Astronomical Ideas – Math Review practice problems 1. The radius
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
... 1. The radius of the Sun is 100 times the Earth’s radius. What is the volume of the Sun, relative to the volume of the Earth? 2. How many days does it take to travel 9.46 * 1012 km at a speed of 3 * 108 m/sec? 3. If you replaced the Earth with a planet of the same mass but three times larger in radi ...
Chapter 3 - The Solar System
... Chapter 3 - The Solar System Section 1 – The Solar System A. Ideas about the night sky have changed over time. 1. Earth - centered model – early Greeks thought planets, Sun, Moon, and stars rotated around Earth. 2. Sun – centered model – Nicholas Copernicus and Galileo Galilei observed that the Moon ...
... Chapter 3 - The Solar System Section 1 – The Solar System A. Ideas about the night sky have changed over time. 1. Earth - centered model – early Greeks thought planets, Sun, Moon, and stars rotated around Earth. 2. Sun – centered model – Nicholas Copernicus and Galileo Galilei observed that the Moon ...
The Sun
... Relative Sizes: Asteroids are the largest objects, but comets and asteroids are often similar in size. Meteoroids are much smaller than either comets or asteroids. ...
... Relative Sizes: Asteroids are the largest objects, but comets and asteroids are often similar in size. Meteoroids are much smaller than either comets or asteroids. ...
The Milky Way
... “an object in the Solar System that orbits the Sun and is not a satellite of a planet or other celestial body. It must be spherical (or nearly so) in shape.” ...
... “an object in the Solar System that orbits the Sun and is not a satellite of a planet or other celestial body. It must be spherical (or nearly so) in shape.” ...
Planets and other Objects in Space
... known planet that supports life. Its atmosphere absorbs part of the solar energy to keep the planet at a temperature suitable to support life. • Mars, fourth planet from the Sun, is called the Red Planet because its soil is dark red‐brown. Mars has two moons and the largest volcano in the solar s ...
... known planet that supports life. Its atmosphere absorbs part of the solar energy to keep the planet at a temperature suitable to support life. • Mars, fourth planet from the Sun, is called the Red Planet because its soil is dark red‐brown. Mars has two moons and the largest volcano in the solar s ...
Greek and Hellenistic Astronomy
... The inner planets (Mercury and Venus) were observed to exhibit similar movements with respect to the Sun. ...
... The inner planets (Mercury and Venus) were observed to exhibit similar movements with respect to the Sun. ...
Written by Abby Cessna Eight Planets The eight planets in our Solar
... called terrestrial planets because they have a solid surface and are similar to Earth. These planets are composed of heavy metal, such as iron and nickel and have few or no moons. Mercury, the smallest planet, has no moons and is comprised mostly of iron and nickel. It is one of the densest planets ...
... called terrestrial planets because they have a solid surface and are similar to Earth. These planets are composed of heavy metal, such as iron and nickel and have few or no moons. Mercury, the smallest planet, has no moons and is comprised mostly of iron and nickel. It is one of the densest planets ...
Name That Planet
... Click after the blue line. Press the Backspace Key one time to erase the blue line. Type the answer. The space will grow as you type. Your answer will be colored blue. ...
... Click after the blue line. Press the Backspace Key one time to erase the blue line. Type the answer. The space will grow as you type. Your answer will be colored blue. ...
Solar System – Odds & Ends - Saint Paul Public Schools
... Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto are planets. No scientific basis. 2) Historical plus: Mercury through Pluto are planets, as is any newly discovered object larger than Pluto. But why is Pluto’s size the cutoff? ...
... Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto are planets. No scientific basis. 2) Historical plus: Mercury through Pluto are planets, as is any newly discovered object larger than Pluto. But why is Pluto’s size the cutoff? ...
The Planets - Cobb Learning
... • outer planets :The planets that are much farther from the sun: –Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune –Outer planets are larger and composed of gas…. Gas giantd ...
... • outer planets :The planets that are much farther from the sun: –Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune –Outer planets are larger and composed of gas…. Gas giantd ...
Instruction for making planet booklet
... This book has been designed to be printed out double sided, but you can make two separate booklets, one of the rock planets and one of the gas planets. For the double sided booklet, Select page 2,3 and print double sided. ...
