Lecture_4
... – Paralogs are genes found in the same organism that arose from a common ancestor. Duplication could have occurred in the species or earlier. ...
... – Paralogs are genes found in the same organism that arose from a common ancestor. Duplication could have occurred in the species or earlier. ...
The 2 alleles on chromosome 13q14 must be inactivated
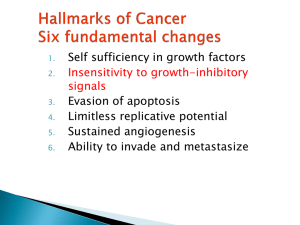
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...
... Antigrowth signals can prevent cell proliferation by 2 mechanism: 1-Cause the dividing cell go to Go phase 2-The cell enter post-mitotic differentiated pool & lose replicative potential The molecular level of antigrowth signals exert their effects on G1-S checkpoint of the cell cycle, controlled by ...
Slide 1
... one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet coloured side up on the table. Leave the o ...
... one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet coloured side up on the table. Leave the o ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles Genes influence the development of traits. • All of an organism’s genetic material is called the g_______. • A g__________ refers to the makeup of a specific set of genes (what genes does the individual have). • A p__________ is the physical expression of a trait. (wh ...
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles Genes influence the development of traits. • All of an organism’s genetic material is called the g_______. • A g__________ refers to the makeup of a specific set of genes (what genes does the individual have). • A p__________ is the physical expression of a trait. (wh ...
Genetics, Exam 2, Sample A Name ___________________________
... 3. A cross between two strains of Sordaria is analyzed. The relative frequencies of MI/MII asci for each of the two linked genes studied is shown below. What does this information tell you about the order of these genes relative to each other and their centromere? ...
... 3. A cross between two strains of Sordaria is analyzed. The relative frequencies of MI/MII asci for each of the two linked genes studied is shown below. What does this information tell you about the order of these genes relative to each other and their centromere? ...
Document
... chromosomes, especially X chromosomes, have genes for many characters unrelated to sex. We call these sex-linked alleles. ...
... chromosomes, especially X chromosomes, have genes for many characters unrelated to sex. We call these sex-linked alleles. ...
GENE REGULATION IN HIGHER ORGANSIMS Although eukaryotes
... make a small amount of alpha2/delta2 hemoglobin as adults; the delta globin gene is beside the beta globin gene. These genes are turned on in bone marrow only, which is where all of our blood cells originate. During most of the gestation period, a fetus has fetal hemoglobin or H b - F. Hb-F is a com ...
... make a small amount of alpha2/delta2 hemoglobin as adults; the delta globin gene is beside the beta globin gene. These genes are turned on in bone marrow only, which is where all of our blood cells originate. During most of the gestation period, a fetus has fetal hemoglobin or H b - F. Hb-F is a com ...
Genetic Inheritance - Mr. Lincoln`s Science Wikipage!
... Genetic Inheritance • A single inherited trait of an individual can be determined by one pair or by many pairs of genes. ...
... Genetic Inheritance • A single inherited trait of an individual can be determined by one pair or by many pairs of genes. ...
Text S1.
... tissue, e.g. 4.4% of all pc-transcripts reported in Novartis' GNF expression data set for "whole brain" tissue carry a transcriptional regulation annotation. Therefore, the fraction of rt-generated nctx that abut these protein-coding genes may be expected to show a similar over-representation in bra ...
... tissue, e.g. 4.4% of all pc-transcripts reported in Novartis' GNF expression data set for "whole brain" tissue carry a transcriptional regulation annotation. Therefore, the fraction of rt-generated nctx that abut these protein-coding genes may be expected to show a similar over-representation in bra ...
lec#18
... • Reversible , heritable changes in gene expression without mutation. • Two types: Histone modifications and DNA methylation. ...
... • Reversible , heritable changes in gene expression without mutation. • Two types: Histone modifications and DNA methylation. ...
Heredity, Prenatal Development and Birth
... Mechanism of Heredity DNA consists of chemical compounds organized into strings wrapped together Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine Order is unique for each individual Cause cells to produce specific amino acids, proteins & enzymes (building blocks) A group of compounds providing set of bioch ...
