Unit 4 Electrical Principles and Technologies
... point in the circuit. Potential difference is commonly referred to as voltage. The standard unit for potential difference is the volt (V), named after Alessandro Volta (1745-1827), who built the first battery. Most electrical devices require potential differences of 1 to 120 V, but higher voltages ar ...
... point in the circuit. Potential difference is commonly referred to as voltage. The standard unit for potential difference is the volt (V), named after Alessandro Volta (1745-1827), who built the first battery. Most electrical devices require potential differences of 1 to 120 V, but higher voltages ar ...
Chapter
... R-L Transients: Storage Cycle ideal inductor (Rl = 0 ) assumes a short-circuit equivalent in a dc network once steady-state conditions have been established For most practical applications, we assume that the storage phase has passed and steady-state conditions have been established once a period ...
... R-L Transients: Storage Cycle ideal inductor (Rl = 0 ) assumes a short-circuit equivalent in a dc network once steady-state conditions have been established For most practical applications, we assume that the storage phase has passed and steady-state conditions have been established once a period ...
MAX4506/MAX4507 Fault-Protected, High-Voltage Signal-Line Protectors General Description
... device clamps the output to 0V. The MAX4506/ MAX4507 provide protection for input signals up to ±36V with the power supplies on and ±40V with the power supplies off. The MAX4506/MAX4507 protect other integrated circuits connected to its output from latching up. Latchup is caused by parasitic SCR(s) ...
... device clamps the output to 0V. The MAX4506/ MAX4507 provide protection for input signals up to ±36V with the power supplies on and ±40V with the power supplies off. The MAX4506/MAX4507 protect other integrated circuits connected to its output from latching up. Latchup is caused by parasitic SCR(s) ...
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from
... E .............................................................. are normally low power transformers used to isolate noise from or to ground electronic circuits. Since a transformer cannot pass DC voltage from primary to secondary, any DC voltage (such as noise) cannot be passed, and the transforme ...
... E .............................................................. are normally low power transformers used to isolate noise from or to ground electronic circuits. Since a transformer cannot pass DC voltage from primary to secondary, any DC voltage (such as noise) cannot be passed, and the transforme ...
1 - LIGO dcc
... b. When no pulse is being applied, M12 is off. The gate drive voltage to M11 and M14 reduces to 2VDC, which is well below threshold. R28 will have ~1mA flowing through it when no pulse is commanded. This results in a power dissipation of ~0.4W, so R28 is sized as a 1 watt part. R28 must also be able ...
... b. When no pulse is being applied, M12 is off. The gate drive voltage to M11 and M14 reduces to 2VDC, which is well below threshold. R28 will have ~1mA flowing through it when no pulse is commanded. This results in a power dissipation of ~0.4W, so R28 is sized as a 1 watt part. R28 must also be able ...
A Home Appliance Recognition System Using the Approach of
... whole house is completely identified. If an appliance is used in more than one place, and these locations are not protected by the same circuit breaker, the load can be registered in both locations without problems. As for example, if a coffee machine is used in the kitchen and in the dining room. I ...
... whole house is completely identified. If an appliance is used in more than one place, and these locations are not protected by the same circuit breaker, the load can be registered in both locations without problems. As for example, if a coffee machine is used in the kitchen and in the dining room. I ...
Multivibrator Circuits using the 555 Timer
... Make sure that the circuit generates the expected signals, namely vC2 triangular wave and vO - square wave. Visualize vR2 and find the value of I2. Visualize simultaneously vO and vC2. Adjust the potentiometers one by one to derive the effect of each of them on the output signals. Set the ...
... Make sure that the circuit generates the expected signals, namely vC2 triangular wave and vO - square wave. Visualize vR2 and find the value of I2. Visualize simultaneously vO and vC2. Adjust the potentiometers one by one to derive the effect of each of them on the output signals. Set the ...
Class B Amplifier
... the transistors T1 and T2 are pre-biased by a small dc current, through the R1, D1, D2, R2 network (Fig II.10.2). Find the values of the dc voltages in the bases of the two transistors from Fig II.10.2, in their bias points (vi=0). Plot vo(t) for vi(t) = 0.3sin2π1000t [V],[Hz]. Plot vo(t) for ...
... the transistors T1 and T2 are pre-biased by a small dc current, through the R1, D1, D2, R2 network (Fig II.10.2). Find the values of the dc voltages in the bases of the two transistors from Fig II.10.2, in their bias points (vi=0). Plot vo(t) for vi(t) = 0.3sin2π1000t [V],[Hz]. Plot vo(t) for ...
Applications of Diodes Word Document
... We can see from the characteristic that below 0.5V, no current flows through the diode. As the voltage increases from 0.5V the current flowing starts to increase, slowly at first and as the voltage reaches 0.7V the increase in current becomes much more significant. Indeed the current can increase mu ...
... We can see from the characteristic that below 0.5V, no current flows through the diode. As the voltage increases from 0.5V the current flowing starts to increase, slowly at first and as the voltage reaches 0.7V the increase in current becomes much more significant. Indeed the current can increase mu ...
