PSI AP Physics 1 Gravitation
... 6. A planet is discovered to orbit around a star in the galaxy Andromeda, with the same orbital diameter as the Earth around our Sun. If that star has 4 times the mass of our Sun, what will the period of revolution of that new planet be, compared to the Earth's orbital period? A) one-fourth as much ...
... 6. A planet is discovered to orbit around a star in the galaxy Andromeda, with the same orbital diameter as the Earth around our Sun. If that star has 4 times the mass of our Sun, what will the period of revolution of that new planet be, compared to the Earth's orbital period? A) one-fourth as much ...
HW: PSI Gravity Problems Worksheet With Answers
... 6. A planet is discovered to orbit around a star in the galaxy Andromeda, with the same orbital diameter as the Earth around our Sun. If that star has 4 times the mass of our Sun, what will the period of revolution of that new planet be, compared to the Earth's orbital period? A) one-fourth as much ...
... 6. A planet is discovered to orbit around a star in the galaxy Andromeda, with the same orbital diameter as the Earth around our Sun. If that star has 4 times the mass of our Sun, what will the period of revolution of that new planet be, compared to the Earth's orbital period? A) one-fourth as much ...
The Development Of Astronomy
... Platonic Solid Model – Kepler believed God must have had some geometric design for placing the six planets (Uranus and Neptune were yet to be discovered) at particular distances from the Sun. A sudden revelation led Kepler to consider that the reason there is only six planets was because there were ...
... Platonic Solid Model – Kepler believed God must have had some geometric design for placing the six planets (Uranus and Neptune were yet to be discovered) at particular distances from the Sun. A sudden revelation led Kepler to consider that the reason there is only six planets was because there were ...
We see apparent retrograde motion when we pass by a
... parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe With rare exceptions such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected the correct explanation (1) because they did n ...
... parallax could mean one of two things: 1. Stars are so far away that stellar parallax is too small to notice with the naked eye 2. Earth does not orbit Sun; it is the center of the universe With rare exceptions such as Aristarchus, the Greeks rejected the correct explanation (1) because they did n ...
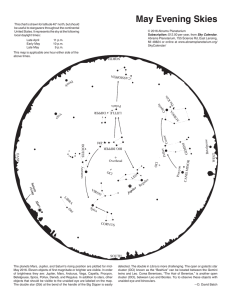
Monday, March 3
... • Revealing great, unusual, and remarkable spectacles, opening these to the consideration of every man, and especially of philosophers and astronomers; • As observed by Galileo Galilei, gentleman of Florence, Professor of Mathematics in the University of Padua • With the aid of a Spyglass recently i ...
... • Revealing great, unusual, and remarkable spectacles, opening these to the consideration of every man, and especially of philosophers and astronomers; • As observed by Galileo Galilei, gentleman of Florence, Professor of Mathematics in the University of Padua • With the aid of a Spyglass recently i ...
History of Astronomy
... I. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse II. The orbital speed of a planet varies so that a line joining the Sun and the planet will sweep out equal areas in equal time intervals III.The amount of time a planet takes to orbit the Sun is related to its orbit’s siz ...
... I. Planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse II. The orbital speed of a planet varies so that a line joining the Sun and the planet will sweep out equal areas in equal time intervals III.The amount of time a planet takes to orbit the Sun is related to its orbit’s siz ...
3536
... times or a super-Earth planet). For an Earth-like planet, Proxima b’s slow rotation rate should not have a significant impact on magnetic field generation, as this is mostly influenced by the internal heat flux that controls the mantle convection rather than a dynamo [2,3] (Christensen & Aubert 2006 ...
... times or a super-Earth planet). For an Earth-like planet, Proxima b’s slow rotation rate should not have a significant impact on magnetic field generation, as this is mostly influenced by the internal heat flux that controls the mantle convection rather than a dynamo [2,3] (Christensen & Aubert 2006 ...
Jan 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... awesome. He was able to show us how to understand a very useful scientific formula on how to measure the distance of stars and we didn’t even have to take an advanced physics or astronomy class. He was a great speaker and I hope he will come back in the future. ...
... awesome. He was able to show us how to understand a very useful scientific formula on how to measure the distance of stars and we didn’t even have to take an advanced physics or astronomy class. He was a great speaker and I hope he will come back in the future. ...
Life in the Universe
... maybe one or two) are gaseous giants and are unlikely to have surface life. ...
... maybe one or two) are gaseous giants and are unlikely to have surface life. ...
ppt file
... so that, e.g., the pattern formed by material in 2:1 is one clump 3:2 is two clumps 4:3 and 5:3 is three clumps which follow(s) the planet around its orbit Detailed dynamics: resonant forces cause resonant argument to librate ...
... so that, e.g., the pattern formed by material in 2:1 is one clump 3:2 is two clumps 4:3 and 5:3 is three clumps which follow(s) the planet around its orbit Detailed dynamics: resonant forces cause resonant argument to librate ...
Recap: High Mass Stars
... • The outer layers of the sun will expand, consuming the inner planets • Sun will become a Red Giant ...
... • The outer layers of the sun will expand, consuming the inner planets • Sun will become a Red Giant ...
The Scientific Method
... remarkably, Galileo observed it again the following night when he noted that the two stars appeared to be further apart. How close he was at that point to discovering that one of the stars was the planet Neptune. Neptune was to be recorded several more times, without being recognized as a planet, ov ...
... remarkably, Galileo observed it again the following night when he noted that the two stars appeared to be further apart. How close he was at that point to discovering that one of the stars was the planet Neptune. Neptune was to be recorded several more times, without being recognized as a planet, ov ...
