Problems 4 File
... where rmax is the maximum distance from the sun and rmin is the minimum distance from the sun. An astronomical unit (A.U.) is the distance from the earth to the sun - its semimajor axis, and equals 92,956,000 miles. Suppose a planet orbits the Sun in an elliptical orbit such that rmin = 4A.U. and ha ...
... where rmax is the maximum distance from the sun and rmin is the minimum distance from the sun. An astronomical unit (A.U.) is the distance from the earth to the sun - its semimajor axis, and equals 92,956,000 miles. Suppose a planet orbits the Sun in an elliptical orbit such that rmin = 4A.U. and ha ...
1 2 3 4 5 6 Orbital Distance (AU) Orbital Period (Years) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
... This portion of the homework investigates the relationship between how long it takes a planet to orbit a star (orbital period) and how far away that planet is from the star (orbital distance). We will start by investigating an imaginary planetary system that has an average star like the Sun at the c ...
... This portion of the homework investigates the relationship between how long it takes a planet to orbit a star (orbital period) and how far away that planet is from the star (orbital distance). We will start by investigating an imaginary planetary system that has an average star like the Sun at the c ...
The Milky Way
... • Already in the stone and bronze ages, human cultures realized the cyclic nature of motions in the sky. • Monuments dating back to ~ 3000 B.C. show ...
... • Already in the stone and bronze ages, human cultures realized the cyclic nature of motions in the sky. • Monuments dating back to ~ 3000 B.C. show ...
Astronomy Club of Asheville July 2016 Sky Events
... Against the background of the constellation Leo, Jupiter is best viewed early in the evening this month, before it sets in the west. Mars, although rapidly fading, remains in great viewing position this month – high in the sky for most of the night in the constellation Libra. The planet Saturn ...
... Against the background of the constellation Leo, Jupiter is best viewed early in the evening this month, before it sets in the west. Mars, although rapidly fading, remains in great viewing position this month – high in the sky for most of the night in the constellation Libra. The planet Saturn ...
summary - guideposts
... In general, planets that are farther from the sun have lower densities. Even among the terrestrial planets, their uncompressed densities decrease with distance from the sun. The outer solar system beyond the ice line could form large amounts of ice particles made of water, methane, and ammonia. Ices ...
... In general, planets that are farther from the sun have lower densities. Even among the terrestrial planets, their uncompressed densities decrease with distance from the sun. The outer solar system beyond the ice line could form large amounts of ice particles made of water, methane, and ammonia. Ices ...
ppt-file 2.4 MB
... have a better chance." The 47 UMa system intrigues experts because the star has roughly the same mass, age and spectrum as the Sun. Moreover, it hosts two giant gas planets, analogous to Jupiter and Saturn. It is thought that such large planets help to shelter Earth from bombardment by comets and as ...
... have a better chance." The 47 UMa system intrigues experts because the star has roughly the same mass, age and spectrum as the Sun. Moreover, it hosts two giant gas planets, analogous to Jupiter and Saturn. It is thought that such large planets help to shelter Earth from bombardment by comets and as ...
Testing
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU) • Discovery of “hot Jupiters” has forced reexamination of nebular theory ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU) • Discovery of “hot Jupiters” has forced reexamination of nebular theory ...
Exoplanet
... (c) has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. (1) A "dwarf planet" is a celestial body that: (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) Reached hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit, and (d) is not a satellite. (1) All other objects except ...
... (c) has cleared the neighborhood around its orbit. (1) A "dwarf planet" is a celestial body that: (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) Reached hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, (c) has not cleared the neighborhood around its orbit, and (d) is not a satellite. (1) All other objects except ...
Intro To The Solar System
... stars with no visible companion: Evidence for the wobbling motion of the star around the common center of mass of a planetary system Over 100 extrasolar planets detected so far. ...
... stars with no visible companion: Evidence for the wobbling motion of the star around the common center of mass of a planetary system Over 100 extrasolar planets detected so far. ...
