design." 62. Sonnet - A fourteen-line poem in iambic pentameter. The Shakespearean or English sonnet is arranged as three quatrains and a final couplet, rhyming abab cdcd efef gg. The Petrarchan or It ...
Poetry
... stressed and unstressed syllables, whose combination gives a particular sense of movement and is meant to appeal to the ear as well as to reinforce meaning. ...
... stressed and unstressed syllables, whose combination gives a particular sense of movement and is meant to appeal to the ear as well as to reinforce meaning. ...
Poetry Terms APOSTROPHE – A literary device in which a speaker
... POETRY - A type of literature that creates an emotional response by the imaginative use of words patterned to produce a desired effect through rhythm, sound, and meaning; it may be rhymed or unrhymed. QUATRAIN – A four-line poem or stanza. REFRAIN – A passage repeated at regular intervals with varia ...
... POETRY - A type of literature that creates an emotional response by the imaginative use of words patterned to produce a desired effect through rhythm, sound, and meaning; it may be rhymed or unrhymed. QUATRAIN – A four-line poem or stanza. REFRAIN – A passage repeated at regular intervals with varia ...
Poetry Terms Glossary
... A lyric poem that is 14 lines long. Italian (or Petrarchan) sonnets are divided into two quatrains and a six-line "sestet," with the rhyme scheme abba abba cdecde (or cdcdcd). English (or Shakespearean) sonnets are composed of three quatrains and a final couplet, with a rhyme scheme of abab cdcd ...
... A lyric poem that is 14 lines long. Italian (or Petrarchan) sonnets are divided into two quatrains and a six-line "sestet," with the rhyme scheme abba abba cdecde (or cdcdcd). English (or Shakespearean) sonnets are composed of three quatrains and a final couplet, with a rhyme scheme of abab cdcd ...
SACAI Eng FAL Poetry Support Material
... May use POETIC LICENCE – they may use words as they please to fit their poem. Enjambment – occurs at the end of lines where there is no punctuation to create a sense of flow and unbroken ideas. Many poetic forms have developed over time, but a poem is mainly narrative or lyrical in structure: 1. N ...
... May use POETIC LICENCE – they may use words as they please to fit their poem. Enjambment – occurs at the end of lines where there is no punctuation to create a sense of flow and unbroken ideas. Many poetic forms have developed over time, but a poem is mainly narrative or lyrical in structure: 1. N ...
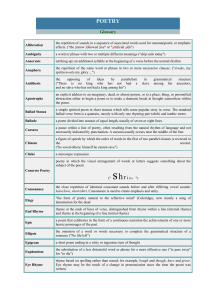
POETRY TERMS 1.ааAlliterationанаthe repetition of initial
... quality to their verses and to emphasize certain words and ideas. Many traditional poems contain END RHYMES, or rhyming words at the ends of lines. Another common device is the use of INTERNAL RHYMES, or rhyming words within lines. EXACT RHYMES have words that are exactly alike, except the c ...
... quality to their verses and to emphasize certain words and ideas. Many traditional poems contain END RHYMES, or rhyming words at the ends of lines. Another common device is the use of INTERNAL RHYMES, or rhyming words within lines. EXACT RHYMES have words that are exactly alike, except the c ...
Reading, writing, Communicating
... • Why are life experiences a foundation for writing poetry? • Life experiences are a foundation for writing poetry, because poems are a unique perspective or commentary on life. • How do poetic techniques engage readers? • Poetic techniques engage readers with meaning and imagery created by word cho ...
... • Why are life experiences a foundation for writing poetry? • Life experiences are a foundation for writing poetry, because poems are a unique perspective or commentary on life. • How do poetic techniques engage readers? • Poetic techniques engage readers with meaning and imagery created by word cho ...
POETERY LITERARY TERMS - Mr. Furman's Web Pages
... Line 1 is one word (the title) Line 2 is two words that describe the title. Line 3 is three words that tell the action Line 4 is four words that express the feeling Line 5 is one word that recalls the title ...
... Line 1 is one word (the title) Line 2 is two words that describe the title. Line 3 is three words that tell the action Line 4 is four words that express the feeling Line 5 is one word that recalls the title ...
Terms
... misunderstood by one or more other characters. Situational irony is when the setting for an event is odd or humorous. (Ex: a fire at a firehouse). Lyric Poetry: The structure of poetry that expresses strong emotional state in a relatively short form. Metaphor: The comparison of two unlike things wit ...
... misunderstood by one or more other characters. Situational irony is when the setting for an event is odd or humorous. (Ex: a fire at a firehouse). Lyric Poetry: The structure of poetry that expresses strong emotional state in a relatively short form. Metaphor: The comparison of two unlike things wit ...
Intro to Creative Writing/Poetry SAT 3 - Co
... thought into two parts (argument and conclusion); the Shakespearean, into four (the final couplet is the summary).” ...
... thought into two parts (argument and conclusion); the Shakespearean, into four (the final couplet is the summary).” ...
British Romantics powerpoint
... sequence of words, usually at the beginning of a word or stressed syllable • Meter: When a rhythmic pattern of stresses recurs in a poem, it is called meter. Metrical patterns are determined by the type and number of feet in a line of verse; combining the name of a line length with the name of a foo ...
