Quasars
... lot of ultraviolet excess. • One of them, 3C273 had its position very accurately measured by C. Hazard and co-workers, using lunar occultations. • In 1962, M. Schmidt obtained a spectrum of this “object", which showed a large redshift of 0.158, indicative of being very far away according to Hubble‟s ...
... lot of ultraviolet excess. • One of them, 3C273 had its position very accurately measured by C. Hazard and co-workers, using lunar occultations. • In 1962, M. Schmidt obtained a spectrum of this “object", which showed a large redshift of 0.158, indicative of being very far away according to Hubble‟s ...
The Nature of SN 1961V - University of Oklahoma
... Our recent VLBI experiment (§2.2) allows us to make a more definitive radio analysis than previously possible with resolution-limited VLA studies. The VLBI non-detection of SN 1961V indicates that its radio emitting region is larger than the VLBI resolution element; thus the minimum diameter of SN 1 ...
... Our recent VLBI experiment (§2.2) allows us to make a more definitive radio analysis than previously possible with resolution-limited VLA studies. The VLBI non-detection of SN 1961V indicates that its radio emitting region is larger than the VLBI resolution element; thus the minimum diameter of SN 1 ...
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
... Potential Energy is transformed into kinetic energy, which gets thermalised, so the temperature goes up. This phase lasts a relatively short time. When the cloud is hot enough, the gas is ionised and OPACITY sets in. When that is the case, the gas finds it harder to lose energy, and becomes hotter e ...
Evolution and nucleosynthesis of extremely metal
... while the relative abundance distribution is not significantly altered. The results from this calculation show a better match to the observed Sr abundance, within a factor of 4, while still producing too much Ba by a factor of at least 18. In this case, Fe is unchanged. The composition of HE 1327-23 ...
... while the relative abundance distribution is not significantly altered. The results from this calculation show a better match to the observed Sr abundance, within a factor of 4, while still producing too much Ba by a factor of at least 18. In this case, Fe is unchanged. The composition of HE 1327-23 ...
Astronomy 535 Stellar Structure Evolution
... Motivation for studying stellar evolution • Evolution of ISM, IGM, gas fraction, composition, star formation, populations, galaxies, baryonic matter in general profoundly depends on stellar evolution • Fits of models to observations by means of free parameters is standard procedure, but gives unrel ...
... Motivation for studying stellar evolution • Evolution of ISM, IGM, gas fraction, composition, star formation, populations, galaxies, baryonic matter in general profoundly depends on stellar evolution • Fits of models to observations by means of free parameters is standard procedure, but gives unrel ...
The End of the Dark Ages
... The effects of a top-heavy IMF on the ionization of the surrounding gas and intergalactic medium are spectacular. Fig. 1 shows a comparison between the final stages (100 Myr after the source turn on) of the I-front evolution for a Larson (upper panel) and a Salpeter (bottom) IMF. The source stellar ...
... The effects of a top-heavy IMF on the ionization of the surrounding gas and intergalactic medium are spectacular. Fig. 1 shows a comparison between the final stages (100 Myr after the source turn on) of the I-front evolution for a Larson (upper panel) and a Salpeter (bottom) IMF. The source stellar ...
Project 8 : Stellar Spectra: Classification
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
... Absorption lines occur when an electron absorbs energy from the spectrum to move up the energy levels in the atom. Since hydrogen has only one electron, this electron is usually in the ground state. But as the temperature rises, the average electron gains m ...
Activities
... not at the center of the ellipse, but at the focus. That means a planet on a highly eccentric orbit can be close to the Sun sometimes, and very far at other times. • Second Law: As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. This means that when the planet is closer to ...
... not at the center of the ellipse, but at the focus. That means a planet on a highly eccentric orbit can be close to the Sun sometimes, and very far at other times. • Second Law: As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. This means that when the planet is closer to ...
Stellar radii from long-baseline interferometry
... (mas) apart on the sky, in the K band (λ = 2.2 µm). As a comparison, the largest solartype star angularly is α Cen A, with θ ≈ 8.5 mas, i.e. more than six times smaller than the resolution limit of the telescope. Now let’s consider the PSF of an interferometer of two 10 m telescopes separated by a b ...
... (mas) apart on the sky, in the K band (λ = 2.2 µm). As a comparison, the largest solartype star angularly is α Cen A, with θ ≈ 8.5 mas, i.e. more than six times smaller than the resolution limit of the telescope. Now let’s consider the PSF of an interferometer of two 10 m telescopes separated by a b ...