The Jovian Planets
... One problem with this idea is that Uranus and Neptune would grow very slowly if they formed where they are presently located. In the 1990’s, an alternate theory was proposed where the cores of Uranus and Neptune formed near Jupiter and Saturn. When Jupiter and Saturn quickly became gas giants, they ...
... One problem with this idea is that Uranus and Neptune would grow very slowly if they formed where they are presently located. In the 1990’s, an alternate theory was proposed where the cores of Uranus and Neptune formed near Jupiter and Saturn. When Jupiter and Saturn quickly became gas giants, they ...
Planets With Detectable Life - International Space Science Institute
... On the other hand Mars (at 1.5 AU) is still within the zone. The problem for Mars is not that it’s too far from the sun, it is too small to sustain the thick atmosphere that would provide the necessary greenhouse effect to keep it warm. An Earth-size planet in the orbit of Mars could be habitable. E ...
... On the other hand Mars (at 1.5 AU) is still within the zone. The problem for Mars is not that it’s too far from the sun, it is too small to sustain the thick atmosphere that would provide the necessary greenhouse effect to keep it warm. An Earth-size planet in the orbit of Mars could be habitable. E ...
Sorting the Solar System - California Academy of Sciences
... group to describe how they categorized it. What characteristics does it share with the others in that category? Could the object fit into more than one category they have created? 5. Different groups will categorize the same object differently. Discuss the differences ...
... group to describe how they categorized it. What characteristics does it share with the others in that category? Could the object fit into more than one category they have created? 5. Different groups will categorize the same object differently. Discuss the differences ...
Across the Universe
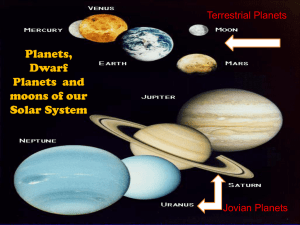
... that is not primarily composed of solid matter. Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are also gas giants. Other terrestrial planets, aside from Earth, are Venus, Mercury, and Mars. Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. The solar system is also made up from other objects including asteroid belts, ...
... that is not primarily composed of solid matter. Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are also gas giants. Other terrestrial planets, aside from Earth, are Venus, Mercury, and Mars. Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. The solar system is also made up from other objects including asteroid belts, ...
Queen`s Observatory Multimedia Guide
... Blue Planet: an IMAX film about the Earth, largely shot from space. Topics: Earth from space; under the oceans; earthquakes; storms; global warming; desertification; life on Earth. Special features: movie trailer. Time: 40 min. ...
... Blue Planet: an IMAX film about the Earth, largely shot from space. Topics: Earth from space; under the oceans; earthquakes; storms; global warming; desertification; life on Earth. Special features: movie trailer. Time: 40 min. ...
The Solar System
... Ammonia, methane, toxic compounds Temp.: -140o C (mean) Moons: 47 Titan, Enceladus, Iapetus, and Mimas Rings: Yes ...
... Ammonia, methane, toxic compounds Temp.: -140o C (mean) Moons: 47 Titan, Enceladus, Iapetus, and Mimas Rings: Yes ...
Objective or GLE: 6.1.A.a: Classify celestial bodies in the solar
... Moon is sometimes classified as a terrestrial "planet" along with Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The gravitational forces between the Earth and the Moon cause some interesting effects. The most obvious is the tides. The Moon's gravitational attraction is stronger on the side of the Earth nearest to ...
... Moon is sometimes classified as a terrestrial "planet" along with Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The gravitational forces between the Earth and the Moon cause some interesting effects. The most obvious is the tides. The Moon's gravitational attraction is stronger on the side of the Earth nearest to ...
Where do we live? How are the other planets compared to Earth?
... the Universe. Our Solar System is a single star system in the Milky Way galaxy which contains other single stars, double stars, star systems, dust & gas. ...