... Mechanism of Heredity DNA consists of chemical compounds organized into strings wrapped together Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine Order is unique for each individual Cause cells to produce specific amino acids, proteins & enzymes (building blocks) A group of compounds providing set of bioch ...
Haploid Human Cells as Genetic Tool to Identify Genes important for
... Genetics can provide a powerful window on the components that play a role in complex biological processes. However, human lines are refractory to efficient mutagenesis-based genetics due to the diploid nature of their genome. Therefore it remains challenging to apply powerful genetic approaches that ...
... Genetics can provide a powerful window on the components that play a role in complex biological processes. However, human lines are refractory to efficient mutagenesis-based genetics due to the diploid nature of their genome. Therefore it remains challenging to apply powerful genetic approaches that ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... 5’ ends of genes 2) Usually overlap the promoter region 3) Aberrant methylation of CpG islands linked to pathologies like cancer or epigenetic diseases like Rhett’s syndrome http://www.sanger.ac.uk/HGP/cgi.shtml ...
... 5’ ends of genes 2) Usually overlap the promoter region 3) Aberrant methylation of CpG islands linked to pathologies like cancer or epigenetic diseases like Rhett’s syndrome http://www.sanger.ac.uk/HGP/cgi.shtml ...
Lecture 10
... The DNA contents does not reflect the complexity of the organism! Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvio ...
... The DNA contents does not reflect the complexity of the organism! Related and structurally similar species may have variation in the amount of their total DNA by a factor of 100 In humans: ~5% of DNA is transcribed and 1.5% represents coding regions (exons). The rest is made of repeats with no obvio ...
reduce
... • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A single genome-wide set of expression ratios, The upstream sequence for each gene, Outputs statistically significant motifs. Extract biologically meaningful information ...
... • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A new method for discovering cis-regulatory elements • A single genome-wide set of expression ratios, The upstream sequence for each gene, Outputs statistically significant motifs. Extract biologically meaningful information ...
Characteristics of linked genes
... 41.5% GRAY body/Normal wings 41.5% BLACK body/small wings 8.5% GRAY body/Small wings 8.5% BLACK body/Normal wings MORGAN’s Conclusion The genes for wing size and body color were so commonly inherited as only two combinations either gray body/normal wing or black body/small wing that they had to be … ...
... 41.5% GRAY body/Normal wings 41.5% BLACK body/small wings 8.5% GRAY body/Small wings 8.5% BLACK body/Normal wings MORGAN’s Conclusion The genes for wing size and body color were so commonly inherited as only two combinations either gray body/normal wing or black body/small wing that they had to be … ...
Gene Mutations and Cancer Part 2
... Mutations in the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 are thought to be associated with breast cancer. The graph shows the incidence of women developing breast cancer below the age of 70 years. What does the data show? BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumour suppressor genes that produce proteins that help to repair damaged DN ...
... Mutations in the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 are thought to be associated with breast cancer. The graph shows the incidence of women developing breast cancer below the age of 70 years. What does the data show? BRCA1 and BRCA2 are tumour suppressor genes that produce proteins that help to repair damaged DN ...
EXAM B
... 40. Homologies are similarities of structure that indicate A.common physical characteristics. B.diversity. C.related ancestry. D.similar biochemistry. ...
... 40. Homologies are similarities of structure that indicate A.common physical characteristics. B.diversity. C.related ancestry. D.similar biochemistry. ...
Chapter 11
... F2 – second filial generation 1) Traits passed from P to F1 through chemical factors (genes). Traits are found in contrasting forms. The alternative (different) forms of a gene are called alleles. 2) The principle of dominance states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive. Dominant ...
... F2 – second filial generation 1) Traits passed from P to F1 through chemical factors (genes). Traits are found in contrasting forms. The alternative (different) forms of a gene are called alleles. 2) The principle of dominance states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive. Dominant ...
Chapter 8: Genetic Epidemiology
... Genetics in a Nutshell (4 of 4) • Single-nucleotide polymorphisms – Result in insertion of a different amino acid in the protein, changing the nature of the protein ...
... Genetics in a Nutshell (4 of 4) • Single-nucleotide polymorphisms – Result in insertion of a different amino acid in the protein, changing the nature of the protein ...