Chemistry EOC Review 2015 Name Per ___ This review is part of
... electrons the radius should get bigger, but it doesn’t. You are also adding in a proton, which adds mass and increases the nuclear force of the nucleus, so it can hold the electrons even tighter. Therefore the largest ionization energies are in the upper right of the periodic table and the lowest ar ...
... electrons the radius should get bigger, but it doesn’t. You are also adding in a proton, which adds mass and increases the nuclear force of the nucleus, so it can hold the electrons even tighter. Therefore the largest ionization energies are in the upper right of the periodic table and the lowest ar ...
ap chemistry unit two notes
... Each element has a fixed fraction of the total mass in a compound. ...
... Each element has a fixed fraction of the total mass in a compound. ...
Chemistry 11 - Sardis Secondary
... a) How many grams of aluminum oxide, Al2O3, would be expected to form in the reaction of 15.0g Al with 18.43g of oxygen gas? ...
... a) How many grams of aluminum oxide, Al2O3, would be expected to form in the reaction of 15.0g Al with 18.43g of oxygen gas? ...
coppin state college
... Dr. Alfred N. Amah This examination consists of 38 multiple choice questions with five possible responses. Read each question carefully and choose the best response. There is only one correct response for each question. You are to answer all questions in this examination. 1. What method is used to d ...
... Dr. Alfred N. Amah This examination consists of 38 multiple choice questions with five possible responses. Read each question carefully and choose the best response. There is only one correct response for each question. You are to answer all questions in this examination. 1. What method is used to d ...
Mole Relationships in chemistry
... in 1 mole of the compound to the TOTAL MASS of 1 mole of the compound O A pure compound should show the same percent mass of each element consistently O So given a formula , you should be able to figure out the percent mass of each element ...
... in 1 mole of the compound to the TOTAL MASS of 1 mole of the compound O A pure compound should show the same percent mass of each element consistently O So given a formula , you should be able to figure out the percent mass of each element ...
Reaction types and Stoichiometry
... The molar mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of its atoms. The molar mass (gram formula mass) equals the mass of one mole of that substance. Ex Fe2O3 molar mass is equal to 2 x 55.85 grams + 3 x 16 grams =159.7 grams ...
... The molar mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of its atoms. The molar mass (gram formula mass) equals the mass of one mole of that substance. Ex Fe2O3 molar mass is equal to 2 x 55.85 grams + 3 x 16 grams =159.7 grams ...
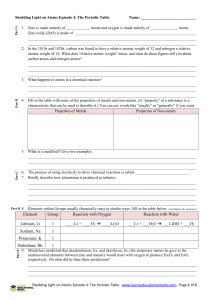
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... atomic weight of 14. What does “relative atomic weight” mean, and what do these figures tell you about carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms? ______________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ...
4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon 4.1 Experiencing Atoms
... the nuclear theory of the atom. 1. Most of the atom s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed. 3. The number of negatively charged electro ...
... the nuclear theory of the atom. 1. Most of the atom s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed. 3. The number of negatively charged electro ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are termed ...
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are termed ...
2 - DrChoChemistryWebSite
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
... 1) Assemble the correct formulas for all the reactants and products, using “+” and “→” 2) Count the number of atoms of each type appearing on both sides 3) Balance the elements one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) where you need more - save balancing the H and O until LAST! ...
Of Atoms, Molecules & Ions I Sing
... Each element is composed of atoms – which are incredibly small. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different el ...
... Each element is composed of atoms – which are incredibly small. All atoms of a given element are identical to one another in mass and other properties, and different from all other atoms. That atoms were indivisible, and were not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. When atoms of different el ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Chemical Reactions • Chemical Reactions – a chemical change in which the covalent or ionic bonds that hold elements or compounds together are broken and new bonds are formed. • Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations. • C6H1206 ...
... Chemical Reactions • Chemical Reactions – a chemical change in which the covalent or ionic bonds that hold elements or compounds together are broken and new bonds are formed. • Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations. • C6H1206 ...
Ch. 6: Chemical Reactions Study Guide
... A synthesis reaction is a reaction between at least two compounds in which a new, more complex compound is formed. The product of the synthesis reaction between sodium and chlorine gas is sodium chloride. In a decomposition reaction, the reactants are broken down into other substances. Most of the e ...
... A synthesis reaction is a reaction between at least two compounds in which a new, more complex compound is formed. The product of the synthesis reaction between sodium and chlorine gas is sodium chloride. In a decomposition reaction, the reactants are broken down into other substances. Most of the e ...
Lecture 2 - Columbia University
... (2) Understand the atomic and molecular interpretation of elements, compounds and mixtures Element: a molecule that contains only one type of atom. Examples: Hydrogen molecules (H2), Oxygen molecules (O2), Ozone (O3), buckyballs (C60), Diamond (Cn), Graphite (Cn), Compound: a molecule that contains ...
