AP358 LOW POWER DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Description
... Large differential input voltages can be easily accommodated and, as input differential voltage protection diodes are not needed, no large input currents result from large differential input voltages. The differential input voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should ...
... Large differential input voltages can be easily accommodated and, as input differential voltage protection diodes are not needed, no large input currents result from large differential input voltages. The differential input voltage may be larger than V+ without damaging the device. Protection should ...
View - Microsemi
... the loop length of the ring trip for the Am79R100/101 devices are increased compared to the Am79R79 device. For the Am79R100 device, the recommended setup where Rrt1 = 604K, Rrt2 = 12K, Crt = 1 uf, CF = 1.26, allows Rloop to be extended to a maximum value of 1.1 kΩ with clear ring trip. For the Am79 ...
... the loop length of the ring trip for the Am79R100/101 devices are increased compared to the Am79R79 device. For the Am79R100 device, the recommended setup where Rrt1 = 604K, Rrt2 = 12K, Crt = 1 uf, CF = 1.26, allows Rloop to be extended to a maximum value of 1.1 kΩ with clear ring trip. For the Am79 ...
High SCCR Overcurrent Protective Devices
... Use Current Limitation: If the PDB is fed by a Cooper Bussmann modern current-limiting LPJ, JJS, or LP-CC fuse rated 60A or less upstream, the current limitation of the fuse can be used to raise the rating of the PDB to 100kA or more. Use NEW PDB Series of Power Distribution Blocks with High Short-C ...
... Use Current Limitation: If the PDB is fed by a Cooper Bussmann modern current-limiting LPJ, JJS, or LP-CC fuse rated 60A or less upstream, the current limitation of the fuse can be used to raise the rating of the PDB to 100kA or more. Use NEW PDB Series of Power Distribution Blocks with High Short-C ...
Single-Supply, 10MHz, Rail-to-Rail Output, Low-Noise, JFET Amplifier OPA141 OPA2141
... Junction-to-board characterization parameter (6) ...
... Junction-to-board characterization parameter (6) ...
EE-35 - International Journal of Advance Research and Innovation
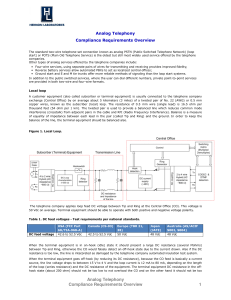
... required. The application for transmission line compensators commenced in the late seventies. Here the objectives are: Show in fig the SVC is connected at bus no.14 because the bus no. 14 is the weakest bus in system, so the SVC is connected at bus no. 14. The rating of SVC is power 100 MV, voltage ...
... required. The application for transmission line compensators commenced in the late seventies. Here the objectives are: Show in fig the SVC is connected at bus no.14 because the bus no. 14 is the weakest bus in system, so the SVC is connected at bus no. 14. The rating of SVC is power 100 MV, voltage ...
DS2731 Cache-Memory Battery-Backup Management IC General Description Features
... J-STD-020 Specification. ...
... J-STD-020 Specification. ...
MAX8667/MAX8668 1.5MHz Dual Step-Down DC-DC Converters with Dual LDOs and Individual Enables
... Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
... Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
BA4558YF-M
... Described here are the terms of electric characteristics used in this datasheet. Items and symbols used are also shown. Note that item name and symbol and their meaning may differ from those on another manufacture’s document or general document. 1. Absolute maximum ratings Absolute maximum rating it ...
... Described here are the terms of electric characteristics used in this datasheet. Items and symbols used are also shown. Note that item name and symbol and their meaning may differ from those on another manufacture’s document or general document. 1. Absolute maximum ratings Absolute maximum rating it ...
HMC866LC3C - seek datasheet
... provides 29 dB of differential gain. The output voltage swing is adjustable up to 800 mVp-p differential by using the VAC analog control input and the additive RMS jitter is less than 300 fs for 32 Gbps operation. The amplifier allows external offset correction function to both inputs and outputs. A ...
... provides 29 dB of differential gain. The output voltage swing is adjustable up to 800 mVp-p differential by using the VAC analog control input and the additive RMS jitter is less than 300 fs for 32 Gbps operation. The amplifier allows external offset correction function to both inputs and outputs. A ...