... the Universe. Our Solar System is a single star system in the Milky Way galaxy which contains other single stars, double stars, star systems, dust & gas. ...
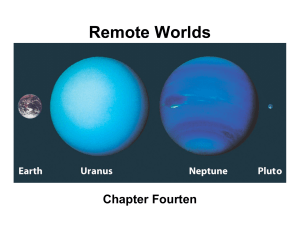
Uranus, Pluto, and the Kuiper Belt
... • Other than those planets seen by naked eyes, Uranus and Neptune were discovered by telescopes • Uranus was recognized as a planet by chance observation in 1781 by William Herschel • Neptune’s position was predicted using Newtonian laws before it was discovered in 1846 – Slight deviations in Uranus ...
... • Other than those planets seen by naked eyes, Uranus and Neptune were discovered by telescopes • Uranus was recognized as a planet by chance observation in 1781 by William Herschel • Neptune’s position was predicted using Newtonian laws before it was discovered in 1846 – Slight deviations in Uranus ...
Uranus: Atmosphere
... • Other than those planets seen by naked eyes, Uranus and Neptune were discovered by telescopes • Uranus was recognized as a planet by chance observation in 1781 by William Herschel • Neptune’s position was predicted using Newtonian laws before it was discovered in 1846 – Slight deviations in Uranus ...
... • Other than those planets seen by naked eyes, Uranus and Neptune were discovered by telescopes • Uranus was recognized as a planet by chance observation in 1781 by William Herschel • Neptune’s position was predicted using Newtonian laws before it was discovered in 1846 – Slight deviations in Uranus ...
Planet formation - problems and future
... - Modern nebular theory suggested that the planets originated in a dense disk, which formed from material in the gas and dust cloud, which collapsed to give the Sun. The density of this disk has to be sufficient to allow the formation of the planets and yet be thin enough for the residual matter to ...
... - Modern nebular theory suggested that the planets originated in a dense disk, which formed from material in the gas and dust cloud, which collapsed to give the Sun. The density of this disk has to be sufficient to allow the formation of the planets and yet be thin enough for the residual matter to ...
What is a Planet
... There are 3 Dwarf Planets in our Solar System; Pluto, Eris (found in the Kupier Belt) and a very large asteroid called Ceres. What is a Planet? – In 2006 the International Astronomical Union define a planet as an object that orbits the sun with sufficient mass and gravity. – Dwarf Planets orbit the ...
... There are 3 Dwarf Planets in our Solar System; Pluto, Eris (found in the Kupier Belt) and a very large asteroid called Ceres. What is a Planet? – In 2006 the International Astronomical Union define a planet as an object that orbits the sun with sufficient mass and gravity. – Dwarf Planets orbit the ...
level 1
... 4. Go to the NASA website for the Jet Propulsion Lab (http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/). Look up the current position of Voyager One. Determine when Voyager One will pass Proxima Centuri and follow its path beyond. ...
... 4. Go to the NASA website for the Jet Propulsion Lab (http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/). Look up the current position of Voyager One. Determine when Voyager One will pass Proxima Centuri and follow its path beyond. ...
The Solar System
... One day on Jupiter takes only 9.8 Earth hours, but it takes 11.86 Earth years for Jupiter to orbit the Sun once ...
... One day on Jupiter takes only 9.8 Earth hours, but it takes 11.86 Earth years for Jupiter to orbit the Sun once ...
Slide 1
... thick, and had not yet been dispelled by the stellar wind. Jovian-jovian gravitational interactions Encounters between planets could expel one, and send the other into an elliptical, near-star orbit. Could terrestrial planets survive the inward migration of Jovian planets? It might be the case that ...
... thick, and had not yet been dispelled by the stellar wind. Jovian-jovian gravitational interactions Encounters between planets could expel one, and send the other into an elliptical, near-star orbit. Could terrestrial planets survive the inward migration of Jovian planets? It might be the case that ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.