CYGNUS CONSTELLATION, the Swan Cygnus is
... Located near Eta Cygni is the X-ray source Cygnus X-1, which is now thought to be caused by a black hole accreting matter in a binary star system. This was the first x-ray source widely believed to be a black hole. There are several other dimmer double and binary stars in Cygnus. 61 Cygni is a binar ...
... Located near Eta Cygni is the X-ray source Cygnus X-1, which is now thought to be caused by a black hole accreting matter in a binary star system. This was the first x-ray source widely believed to be a black hole. There are several other dimmer double and binary stars in Cygnus. 61 Cygni is a binar ...
Nebulae.The Lagoon and Dumbbell Nebulae
... a remnant of a dying star which is approximately 2 times smaller than the Sun. The star is hot and blue with temperature of 85000K (Most of these stars usually turn into red giants. They lose their mass by ejection of the outer gas layers. These layers expand in space, forming a temporary wrap aroun ...
... a remnant of a dying star which is approximately 2 times smaller than the Sun. The star is hot and blue with temperature of 85000K (Most of these stars usually turn into red giants. They lose their mass by ejection of the outer gas layers. These layers expand in space, forming a temporary wrap aroun ...
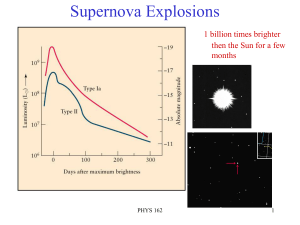
Absolute Magnitudes of Supernovae
... determine the absolute magnitudes of Type Ia supernovae occurring in distant galaxies. Background - During a three-week period in 1997, the Hubble Space Telescope was used to observe a supernova - an exploding star in a distant galaxy. These exploding stars appear suddenly, as they increase rapidly ...
... determine the absolute magnitudes of Type Ia supernovae occurring in distant galaxies. Background - During a three-week period in 1997, the Hubble Space Telescope was used to observe a supernova - an exploding star in a distant galaxy. These exploding stars appear suddenly, as they increase rapidly ...
Investigating Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... called a red giant. The star brightens by a factor of 1,000 to 10,000, and the surface temperature of the extended envelope drops to about 3,000K to 4,000K, giving the star its reddish appearance. A strong wind begins to blow from the star's surface, carrying away most of the hydrogen envelope surro ...
... called a red giant. The star brightens by a factor of 1,000 to 10,000, and the surface temperature of the extended envelope drops to about 3,000K to 4,000K, giving the star its reddish appearance. A strong wind begins to blow from the star's surface, carrying away most of the hydrogen envelope surro ...
File
... hydrogen-rich outer layers to its companion star. *The remains of the massive star could develop an ...
... hydrogen-rich outer layers to its companion star. *The remains of the massive star could develop an ...
Supernovas 10/19
... Fe(26p + 31n) U(92p + 146n) • new nuclei form that have 10-20-50 “too many” neutrons • they Beta decay n p very rapidly now having nuclei with more protons than Iron • Cycle repeats itself – happens very fast “rapid” ...
... Fe(26p + 31n) U(92p + 146n) • new nuclei form that have 10-20-50 “too many” neutrons • they Beta decay n p very rapidly now having nuclei with more protons than Iron • Cycle repeats itself – happens very fast “rapid” ...
Trapezium Fracture
... When we look at this structure whose light has taken 1,500 years to reach us, we are glimpsing a vision of our own Sun and solar system’s creation 4.5 billion years ago. Current theory holds that our own Solar system was created out of a similar massive nebula. Within M42 are thousands of protostar ...
... When we look at this structure whose light has taken 1,500 years to reach us, we are glimpsing a vision of our own Sun and solar system’s creation 4.5 billion years ago. Current theory holds that our own Solar system was created out of a similar massive nebula. Within M42 are thousands of protostar ...
The double-degenerate, super-Chandrasekhar nucleus of the
... The most striking result is the total mass of the system, which amounts to 1.76 M⊙ . This mass is above the Chandrasekhar limit without any ambiguity, even when considering the lowest mass allowed within the confidence range (1.5 M⊙ ). This is, to our knowledge, the first unequivocal determination o ...
... The most striking result is the total mass of the system, which amounts to 1.76 M⊙ . This mass is above the Chandrasekhar limit without any ambiguity, even when considering the lowest mass allowed within the confidence range (1.5 M⊙ ). This is, to our knowledge, the first unequivocal determination o ...