Review Astronomy - Cowley`s Earth Systems
... d. Scientists are not really interested in whether or not there is life on Mars 3. In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were ...
... d. Scientists are not really interested in whether or not there is life on Mars 3. In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were ...
Chapter 29: Our Solar System
... circle. The two points are called the foci (sing. focus). The major axis is the line that runs through both foci; it is the maximum diameter of the ellipse, as illustrated in Figure 29-2. You will experiment with the foci and shapes of ellipses in the MiniLab on this page. Each planet’s elliptical o ...
... circle. The two points are called the foci (sing. focus). The major axis is the line that runs through both foci; it is the maximum diameter of the ellipse, as illustrated in Figure 29-2. You will experiment with the foci and shapes of ellipses in the MiniLab on this page. Each planet’s elliptical o ...
Neither Star nor Planet - Max-Planck
... Stars are formed when individual regions in the interior of a large cloud of gas and dust contract under the effects of gravity. The core of such a cloud rotates and forms a disk. The material in the cloud center becomes more and more compressed until hydrogen fusion begins. The young star is then s ...
... Stars are formed when individual regions in the interior of a large cloud of gas and dust contract under the effects of gravity. The core of such a cloud rotates and forms a disk. The material in the cloud center becomes more and more compressed until hydrogen fusion begins. The young star is then s ...
RTF - Cosmic Adventures Traveling Planetarium
... (energy) through nuclear fusion and rotates on its axis, but it remains in an essentially constant position. A planet rotates on its axis and orbits a star. A moon rotates on its axis and orbits a planet while the planet orbits its star. Note: The above is a very simple and broad definition for plan ...
... (energy) through nuclear fusion and rotates on its axis, but it remains in an essentially constant position. A planet rotates on its axis and orbits a star. A moon rotates on its axis and orbits a planet while the planet orbits its star. Note: The above is a very simple and broad definition for plan ...
Planetary Evolution - Lincoln-Sudbury Regional High School
... see the heat released from the Earth’s still hot mantle in volcanic activity. There is another particularly clear piece of evidence for this: ...
... see the heat released from the Earth’s still hot mantle in volcanic activity. There is another particularly clear piece of evidence for this: ...
Asteroids and Comets
... billions to trillions of comets. It has not been directly observed. they have orbital periods of 100,000's to millions of years. However, their orbits are so elliptical that they spend only 2 to 4 years in the inner part of the solar system where the planets are and most of their time at 50,000 to 1 ...
... billions to trillions of comets. It has not been directly observed. they have orbital periods of 100,000's to millions of years. However, their orbits are so elliptical that they spend only 2 to 4 years in the inner part of the solar system where the planets are and most of their time at 50,000 to 1 ...
Jupiter`s Galilean Moons
... explain this fairly clearly for the tidal interaction between the earth and the moon. The same considerations apply to all the other systems mentioned, and also to binary stars that orbit each other at distances of only several stellar radii. radii The ultimate result of all the tidal interactions, ...
... explain this fairly clearly for the tidal interaction between the earth and the moon. The same considerations apply to all the other systems mentioned, and also to binary stars that orbit each other at distances of only several stellar radii. radii The ultimate result of all the tidal interactions, ...
SPECTRAL WORKSHOP
... Show a solar absorption spectra, and ask if the student can identify the element corresponding to the dark lines. These correspond to Helium, which was first discovered on the sun (hence the name – from the Greek 'helios'). ...
... Show a solar absorption spectra, and ask if the student can identify the element corresponding to the dark lines. These correspond to Helium, which was first discovered on the sun (hence the name – from the Greek 'helios'). ...
Celestial Objects
... Planets – Today, the term planet is defined as an object in orbit around a star. However, this ancient Greek word originally meant “wandering star”, because they appeared to shift amongst the stars of the zodiac constellations. ...
... Planets – Today, the term planet is defined as an object in orbit around a star. However, this ancient Greek word originally meant “wandering star”, because they appeared to shift amongst the stars of the zodiac constellations. ...
Definition of planet

The definition of planet, since the word was coined by the ancient Greeks, has included within its scope a wide range of celestial bodies. Greek astronomers employed the term asteres planetai (ἀστέρες πλανῆται), ""wandering stars"", for star-like objects which apparently moved over the sky. Over the millennia, the term has included a variety of different objects, from the Sun and the Moon to satellites and asteroids.By the end of the 19th century the word planet, though it had yet to be defined, had become a working term applied only to a small set of objects in the Solar System. After 1992, however, astronomers began to discover many additional objects beyond the orbit of Neptune, as well as hundreds of objects orbiting other stars. These discoveries not only increased the number of potential planets, but also expanded their variety and peculiarity. Some were nearly large enough to be stars, while others were smaller than Earth's moon. These discoveries challenged long-perceived notions of what a planet could be.The issue of a clear definition for planet came to a head in 2005 with the discovery of the trans-Neptunian object Eris, a body more massive than the smallest then-accepted planet, Pluto. In its 2006 response, the International Astronomical Union (IAU), recognised by astronomers as the world body responsible for resolving issues of nomenclature, released its decision on the matter. This definition, which applies only to the Solar System, states that a planet is a body that orbits the Sun, is massive enough for its own gravity to make it round, and has ""cleared its neighbourhood"" of smaller objects around its orbit. Under this new definition, Pluto and the other trans-Neptunian objects do not qualify as planets. The IAU's decision has not resolved all controversies, and while many scientists have accepted the definition, some in the astronomical community have rejected it outright.