Schinkel - TAMU E.C.E. DEPT.
... which uses one tail for the input stage and another for the latch- by the SA is 113fJ/decision when AVi is 5OmV (f[1k = 1GHz, VDD = ing stage, as shown in Fig. 17.7.2. This topology has less stack- 1.2V, P = 113gtW f 1GHz, or 225gW @ 2 GHz), which drops to ing and can therefore operate at lower supp ...
... which uses one tail for the input stage and another for the latch- by the SA is 113fJ/decision when AVi is 5OmV (f[1k = 1GHz, VDD = ing stage, as shown in Fig. 17.7.2. This topology has less stack- 1.2V, P = 113gtW f 1GHz, or 225gW @ 2 GHz), which drops to ing and can therefore operate at lower supp ...
Product Brief TLE7183F Three-Phase Bridge driver IC for MOSFET power
... current applications. Integrated 2-stage charge pump allows ...
... current applications. Integrated 2-stage charge pump allows ...
21676 Select test equipment and test an automotive
... are documented in memo or manual format and are available in the workplace. These requirements include but are not limited to – company specifications and procedures, work instructions, manufacturer specifications, product quality specifications and legislative requirements. Service information may ...
... are documented in memo or manual format and are available in the workplace. These requirements include but are not limited to – company specifications and procedures, work instructions, manufacturer specifications, product quality specifications and legislative requirements. Service information may ...
Ignitron Driver Manual - Wide Bandwidth High Voltage Probes
... This accessory prevents positive voltages of greater than 3 kV from being applied to the trigger unit. Negative voltages are protected by diodes in the unit itself. Such voltages are sometimes applied to the ignitor during a ringing discharge. The current output is reduced by about 50 A when this bo ...
... This accessory prevents positive voltages of greater than 3 kV from being applied to the trigger unit. Negative voltages are protected by diodes in the unit itself. Such voltages are sometimes applied to the ignitor during a ringing discharge. The current output is reduced by about 50 A when this bo ...
Simulation of Multi Converter Unified Power Quality Conditioner for
... In this measured load currents are transformed into synchronous dqo reference frame by using ...
... In this measured load currents are transformed into synchronous dqo reference frame by using ...
Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors
... system shall not utilize gas tubes, spark gaps, silicon avalanche diodes or other components which might short or crowbar the line, thus leading to interruption of normal power flow to or system upset of connected loads. The suppression system shall not incorporate non-field replaceable encapsulated ...
... system shall not utilize gas tubes, spark gaps, silicon avalanche diodes or other components which might short or crowbar the line, thus leading to interruption of normal power flow to or system upset of connected loads. The suppression system shall not incorporate non-field replaceable encapsulated ...
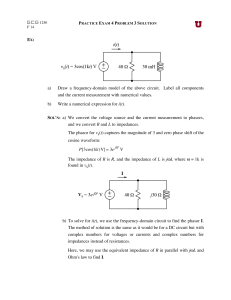
EX: a) Draw a frequency-domain model of the above circuit. Label
... SOL'N: a) We convert the voltage source and the current measurement to phasors, and we convert R and L to impedances. The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
... SOL'N: a) We convert the voltage source and the current measurement to phasors, and we convert R and L to impedances. The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
power system strength - Australian Energy Market Operator
... PEC GENERATION IN WEAK SYSTEMS SHEET: SYSTEM STRENGTH Generation that is interfaced to the network using PEC’s requires a minimum system strength to remain stable and maintain continuous uninterrupted operation. Different types of converters use different strategies to match their output to the freq ...
... PEC GENERATION IN WEAK SYSTEMS SHEET: SYSTEM STRENGTH Generation that is interfaced to the network using PEC’s requires a minimum system strength to remain stable and maintain continuous uninterrupted operation. Different types of converters use different strategies to match their output to the freq ...
Electrical Circuits ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS
... examples, see page 6 in the Ohms law section. Voltage drop is the difference in voltage (pressure) on one side of a load compared to the ...
... examples, see page 6 in the Ohms law section. Voltage drop is the difference in voltage (pressure) on one side of a load compared to the ...
Surge protector

A surge protector (or surge suppressor) is an appliance/device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes. A surge protector attempts to limit the voltage supplied to an electric device by either blocking or by shorting to ground any unwanted voltages above a safe threshold. This article primarily discusses specifications and components relevant to the type of protector that diverts (shorts) a voltage spike to ground; however, there is some coverage of other methods.The terms surge protection device (SPD), or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS), are used to describe electrical devices typically installed in power distribution panels, process control systems, communications systems, and other heavy-duty industrial systems, for the purpose of protecting against electrical surges and spikes, including those caused by lightning. Scaled-down versions of these devices are sometimes installed in residential service entrance electrical panels, to protect equipment in a household from similar hazards.Many power strips have basic surge protection built in; these are typically clearly labeled as such. However, power strips that do not provide surge protection are sometimes erroneously referred to as ""surge protectors"".