Plotting Supernova Light Curves
... galaxy M100, taken with the Faulkes Telescopes. The software package, SalsaJ will be used to carry out photometry on the supernova in the galaxy and standard star (a star which has already had its magnitude accurately calculated) close to the galaxy. The images you will use were taken on different d ...
... galaxy M100, taken with the Faulkes Telescopes. The software package, SalsaJ will be used to carry out photometry on the supernova in the galaxy and standard star (a star which has already had its magnitude accurately calculated) close to the galaxy. The images you will use were taken on different d ...
Observing Orion
... The Great Hunter. Orion boasted that no animal could defeat him and he boasted that so great was his might and skill as a hunter that he could kill all the animals on the face of the Earth. Gaea, Goddess of Earth, was alarmed at such an unecological and inappropriate statement. She decided that Orio ...
... The Great Hunter. Orion boasted that no animal could defeat him and he boasted that so great was his might and skill as a hunter that he could kill all the animals on the face of the Earth. Gaea, Goddess of Earth, was alarmed at such an unecological and inappropriate statement. She decided that Orio ...
Stellar Explosions
... Material falls onto the white dwarf from its mainsequence companion When enough material has accreted, fusion can reignite very suddenly, burning off the new material Material keeps being transferred to the white dwarf, and the process repeats, as illustrated here ...
... Material falls onto the white dwarf from its mainsequence companion When enough material has accreted, fusion can reignite very suddenly, burning off the new material Material keeps being transferred to the white dwarf, and the process repeats, as illustrated here ...
A Study of the Nature and Representative Features of Supernova
... closely related (Moore D. 2001). A brief description of each type follows. Type Ia Exhibit no hydrogen or helium lines but show a prominent silicon (Si II) line. Believed to be caused by runaway carbon burning in a white dwarf with a binary companion, from which the required matter to cause the expl ...
... closely related (Moore D. 2001). A brief description of each type follows. Type Ia Exhibit no hydrogen or helium lines but show a prominent silicon (Si II) line. Believed to be caused by runaway carbon burning in a white dwarf with a binary companion, from which the required matter to cause the expl ...
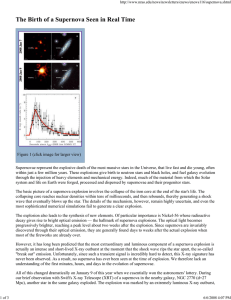
The Birth of a Supernova Seen in Real Time
... Hz-1, a factor of 104 lower than those of typical GRB afterglows, but comparable to the radio luminosities observed for nearby core-collapse SNe. Based on our modeling of the temporal and spectral evolution of the radio emission, we firmly constrain the velocity of the fastest ejecta to be just υ =0 ...
... Hz-1, a factor of 104 lower than those of typical GRB afterglows, but comparable to the radio luminosities observed for nearby core-collapse SNe. Based on our modeling of the temporal and spectral evolution of the radio emission, we firmly constrain the velocity of the fastest ejecta to be just υ =0 ...
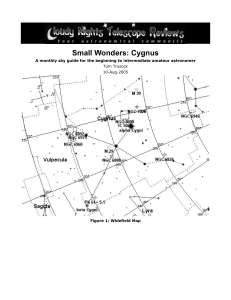
Small Wonders: Cygnus
... Small Wonders: Cygnus A monthly sky guide for the beginning to intermediate amateur astronomer ...
... Small Wonders: Cygnus A monthly sky guide for the beginning to intermediate amateur astronomer ...
The Death of Stars
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
CHP 13
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
... 2. A planetary nebula is a. the expelled outer envelope of a medium mass star. b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can ...
Exam 2
... structures. This diversity holds clues about stellar evolution and about numerous ways in which stars interact with their environments. For example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements ...
... structures. This diversity holds clues about stellar evolution and about numerous ways in which stars interact with their environments. For example, some of the heavy elements (such as carbon, nitrogen and oxygen) that form in a star’s core move into its outer layers. The abundance of these elements ...
Micro_lect20a
... Orionis, one of the brightest stars in the familiar constellation of Orion, the Hunter. 4. The name Betelgeuse is Arabic in origin. As a massive red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life and will soon become a supernova. In this historic image, a bright hotspot is revealed on the star's surf ...