A dust ring around Epsilon Eridani: analogue to the young Solar
... explain the reduced emission close to ǫ Eri. The total mass of the ǫ Eri ring depends on the presence of gas, but is at least ∼ 0.01 M⊕ , and possibly as high as 0.4 M⊕ . This range encompasses the present-day mass of comets in the Kuiper Belt, ≈ 0.04–0.3 M⊕ between 30 and 100 AU (Backman, Dasgupta ...
... explain the reduced emission close to ǫ Eri. The total mass of the ǫ Eri ring depends on the presence of gas, but is at least ∼ 0.01 M⊕ , and possibly as high as 0.4 M⊕ . This range encompasses the present-day mass of comets in the Kuiper Belt, ≈ 0.04–0.3 M⊕ between 30 and 100 AU (Backman, Dasgupta ...
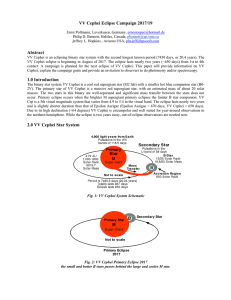
VV Cephei Eclipse Campaign 2017/19
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
... The binary star system VV Cephei is a cool red supergiant star (M2 Iab) with a smaller hot blue companion star (B02V). The primary star of VV Cephei is a massive red supergiant star, with an estimated mass of about 20 solar masses. The two stars in this binary are well-separated and significant mass ...
L69 CONVERSION OF NEUTRON STARS TO
... capable of releasing a total energy of a few times 1053 ergs. Many cosmological models for GRBs have been proposed. Among the most popular is the merging of two neutron stars (or a neutron star and a black hole) in a binary system (Paczyński 1998). Recent results (Janka & Ruffert 1996) within this ...
... capable of releasing a total energy of a few times 1053 ergs. Many cosmological models for GRBs have been proposed. Among the most popular is the merging of two neutron stars (or a neutron star and a black hole) in a binary system (Paczyński 1998). Recent results (Janka & Ruffert 1996) within this ...
Lecture Topics 1023
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
Formation of high-field magnetic white dwarfs from common envelopes
... at the radiative-convective boundary may not be able to produce strongly magnetized material in the vicinity of the WD. First, as shown below, a robust upper limit to the magnitude of the envelope dynamo generated field is a few times 104 G. To explain megagauss fields at the WD surface, this requir ...
... at the radiative-convective boundary may not be able to produce strongly magnetized material in the vicinity of the WD. First, as shown below, a robust upper limit to the magnitude of the envelope dynamo generated field is a few times 104 G. To explain megagauss fields at the WD surface, this requir ...
A historical perspective on the discovery of neutron stars
... astronomers. The "star" remained visible in daytime for 23 days and disappeared from the night sky after two years. ...
... astronomers. The "star" remained visible in daytime for 23 days and disappeared from the night sky after two years. ...
San Diego Astronomy Association CONTENTS
... sequence, into a red giant with a core containing carbon, helium, and hydrogen concentric shells, and through the planetary nebula ejection of the outer atmosphere to the white dwarf carbon core. In the common envelope phase of a binary system when the first heavier star reaches the planetary nebula ...
... sequence, into a red giant with a core containing carbon, helium, and hydrogen concentric shells, and through the planetary nebula ejection of the outer atmosphere to the white dwarf carbon core. In the common envelope phase of a binary system when the first heavier star reaches the planetary nebula ...
Asteroseismic constraints on Asymmetric Dark Matter: Light particles
... parameters near the star, by the galactic orbital velocity v∗ of the object and by the escape velocity at the surface of the target vesc [31]. The two stars studied here besides the Sun are located close to it, thus local DM halo parameters are used for all models, namely a density ρχ = 0.38 GeV/cm3 ...
... parameters near the star, by the galactic orbital velocity v∗ of the object and by the escape velocity at the surface of the target vesc [31]. The two stars studied here besides the Sun are located close to it, thus local DM halo parameters are used for all models, namely a density ρχ = 0.38 GeV/cm3 ...
Introduction - Cambridge University Press
... The starting point for the formation of a star is a cloud of cold gas, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with traces of heavier elements (usually referred to as metals). The cloud collapses due to its own gravity, and as gravitational potential energy is released and converted into heat, th ...