Low-Drift, Low-Power, Dual-Output, VREF and VREF / 2 Voltage
... the precision of the signal chain and decrease board space, while reducing the cost of the system as compared to a discrete solution. Extremely low dropout voltage of only 10 mV allows operation from very low input voltages, which can be very useful in battery-operated systems. Both the VREF and VBI ...
... the precision of the signal chain and decrease board space, while reducing the cost of the system as compared to a discrete solution. Extremely low dropout voltage of only 10 mV allows operation from very low input voltages, which can be very useful in battery-operated systems. Both the VREF and VBI ...
Half-Wave Rectifier
... then reverse-biased, during each cycle of the AC sine-wave. When a single diode is used in a rectifier circuit, current will flow through the circuit only during one-half of the input voltage cycle. For this reason, this rectifier circuit is called a half-wave rectifier. The output of a half-wave re ...
... then reverse-biased, during each cycle of the AC sine-wave. When a single diode is used in a rectifier circuit, current will flow through the circuit only during one-half of the input voltage cycle. For this reason, this rectifier circuit is called a half-wave rectifier. The output of a half-wave re ...
KS2518741883
... rectifier is 10 kHz, the control method applied in Fig. 4(a) generates a new symmetrical carrier that has a frequency of approximately 20 kHz. This is approximately twice the primary-side switching frequency. Alternatively, according to Fig. 4(b), an inverter carrier can be formed based on the duty ...
... rectifier is 10 kHz, the control method applied in Fig. 4(a) generates a new symmetrical carrier that has a frequency of approximately 20 kHz. This is approximately twice the primary-side switching frequency. Alternatively, according to Fig. 4(b), an inverter carrier can be formed based on the duty ...
BDTIC T D A 4 8 6 3
... and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may be endangered. ...
... and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may be endangered. ...
Resistors
... μC is discharged through a 1 kΩ resistor. How long does it take to reduce the capacitor’s charge to 10 μC? Answer: 10 μC = (20 μC) et/0.010 s Take the natural logarithm of both sides: ...
... μC is discharged through a 1 kΩ resistor. How long does it take to reduce the capacitor’s charge to 10 μC? Answer: 10 μC = (20 μC) et/0.010 s Take the natural logarithm of both sides: ...
Methods of Analysis
... 7. If a branch not connected to ground contains a voltage source, the two nodes at both ends are collapsed into a single node called a supernode, and the voltage source and any elements connected in parallel with it removed. However, KCL must still be satisfied at a supernode using the old node volt ...
... 7. If a branch not connected to ground contains a voltage source, the two nodes at both ends are collapsed into a single node called a supernode, and the voltage source and any elements connected in parallel with it removed. However, KCL must still be satisfied at a supernode using the old node volt ...
Ohm`s Law - Parts 1 and 2
... order for it to be measured. If you use your finger to trace the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(b) after it leaves the power supply, you will see that it must go through both the resistor and the ammeter. In contrast, tracing the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(a) you will see that it has two “parallel” p ...
... order for it to be measured. If you use your finger to trace the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(b) after it leaves the power supply, you will see that it must go through both the resistor and the ammeter. In contrast, tracing the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(a) you will see that it has two “parallel” p ...
AN1681: Grounding Techniques
... continuous. Notice that each of the ground planes connects to the others, but only at one place. This is an example of a single-point or star ground. Currents cannot travel haphazardly throughout the ground plane; they are steered through specific paths we create and control. This type of set-up wil ...
... continuous. Notice that each of the ground planes connects to the others, but only at one place. This is an example of a single-point or star ground. Currents cannot travel haphazardly throughout the ground plane; they are steered through specific paths we create and control. This type of set-up wil ...
Biomedical Measurements in Embedded Applications
... Capacitor Parallel metal plates A = area of plate D = distance between plates Apply voltage → separate charges Capacitance = charge stored per volt q = C×V ...
... Capacitor Parallel metal plates A = area of plate D = distance between plates Apply voltage → separate charges Capacitance = charge stored per volt q = C×V ...
Surge protector

A surge protector (or surge suppressor) is an appliance/device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. This article primarily discusses specifications and components relevant to the type of protector that diverts (shorts) a voltage spike to ground; however, there is some coverage of other methods.The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused by lightning. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels, to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, power strips that do not provide surge protection are sometimes erroneously referred to as ""surge protectors"".