P - Bakers Math Class
... A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. A conjecture is a statement that is being proposed to be true. Once a proof of a conjecture is found, it becomes a theorem. It may turn out to be false. ...
... A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. A conjecture is a statement that is being proposed to be true. Once a proof of a conjecture is found, it becomes a theorem. It may turn out to be false. ...
x - Koc Lab
... A lemma is a ‘helping theorem’ or a result which is needed to prove a theorem. A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. A conjecture is a statement that is being proposed to be true. Once a proof of a conjecture ...
... A lemma is a ‘helping theorem’ or a result which is needed to prove a theorem. A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. A conjecture is a statement that is being proposed to be true. Once a proof of a conjecture ...
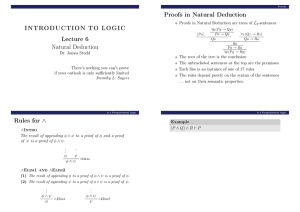
INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC Lecture 6 Natural Deduction Proofs in
... Proofs in Natural Deduction Proofs in Natural Deduction are trees of L2 -sentences ...
... Proofs in Natural Deduction Proofs in Natural Deduction are trees of L2 -sentences ...
Keys GEO Openers 4-15
... For all numbers a & b, if a = b, then b = a. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b and b = c, then a = c. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c & a – c = b – c. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b, then a * c = b * c & a ÷ c = b ÷ c. For all numbers a & b, if a = b, then a may be replac ...
... For all numbers a & b, if a = b, then b = a. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b and b = c, then a = c. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c & a – c = b – c. For all numbers a, b & c, if a = b, then a * c = b * c & a ÷ c = b ÷ c. For all numbers a & b, if a = b, then a may be replac ...
A Note on Bootstrapping Intuitionistic Bounded Arithmetic
... BBASIC axioms. Proof (B-1) follows from formula (b) of Proposition 1 and (CU-4). (B-4) is an immediate consequence of (CU-3) and (b) and (c) of Proposition 1. To show CUBASIC+ |= (B-5), first note that x 6= 0 ⊃ 1 ≤ x by (CU-2) and (CU-3); hence x 6= 0 ⊃ 0 6= |2x| by (CU-8) and (e) of Proposition 1 ...
... BBASIC axioms. Proof (B-1) follows from formula (b) of Proposition 1 and (CU-4). (B-4) is an immediate consequence of (CU-3) and (b) and (c) of Proposition 1. To show CUBASIC+ |= (B-5), first note that x 6= 0 ⊃ 1 ≤ x by (CU-2) and (CU-3); hence x 6= 0 ⊃ 0 6= |2x| by (CU-8) and (e) of Proposition 1 ...
The Future of Post-Human Mathematical Logic
... (and Other Mental States) ............................................................67 Table 1.11. The Theoretical Levels of Consciousness (and Other Mental States) ............................................................68 Table 1.12. The Thematic Issues of Consciousness (and Other Mental Sta ...
... (and Other Mental States) ............................................................67 Table 1.11. The Theoretical Levels of Consciousness (and Other Mental States) ............................................................68 Table 1.12. The Thematic Issues of Consciousness (and Other Mental Sta ...







![The full Müntz Theorem in C[0,1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/019844035_1-f7b6943c075c22a54f0d5d67f46bc0e0-300x300.png)