... The starting point for the formation of a star is a cloud of cold gas, composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, with traces of heavier elements (usually referred to as metals). The cloud collapses due to its own gravity, and as gravitational potential energy is released and converted into heat, th ...
13.1 Introduction 13.2 The Red Giant Branch
... phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stellar surface via radiation pressure (Lecture 9.2.2) on atoms and grains. Gr ...
... phase is mass loss. As the stellar luminosity and radius increase while a star evolves along the giant branch, the envelope becomes loosely bound and it is relatively easy for the large photon flux to remove mass from the stellar surface via radiation pressure (Lecture 9.2.2) on atoms and grains. Gr ...
2. The Anatomy of Stellar Life and Death
... Over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has grown hotter and slightly larger, and is now more luminous in response to this effect; the same is true for more massive stars. As the fuel is consumed the luminosity slowly increases. The effect is quite subtle in comparison to later changes, but over the ...
... Over the last 4.5 billion years the Sun has grown hotter and slightly larger, and is now more luminous in response to this effect; the same is true for more massive stars. As the fuel is consumed the luminosity slowly increases. The effect is quite subtle in comparison to later changes, but over the ...
Local group
... Mtotal=Mgas+Mstar=constant (Mbaryons) ; Mhmass of heavy elements in gas =ZMgas dM'stars =total mass made into stars, dM''stars =amount of mass instantaneously returned to ISM enriched with metals dMstars =dM'stars -dM''stars net matter turned into stars define y as the yield of heavy elements- yMsta ...
... Mtotal=Mgas+Mstar=constant (Mbaryons) ; Mhmass of heavy elements in gas =ZMgas dM'stars =total mass made into stars, dM''stars =amount of mass instantaneously returned to ISM enriched with metals dMstars =dM'stars -dM''stars net matter turned into stars define y as the yield of heavy elements- yMsta ...
TDE in the XMM-Newton slew survey
... 7 events found in slew survey, 3 are well monitored Mix of soft and soft+hard – don’t know how many just hard Index=5/3 over long-term curve but highly variable in detail. Unsure if variability intrinsic or ionised absorption or both. At least one found in E+A galaxy Hard emission most likely from C ...
... 7 events found in slew survey, 3 are well monitored Mix of soft and soft+hard – don’t know how many just hard Index=5/3 over long-term curve but highly variable in detail. Unsure if variability intrinsic or ionised absorption or both. At least one found in E+A galaxy Hard emission most likely from C ...
Cygnus X-1
Cygnus X-1 (abbreviated Cyg X-1) is a well-known galactic X-ray source, thought to be a black hole, in the constellation Cygnus. It was discovered in 1964 during a rocket flight and is one of the strongest X-ray sources seen from Earth, producing a peak X-ray flux density of 6977229999999999999♠2.3×10−23 Wm−2 Hz−1 (7003230000000000000♠2.3×103 Jansky). Cygnus X-1 was the first X-ray source widely accepted to be a black hole and it remains among the most studied astronomical objects in its class. The compact object is now estimated to have a mass about 14.8 times the mass of the Sun and has been shown to be too small to be any known kind of normal star, or other likely object besides a black hole. If so, the radius of its event horizon is about 7004440000000000000♠44 km.Cygnus X-1 belongs to a high-mass X-ray binary system about 7019574266339685654♠6070 ly from the Sun that includes a blue supergiant variable star designated HDE 226868 which it orbits at about 0.2 AU, or 20% of the distance from the Earth to the Sun. A stellar wind from the star provides material for an accretion disk around the X-ray source. Matter in the inner disk is heated to millions of degrees, generating the observed X-rays. A pair of jets, arranged perpendicular to the disk, are carrying part of the energy of the infalling material away into interstellar space.This system may belong to a stellar association called Cygnus OB3, which would mean that Cygnus X-1 is about five million years old and formed from a progenitor star that had more than 7001400000000000000♠40 solar masses. The majority of the star's mass was shed, most likely as a stellar wind. If this star had then exploded as a supernova, the resulting force would most likely have ejected the remnant from the system. Hence the star may have instead collapsed directly into a black hole.Cygnus X-1 was the subject of a friendly scientific wager between physicists Stephen Hawking and Kip Thorne in 1975, with Hawking betting that it was not a black hole. He conceded the bet in 1990 after observational data had strengthened the case that there was indeed a black hole in the system. This hypothesis has not been confirmed due to a lack of direct observation but has generally been accepted from indirect evidence.