... (2) Understand the atomic and molecular interpretation of elements, compounds and mixtures Element: a molecule that contains only one type of atom. Examples: Hydrogen molecules (H2), Oxygen molecules (O2), Ozone (O3), buckyballs (C60), Diamond (Cn), Graphite (Cn), Compound: a molecule that contains ...
Chapter 3 - Stoichiometry
... Limiting reactants: If _____ or more reactants are needed in a reaction, one of the reactants will be used up first. This reactant determines: If the reactants run out equally, this is called a: Usually, one reactant is in excess (inxs), and the other is the: The limiting reactant determines: sample ...
... Limiting reactants: If _____ or more reactants are needed in a reaction, one of the reactants will be used up first. This reactant determines: If the reactants run out equally, this is called a: Usually, one reactant is in excess (inxs), and the other is the: The limiting reactant determines: sample ...
Name
... element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The average atomic mass of an element is usually closest to that of the isotope with the highest ...
... element and the relative abundance of its isotopes. a. In nature, most elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes. b. Isotopes of an element do not have a specific natural percent abundance. c. The average atomic mass of an element is usually closest to that of the isotope with the highest ...
Empirical Formula
... the reactants and in the products, and record the results in a table. • Identify elements that appear in only one reactant and in only one product, and balance the atoms of those elements first. Delay the balancing of atoms (often hydrogen and oxygen) that appear in more that one reactant or product ...
... the reactants and in the products, and record the results in a table. • Identify elements that appear in only one reactant and in only one product, and balance the atoms of those elements first. Delay the balancing of atoms (often hydrogen and oxygen) that appear in more that one reactant or product ...
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
... Atoms join together to form molecules. These molecules are held together by bonds. In this lab you will use toothpicks to represent the bonds. Important note: use one toothpick to represent a single covalent bond, and two toothpicks to represent a double covalent bond. Remember, covalent bonds are b ...
Types of Reactions notes 02 Types of chemical reactions
... When you see a chemical formula, often the formula is followed by a symbol in parentheses. For example: H2O(l) - the water is liquid H2O(s) - the water is solid (ice) H2O(g)- the water is a gas (steam) NaCl(aq) – means that the chemical is disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dis ...
... When you see a chemical formula, often the formula is followed by a symbol in parentheses. For example: H2O(l) - the water is liquid H2O(s) - the water is solid (ice) H2O(g)- the water is a gas (steam) NaCl(aq) – means that the chemical is disolved in water. In this case it would be salt dis ...
What are atoms?
... You may wonder how we could know anything about a particle of matter that is too small to see and almost too small to measure. Scientists have learned how to study atoms. They study atoms by studying how matter behaves. They use very complicated equipment. However, you can learn about atoms by study ...
... You may wonder how we could know anything about a particle of matter that is too small to see and almost too small to measure. Scientists have learned how to study atoms. They study atoms by studying how matter behaves. They use very complicated equipment. However, you can learn about atoms by study ...
CHAPTER TWO ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS
... a. Both compounds have C2 H6 O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. b. ...
... a. Both compounds have C2 H6 O as the formula. Because they have the same formula, their mass percent composition will be identical. However, these are different compounds with different properties since the atoms are bonded together differently. These compounds are called isomers of each other. b. ...
print
... • Also used are: atomic mass, formula mass, and molecular mass depending on the material described. Or, the word weight might substitute for mass. • To calculate the molar mass for a compound, add together the atomic masses for all of the atoms in a molecule or formula unit of the compound. • Uni ...
... • Also used are: atomic mass, formula mass, and molecular mass depending on the material described. Or, the word weight might substitute for mass. • To calculate the molar mass for a compound, add together the atomic masses for all of the atoms in a molecule or formula unit of the compound. • Uni ...
Summer Assignment Packet
... 1. Classify each substance as a pure substance or a mixture. If it is a pure substance, classify it as an element or a compound. If it is a mixture, classify it as homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
... 1. Classify each substance as a pure substance or a mixture. If it is a pure substance, classify it as an element or a compound. If it is a mixture, classify it as homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.1 – Matter and Measurement Date: Period:
... 1. Classify each substance as a pure substance or a mixture. If it is a pure substance, classify it as an element or a compound. If it is a mixture, classify it as homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
... 1. Classify each substance as a pure substance or a mixture. If it is a pure substance, classify it as an element or a compound. If it is a mixture, classify it as homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
VIEW
... The atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 of the mass of an atom of the carbon-12 isotope. 1 amu = 1/12 mass of C-12 ...
... The atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 of the mass of an atom of the carbon-12 isotope. 1 amu = 1/12 mass of C-12 ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.