... This book has been designed to be printed out double sided, but you can make two separate booklets, one of the rock planets and one of the gas planets. For the double sided booklet, Select page 2,3 and print double sided. ...
How is the pace of the course? Next: Introduction to the Solar
... It rises East and sets West It rises West and sets East It rises East and sets South It rises South and sets North It rises West and sets South ...
... It rises East and sets West It rises West and sets East It rises East and sets South It rises South and sets North It rises West and sets South ...
The Solar System 2003
... A mutual attraction, a gravitational force acts among all of them and governs their motion. The Sun is by far the most massive, therefore other bodies orbit around it. The closer to the Sun a body is, the higher its orbital speed is. Orbital trajectories of planets, an astaroid and a comet are paint ...
... A mutual attraction, a gravitational force acts among all of them and governs their motion. The Sun is by far the most massive, therefore other bodies orbit around it. The closer to the Sun a body is, the higher its orbital speed is. Orbital trajectories of planets, an astaroid and a comet are paint ...
Spring `03 final exam study guide
... 20. What is a blink comparator and for what is it used? 21. Is it probable that Pluto is a former moon of Neptune? Why or why not? 22. Draw a sketch of a comet, labeling its coma, nucleus, and tail. 23. Please distinguish among meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites. 24. Describe the nature and types o ...
... 20. What is a blink comparator and for what is it used? 21. Is it probable that Pluto is a former moon of Neptune? Why or why not? 22. Draw a sketch of a comet, labeling its coma, nucleus, and tail. 23. Please distinguish among meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites. 24. Describe the nature and types o ...
Planets of the Solar System Section 2 Kepler`s Laws, continued
... • Aristotle suggested an Earth-centered, or geocentric, model of the solar system. In this model, the sun, the stars, and the planets revolved around Earth. • Ptolemy proposed changes to Aristotle’s model. He thought that planets moved in small circles, called epicycles, as they revolved in larger c ...
... • Aristotle suggested an Earth-centered, or geocentric, model of the solar system. In this model, the sun, the stars, and the planets revolved around Earth. • Ptolemy proposed changes to Aristotle’s model. He thought that planets moved in small circles, called epicycles, as they revolved in larger c ...
Planets Study guide
... Formative 1: The Planets Study Guide Date of quiz: ______________________ Identify if each statement below is True or False. 1. _________ A planet must have a moon to be considered a classical planet 2. _________ Pluto is a dwarf planet because it is too small. 3. _________ A dwarf planet does not c ...
... Formative 1: The Planets Study Guide Date of quiz: ______________________ Identify if each statement below is True or False. 1. _________ A planet must have a moon to be considered a classical planet 2. _________ Pluto is a dwarf planet because it is too small. 3. _________ A dwarf planet does not c ...
File
... Tycho Brahe: built special instruments and influenced another scientist (Kepler) to determine the true shape of orbits Galileo Galilei: Observed moons orbiting Jupiter using his telescope Johannes Kepler: Successfully described planetary motion Formulated ...
... Tycho Brahe: built special instruments and influenced another scientist (Kepler) to determine the true shape of orbits Galileo Galilei: Observed moons orbiting Jupiter using his telescope Johannes Kepler: Successfully described planetary motion Formulated ...
Formation of the Solar System
... Composition of the planets (inner and outer) Motion of planets and sun Law of gravity Existence of solar wind Asteroids – a broken or unformed planet? What appear to be accretion disks have been observed around protostars (Hubble photos of the Horsehead nebula) We are always learning more. ...
... Composition of the planets (inner and outer) Motion of planets and sun Law of gravity Existence of solar wind Asteroids – a broken or unformed planet? What appear to be accretion disks have been observed around protostars (Hubble photos of the Horsehead nebula) We are always learning more. ...
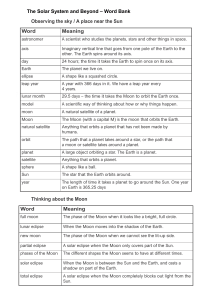
Word Meaning The Solar System and Beyond – Word Bank
... Imaginary vertical line that goes from one pole of the Earth to the other. The Earth spins around its axis. ...
... Imaginary vertical line that goes from one pole of the Earth to the other. The Earth spins around its axis. ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.