(Honors Physics) Universal Law of Gravitation
... Determine each of the following for the spacecraft when it is at point A . a. The total mechanical energy of the spacecraft, assuming that the gravitational potential energy is zero at an infinite distance from the Earth. b. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the spacecraft about the center of ...
... Determine each of the following for the spacecraft when it is at point A . a. The total mechanical energy of the spacecraft, assuming that the gravitational potential energy is zero at an infinite distance from the Earth. b. The magnitude of the angular momentum of the spacecraft about the center of ...
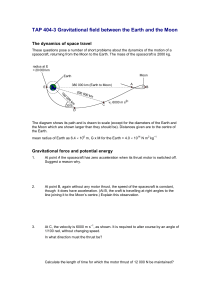
TAP 404-3 Gravitational field between the Earth and the Moon
... The measured distance from D to the Moon is three times the distance from D to the Earth. This means that the gravitational force of attraction on the spacecraft due to the Moon (an inverse square law) would be 1/9 that due to the Earth if the Earth and Moon had the same mass. But the Moon’s mass is ...
... The measured distance from D to the Moon is three times the distance from D to the Earth. This means that the gravitational force of attraction on the spacecraft due to the Moon (an inverse square law) would be 1/9 that due to the Earth if the Earth and Moon had the same mass. But the Moon’s mass is ...
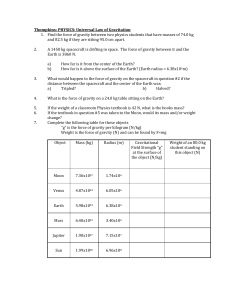
Glossary of Terms Handout
... Acceleration -- Change in velocity. Note that since velocity comprises both direction and magnitude (speed), a change in either direction or speed constitutes acceleration. Asteroids -- Small bodies composed of rock and metal in orbit about the sun. AU -- Astronomical Unit, based on the mean Earth-t ...
... Acceleration -- Change in velocity. Note that since velocity comprises both direction and magnitude (speed), a change in either direction or speed constitutes acceleration. Asteroids -- Small bodies composed of rock and metal in orbit about the sun. AU -- Astronomical Unit, based on the mean Earth-t ...
here
... low topography of Snake River Plain eventually is removed due to sedimentary deposit (density ~2700 kg/m3), what will be the crustal thickness then? Information that might be helpful: Gravitational constant G=6.67384 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 Earth radius 6371 km Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational ...
... low topography of Snake River Plain eventually is removed due to sedimentary deposit (density ~2700 kg/m3), what will be the crustal thickness then? Information that might be helpful: Gravitational constant G=6.67384 × 10-11 m3 kg-1 s-2 Earth radius 6371 km Earth mass 5.972×1024 kg The gravitational ...