... Orionis, one of the brightest stars in the familiar constellation of Orion, the Hunter. 4. The name Betelgeuse is Arabic in origin. As a massive red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life and will soon become a supernova. In this historic image, a bright hotspot is revealed on the star's surf ...
The Marathon
... As soon as it is possible to see the guide stars for the first objects, begin looking for the first objects. As darkness begins to prevail over twilight, the first objects must be hunted quickly. Do not linger over them, as they will be difficult to find and see at best. The first hour of observing ...
... As soon as it is possible to see the guide stars for the first objects, begin looking for the first objects. As darkness begins to prevail over twilight, the first objects must be hunted quickly. Do not linger over them, as they will be difficult to find and see at best. The first hour of observing ...
Powerpoint
... Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to ...
... Some collapse under their own gravity. Others may be more stable. Magnetic fields and rotation also have some influence. Gravity makes cloud want to ...
Fate of Stars
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
PHYS3380_111615_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - star blinking on and off would create pulse smeared out by time it takes for light to travel from one side of star to other - In other words, an object cannot change its brightness appreciably in an interval shorter than it takes light cross its diameter - therefore size had to be less than 300 km ...
... - star blinking on and off would create pulse smeared out by time it takes for light to travel from one side of star to other - In other words, an object cannot change its brightness appreciably in an interval shorter than it takes light cross its diameter - therefore size had to be less than 300 km ...
March 15 Newsletter
... take a microscope to see any irregularities. It is spinning about its axis thirty times a second, and is so hot that it glows not red hot like metal, not white like the stars, but in X-rays. It has an atmosphere a few inches thick that is violently streaming away into space. Now I am past it. It was ...
... take a microscope to see any irregularities. It is spinning about its axis thirty times a second, and is so hot that it glows not red hot like metal, not white like the stars, but in X-rays. It has an atmosphere a few inches thick that is violently streaming away into space. Now I am past it. It was ...
Document
... Red Dwarfs : Stars with a core mass of .08 to 0.4 solar mass Coolest and dimmest of all MS stars. They remain on MS hundreds of billions of years. When all the H is converted to He fusion ceases, they cool down, moving down and to the right in the H-R diagram. ...
... Red Dwarfs : Stars with a core mass of .08 to 0.4 solar mass Coolest and dimmest of all MS stars. They remain on MS hundreds of billions of years. When all the H is converted to He fusion ceases, they cool down, moving down and to the right in the H-R diagram. ...
Activity: Multiwavelength Bingo - Chandra X
... the most energetic event known in the Universe since the Big Bang. Data from the Hubble Space Telescope and visible light telescopes on the ground show how dark matter (blue) has separated from "normal" matter in the form of hot gas (pink) detected by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
... the most energetic event known in the Universe since the Big Bang. Data from the Hubble Space Telescope and visible light telescopes on the ground show how dark matter (blue) has separated from "normal" matter in the form of hot gas (pink) detected by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. ...
Crab Nebula

The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. It is not, as its name might suggest, in Cancer. The now-current name is due to William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1840 using a 36-inch telescope and produced a drawing that looked somewhat like a crab. Corresponding to a bright supernova recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054, the nebula was observed later by English astronomer John Bevis in 1731. The nebula was the first astronomical object identified with a historical supernova explosion.At an apparent magnitude of 8.4, comparable to that of Saturn's moon Titan, it is not visible to the naked eye but can be made out using binoculars under favourable conditions. The nebula lies in the Perseus Arm of the Milky Way galaxy, at a distance of about 2.0 kiloparsecs (6,500 ly) from Earth. It has a diameter of 3.4 parsecs (11 ly), corresponding to an apparent diameter of some 7 arcminutes, and is expanding at a rate of about 1,500 kilometres per second (930 mi/s), or 0.5% c.At the center of the nebula lies the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star 28–30 kilometres (17–19 mi) across with a spin rate of 30.2 times per second, which emits pulses of radiation from gamma rays to radio waves. At X-ray and gamma ray energies above 30 keV, the Crab is generally the strongest persistent source in the sky, with measured flux extending to above 10 TeV. The nebula's radiation allows for the detailed studying of celestial bodies that occult it. In the 1950s and 1960s, the Sun's corona was mapped from observations of the Crab's radio waves passing through it, and in 2003, the thickness of the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan was measured as it blocked out X-rays from the nebula.