... sequence of words, usually at the beginning of a word or stressed syllable • Meter: When a rhythmic pattern of stresses recurs in a poem, it is called meter. Metrical patterns are determined by the type and number of feet in a line of verse; combining the name of a line length with the name of a foo ...
poetry information sheets
... This information comes from your textbook, but I picked out some important points to remember as we read examples of this poetry. Tanka Tanka first appeared in the Manyoshu, which means Collection of Tean Thousand Leaves. This work was published during the eighth century. “Tanka” means “short so ...
... This information comes from your textbook, but I picked out some important points to remember as we read examples of this poetry. Tanka Tanka first appeared in the Manyoshu, which means Collection of Tean Thousand Leaves. This work was published during the eighth century. “Tanka” means “short so ...
Defining Poetry and Characteristics of Poetry
... Rhyme • the identical final syllables of words • may appear in two successive lines, in alternating lines, or at intervals of four, five, or more lines • if rhyming sounds are too far away from each other, they lose their immediacy and ...
... Rhyme • the identical final syllables of words • may appear in two successive lines, in alternating lines, or at intervals of four, five, or more lines • if rhyming sounds are too far away from each other, they lose their immediacy and ...
Poetry
... • Concrete Poem: poem whose meaning is conveyed through shape or pattern printed on a page • Epic: A long narrative poem about the deeds of gods or heroes. (“The Odyssey” by Homer is an epic poem) • Free Verse: Poetry not written in a regular rhythmical pattern, or meter. It seeks to recapture the r ...
... • Concrete Poem: poem whose meaning is conveyed through shape or pattern printed on a page • Epic: A long narrative poem about the deeds of gods or heroes. (“The Odyssey” by Homer is an epic poem) • Free Verse: Poetry not written in a regular rhythmical pattern, or meter. It seeks to recapture the r ...
Poetry Vocabulary List
... Stress – the emphasis placed on a word or syllable. Trochee – a metrical foot consisting of two syllables, an accented syllable followed by an unaccented syllable, as in the word fortune. Verse – poetry as distinct from prose. The term is usually more neutral than poetry, indicating that the technic ...
... Stress – the emphasis placed on a word or syllable. Trochee – a metrical foot consisting of two syllables, an accented syllable followed by an unaccented syllable, as in the word fortune. Verse – poetry as distinct from prose. The term is usually more neutral than poetry, indicating that the technic ...
POETRY
... unaccented flower/power). Beside the perfect rhyme there are less strict patterns as the eyerhyme (dies/calamities) and other imperfect rhymes (assonance, consonance, nasal rhyme etc.) ...
... unaccented flower/power). Beside the perfect rhyme there are less strict patterns as the eyerhyme (dies/calamities) and other imperfect rhymes (assonance, consonance, nasal rhyme etc.) ...
Poetry - mssnyder8
... And sorry I could not travel both And be one traveler, long I stood And looked down one as far as I could To where it bent in the undergrowth; Then took the other, as just as fair, And having perhaps the better claim, Because it was grassy and wanted wear; Though as for that the passing there Had wo ...
... And sorry I could not travel both And be one traveler, long I stood And looked down one as far as I could To where it bent in the undergrowth; Then took the other, as just as fair, And having perhaps the better claim, Because it was grassy and wanted wear; Though as for that the passing there Had wo ...
Poetry

Poetry is a form of literature that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language—such as phonaesthetics, sound symbolism, and metre—to evoke meanings in addition to, or in place of, the prosaic ostensible meaning.Poetry has a long history, dating back to the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh. Early poems evolved from folk songs such as the Chinese Shijing, or from a need to retell oral epics, as with the Sanskrit Vedas, Zoroastrian Gathas, and the Homeric epics, the Iliad and the Odyssey. Ancient attempts to define poetry, such as Aristotle's Poetics, focused on the uses of speech in rhetoric, drama, song and comedy. Later attempts concentrated on features such as repetition, verse form and rhyme, and emphasized the aesthetics which distinguish poetry from more objectively informative, prosaic forms of writing. From the mid-20th century, poetry has sometimes been more generally regarded as a fundamental creative act employing language.Poetry uses forms and conventions to suggest differential interpretation to words, or to evoke emotive responses. Devices such as assonance, alliteration, onomatopoeia and rhythm are sometimes used to achieve musical or incantatory effects. The use of ambiguity, symbolism, irony and other stylistic elements of poetic diction often leaves a poem open to multiple interpretations. Similarly figures of speech such as metaphor, simile and metonymy create a resonance between otherwise disparate images—a layering of meanings, forming connections previously not perceived. Kindred forms of resonance may exist, between individual verses, in their patterns of rhyme or rhythm.Some poetry types are specific to particular cultures and genres and respond to characteristics of the language in which the poet writes. Readers accustomed to identifying poetry with Dante, Goethe, Mickiewicz and Rumi may think of it as written in lines based on rhyme and regular meter; there are, however, traditions, such as Biblical poetry, that use other means to create rhythm and euphony. Much modern poetry reflects a critique of poetic tradition, playing with and testing, among other things, the principle of euphony itself, sometimes altogether forgoing rhyme or set rhythm. In today's increasingly globalized world, poets often adapt forms, styles and techniques from diverse cultures and languages.